Accelerate IT operations with AI-driven Automation
Automation in IT operations enable agility, resilience, and operational excellence, paving the way for organizations to adapt swiftly to changing environments, deliver superior services, and achieve sustainable success in today's dynamic digital landscape.
Driving Innovation with Next-gen Application Management
Next-generation application management fueled by AIOps is revolutionizing how organizations monitor performance, modernize applications, and manage the entire application lifecycle.
AI-powered Analytics: Transforming Data into Actionable Insights
AIOps and analytics foster a culture of continuous improvement by providing organizations with actionable intelligence to optimize workflows, enhance service quality, and align IT operations with business goals.
In 1999, NASA lost Mars Climate Orbiter spacecraft worth a whopping $327 million not to an explosion or a mechanical failure, but to a simple, oversight – one that proper testing should have prevented.
Think about how a minor oversight in validation and verification destroyed years of work, millions in investment, and a critical scientific mission.
This isn’t just a cautionary tale from space exploration – it’s a wake-up call for every organization building software and digital systems. Whether it’s launching a spacecraft or deploying a business application, the principle is the same:
- Unvalidated assumptions lead to failure
- Poor testing can undo months or years of work
- The cost of fixing a defect post-release is exponentially higher than catching it early
Application testing isn’t a checkbox. It’s the backbone of reliable, high-performing systems. When done right, it prevents catastrophic errors, protects reputations, saves costs, and ensures seamless user experiences.
So, the next time someone says, “We can skip a few test cycles to save time,” just remember:
NASA didn’t. And it still cost them a spacecraft.
In this guide, we’ll walk you through everything you need to know about application testing. We’ll explain how it works, the main types and methods, the most common problems, and the best ways to do it.
We’ll also cover modern trends like Agile, CI/CD, and AI-powered intelligent testing frameworks such as Quinnox’s Shift SMART.
Whether you’re a developer, tester, or tech leader, this guide gives you the foundation you need to build reliable software in 2026.
What is Application Testing?
Application testing makes sure that a piece of software or an app works the way it should. It helps you find bugs, fix problems, and make sure the app is safe, reliable, and gives users the experience and results they expect.
When you think of testing, you might think of finding mistakes. But the main goal is to make your apps better, which will make the user experience better in the end.
It can be done manually or with test automation tools and services throughout different stages of development.
Whether it’s a complex enterprise application, mobile app or a simple website, testing is a must before you launch it.
Software Application Testing Process
Testing an application isn’t something you do just once at the end of development. It has a step-by-step process that helps you find problems early and make better software.
Here’s how it typically works:
1. Test Planning
You start by understanding what needs to be tested. This includes setting goals, understanding requirements, identifying test types, choosing tools, and planning timelines.
2. Test Design
Next, you write test cases that say what to test, how to test it, and what the expected result should be.
3. Test Execution
Now it’s time to run your tests. You follow your test cases, record what happens, and look for any deviations.
4. Defect Identification & Retesting
You log a defect if something isn’t working the way it should. Once it’s fixed, you test again to make sure the issue is resolved.
5. Regression Testing
After changes are made, you retest existing features again to ensure they still work. This helps you avoid breaking anything accidentally.
6. Test Reporting and Closure
You document the test results – what passed, what failed, and what needs attention. Once all tests are done, the cycle is closed.
7. Continuous Testing in Agile and DevOps
In fast-moving teams, testing happens continuously. Automated tests run with every code change to give you quick feedback and confidence to deploy faster.
Application Testing Methodologies
There’s no one way to test an application. Different projects need different approaches. Here are the most common testing methodologies you should know:
Black Box Testing – You test the application from the user’s point of view. You don’t need to know how the code works inside. You focus on input and output.
White Box Testing – Here, you look inside the code. You test how functions and logic are written. This is often done by developers.
Gray Box Testing – This is a mix of black box and white box testing. You know some internal details, but not everything. It helps find hidden bugs.
Shift-Left Testing – You test early, even before the app is fully built. This helps catch issues sooner and save time later in the cycle.
Agile and CI/CD Testing – In fast-moving projects, testing is continuous. You write and run tests for every update. This helps you release features quickly and with confidence.
Types of Application Testing
Different types of testing help you check different parts of your application. Here’s a quick overview of the most important ones:
Manual Testing vs Automated Testing – Manual testing is done by humans, step by step. Automated testing uses tools to run tests quickly and repeatedly.
Unit Testing – You test small pieces of code, usually individual functions. This is often done by developers during coding.
Integration Testing – You check how different parts of the app work together. It helps you catch problems between connected components.
System Testing –You test the complete app to make sure everything works as expected.
Sanity and Smoke Testing – These are quick checks to see if the basic functions work before deeper testing begins.
