Accelerate IT operations with AI-driven Automation
Automation in IT operations enable agility, resilience, and operational excellence, paving the way for organizations to adapt swiftly to changing environments, deliver superior services, and achieve sustainable success in today's dynamic digital landscape.
Driving Innovation with Next-gen Application Management
Next-generation application management fueled by AIOps is revolutionizing how organizations monitor performance, modernize applications, and manage the entire application lifecycle.
AI-powered Analytics: Transforming Data into Actionable Insights
AIOps and analytics foster a culture of continuous improvement by providing organizations with actionable intelligence to optimize workflows, enhance service quality, and align IT operations with business goals.
Think of an enterprise where decisions are made before problems arise, workflows evolve in real time, and productivity scales without a proportional increase in headcount. This isn’t a futuristic fantasy; it’s the new reality ushered in by AI agents.
Once relegated to simple support tasks, AI agents are now stepping into the spotlight as frontline decision-makers. These intelligent systems do more than automate; they observe, analyze, and act with a level of precision and speed that’s redefining how work gets done.
According to a Forrester report, companies implementing AI agents have seen a 40–60% increase in operational efficiency within the first year. That’s not incremental change; it’s transformational. From streamlining IT operations and enhancing customer service to optimizing logistics and reducing financial risk, AI agents are becoming indispensable across sectors.
But what exactly are these agents? How do they function? And what makes them so much more powerful than traditional automation? This blog unpacks the world of AI agents, starting with what are AI agents, how they work, the different types in use today, and where they’re creating the most business value.
A recent survey found that 48% of M&A professionals are now using AI in their due diligence processes, a substantial increase from just 20% in 2018, highlighting the growing recognition of AI’s potential to transform M&A practices.
What Is an AI Agent and How Do They Work?
AI agents are not just reactive bots; they’re intelligent digital coworkers capable of sensing, thinking, and acting autonomously across complex business workflows.
At the core of every AI agent is the Sense → Think → Act loop:
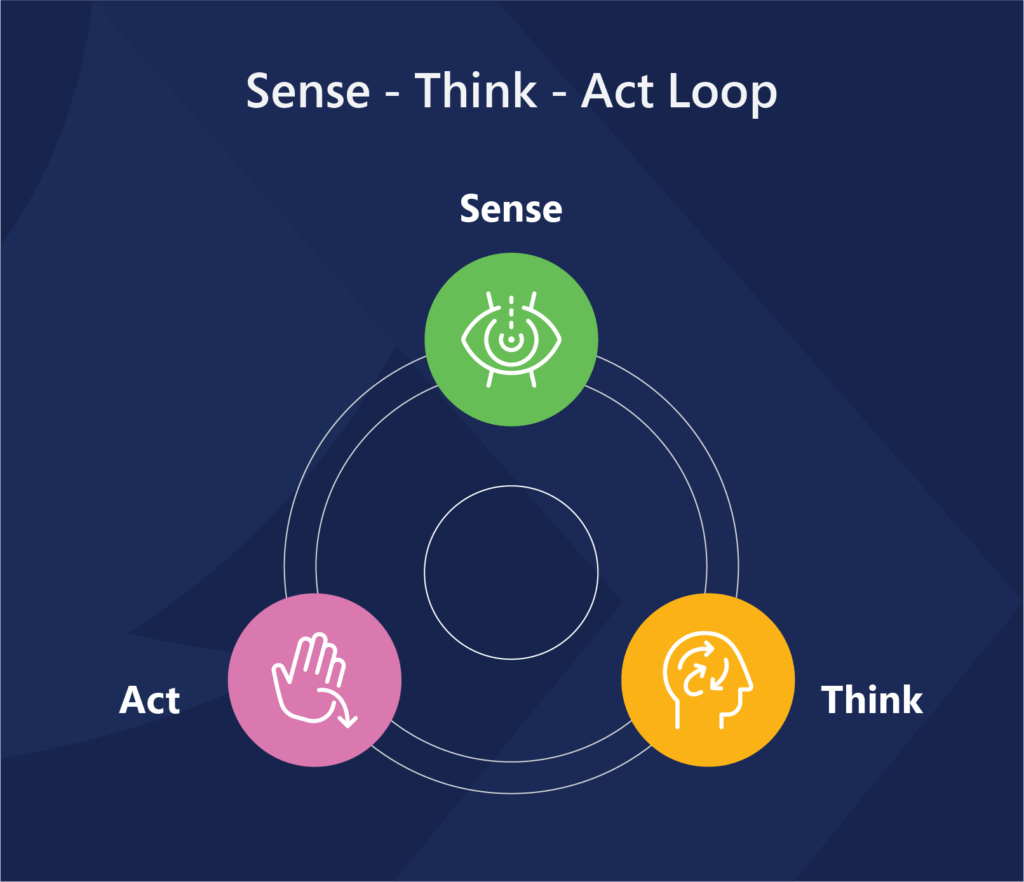
- Sense: They gather real-time data from APIs, sensors, databases, and dashboards.
- Think: They process this input using AI models – machine learning, logic-based reasoning, or probabilistic planning.
- Act: They execute decisions – triggering workflows, sending alerts, or adjusting systems – all without human input.
What Makes AI Agents Truly Powerful?
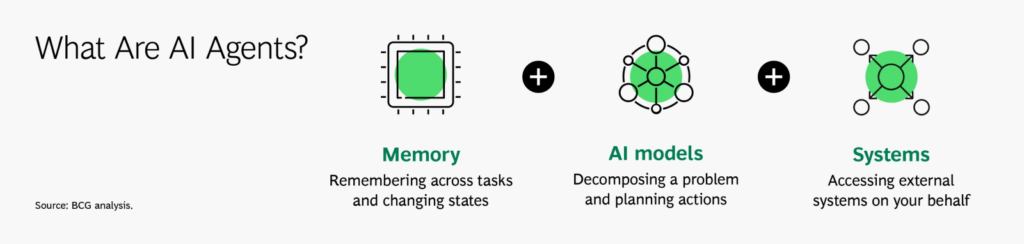
As shown in the above figure, AI agents bring together three critical components:
- Memory: They retain information across tasks and sessions, enabling contextual decision-making and continuous improvement.
- AI Models: They analyze data, plan actions, and make predictions with growing precision.
- Systems: They connect with enterprise platforms to take real-time action—automating, optimizing, and intervening where needed.
According to BCG, Agentic AI adoption can lead to a 30–50% improvement in decision-making efficiency across cross-functional teams.
From simple rule-based bots to advanced, autonomous agents that negotiate priorities, learn on the go, and collaborate with other agents. This evolution is shaping a new paradigm – Agentic AI – where machines take initiative, not just orders.
Don’t Miss: Why Agentic AI Is the Future of IT Operations
Types of AI Agents
AI Agents span a spectrum of intelligence and autonomy, each suited for different levels of complexity and decision-making. As enterprises deploy AI across various functions, understanding these types helps in selecting the right fit for specific use cases, from automating routine support to orchestrating entire business processes.