End-to-End (E2E) Testing – You test the entire flow, from start to finish, to see if the user journey works well.
Performance, Load, and Stress Testing – You test how fast the app is, how much traffic it can handle, and how it behaves under pressure.
Usability and Accessibility Testing – You make sure the app is easy to use and can be accessed by everyone, including people with disabilities.
Cross-Browser and Device Compatibility Testing – You test your app on different browsers, devices, and screen sizes to make sure it works everywhere.
Exploratory and Visual Regression Testing – You test without a fixed plan to find unexpected bugs. Visual regression testing checks if the layout or design has changed by mistake.
Monkey Testing – You randomly test inputs and actions to see how the app behaves under unexpected conditions.
Test Plan for Application Testing
A test plan is your roadmap for testing. It helps you stay organized and makes sure nothing important is missed.
Here’s what a good test plan usually includes:
- Scope – What will be tested and what won’t
- Objectives – What you want to achieve through testing
- Test Strategy – Manual, automated, or a mix of both
- Resources – People, tools, environments needed
- Schedule – Timelines for planning, execution, and reporting
- Risk Areas – Features that are complex or likely to fail
- Exit Criteria – When to stop testing
Having a clear plan saves time, improves test coverage, and gives everyone on the team a shared understanding of the goals and help you achieve the desired quality.
Mobile Application Testing
Testing mobile apps comes with its own set of challenges. You need to make sure the app works smoothly on different devices, screen sizes, and operating systems. Testing mobile apps well ensures better ratings, fewer uninstalls, and a smooth user experience across all devices.
Here are a few key things to consider:
- Device Fragmentation – You will need to test on a variety of devices, including Android and iOS phones and tablets, as well as new and old versions.
- Network Conditions – Mobile apps must work in different network environments- Wi-Fi, 4G, low signal, or no signal.
- Touch and Gesture Inputs – You should test swipes, taps, pinches, and other gestures that are common in mobile apps.
- Battery and Performance – A good app shouldn’t use up the battery or slow down the device.
- Real Devices vs Emulators – Use emulators for quick tests, but test on real devices as well.
Application Testing Tools
If you search for best application testing tools, you’ll come across many tools available in the market to help with different types of testing – automation, performance, API, mobile, and more.
You’ll probably recognize names like Selenium, JMeter, Postman, Appium, and Cypress. They’re all great at what they do, but they usually operate on their own – meaning testers often end up juggling between tools, writing custom scripts, and maintaining different frameworks just to get things done.
This is where Quinnox’s test automation platform, Qyrus stands out.
Qyrus is an AI-powered, no-code testing platform for all types of testing in one place. Qyrus offers end-to-end test automation, intelligent defect detection, and real-time reporting – in a single, easy-to-use interface.
Best Practices for Application Testing
Good testing isn’t about doing more, it’s about doing it smarter. It isn’t also about ticking boxes, it’s about making sure your application works the way your users expect it to.
Start early – Start early – testing from the beginning helps find problems before they get worse. It saves time, money, and work.
Write clear, reusable tests – Make test cases easy to understand. This helps when your app changes or new people join the team.
Automate what you repeat – If you have to conduct the same test again and over, automate it. It frees you up to focus on what really matters.
Test like your users – Try your app on different devices, browsers, and network speeds. That’s how real users experience it.

Stay connected – Testing goes best when developers, testers, and business teams all communicate updates and work together.
These simple practices can lead to faster releases and better user experiences.
Application Testing Challenges
Testing could appear to be a simple process, but in reality, there are a lot of obstacles to overcome in the course of real-world projects. You might encounter the following difficulties on a regular basis:
Tight deadlines – You’re expected to test quickly, but rushing can lead to missed bugs. Balancing speed and quality is always tricky.
Flaky tests – Some tests pass one day and fail the next, even when nothing changed. These unstable tests can erode trust in your results.
Tool overload – Using too many tools for different types of testing can slow things down and make your process difficult to manage.
Limited test environments – Testing on outdated or misconfigured systems can lead to results that don’t match what users see in production.
Poor test coverage – It’s easy to focus on new features and forget to test edge cases or older parts of the app.
Keeping up with changes – As apps grow and change, your test cases need constant updates. Without proper maintenance, things break.
Lack of collaboration – When testers and developers work in silos, issues take longer to fix and feedback loops get slower.
These challenges are common, but not impossible to solve. With the right approach, tools, and mindset, testing can become faster, smarter, and more effective.
Common Mistakes in Application Testing
Remember the NASA incident in the beginning of this guide? The Mars Climate Orbiter, a $125 million spacecraft, was lost because a simple software issue wasn’t caught during testing.
The actual reason? While one group utilized imperial units, another other utilized metric units. In the end, the discrepancy was not detected, which led to the failure of the mission in its entirety!
In everyday projects, common testing errors can still lead to crashes, bugs, and poor user experiences. One of the biggest mistakes is testing too late. Fixing bugs at the end takes more time and effort. Ignoring regression testing in favor of concentrating solely on new features is yet another mistake that frequently results in the return of previously fixed defects.

skipping edge cases, writing unclear test steps, or not knowing when to stop testing are other common mistakes that weaken your quality process.
Avoiding these issues can help you ship better software, faster, and with fewer surprises.
How Quinnox’s Shift SMART with Intelligent Quality(IQ) Helps
To overcome the mistakes above and meet the demands of modern testing, you need more than just speed or automation, you need intelligence. That’s where Quinnox’s Intelligent Quality (IQ) and the Shift SMART framework come in.

Intelligent Quality is a holistic approach that integrates AI-driven capabilities into every facet of the software testing process. It enhances traditional testing by embedding machine learning, predictive analytics, and real-time automation to improve decision-making, coverage, and test effectiveness. IQ transforms quality assurance from a reactive activity into a proactive, data-driven process that ensures both speed and accuracy.
The Shift SMART framework is built on five pillars: Shift Start, Zero Maintenance, AI & Automation, Reliability, and Total Cost of Quality.
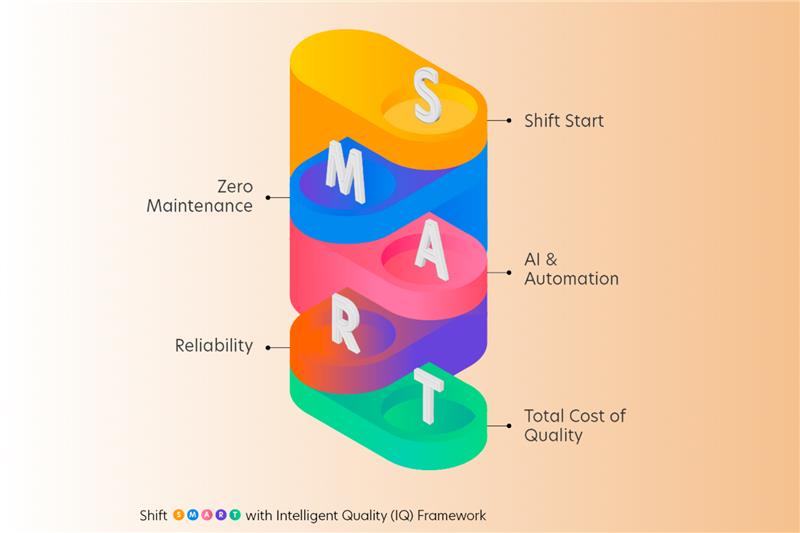
With Shift SMART, you don’t just find bugs, you prevent them. You don’t just automate tests, you optimize them. And you don’t just improve quality; you do it at scale at every quality gate.
So, while traditional testing catches up, Shift SMART helps you leap forward. Not just that, you save at least 50% of your testing time and cost!
Download: The Next-Gen Testing Blueprint: Shift SMART with Intelligent Quality (IQ)
Conclusion
Software testing has evolved into a strategic function that directly impacts product quality, user experience, and business success. In today’s fast-paced digital world, ensuring reliable, secure, and high-performing applications is more critical than ever.
Modern testing approaches powered by AI and automation are helping teams move faster, catch issues earlier, and deliver reliable quality with less effort. Frameworks like Shift SMART are not just improving test efficiency, they’re reshaping how quality is built into every stage of the development lifecycle.
If you want to stay ahead in 2026, it’s time to make testing smarter, simpler, and more intelligent – Shift SMART!
FAQs About Application Testing
Application testing ensures that a software application works as intended. It helps find bugs, ensure quality, and deliver a better user experience.
Some of the key types include unit testing, integration testing, system testing, regression testing, performance testing, and usability testing.
Ideally, testing should start early in the development cycle. This is known as shift-left testing and helps catch issues before they grow.
Tight deadlines, flaky tests, limited environments, and tool overload are some of the frequent challenges teams face.
Qyrus combines web, mobile, and API testing into one intelligent platform. It offers AI-powered automation, easy collaboration, and seamless integration into your CI/CD pipelines, making it a complete solution for modern testing.
Shift SMART is Quinnox’s intelligent testing framework designed to improve quality at speed. It stands for Shift Start, Zero Maintenance, AI & Automation, Reliability, and Total Cost of Quality. The approach enables early testing, reduces test maintenance, brings in AI-powered automation, and focuses on long-term cost and quality gains. It helps teams move beyond traditional testing to a smarter, scalable model built for modern development.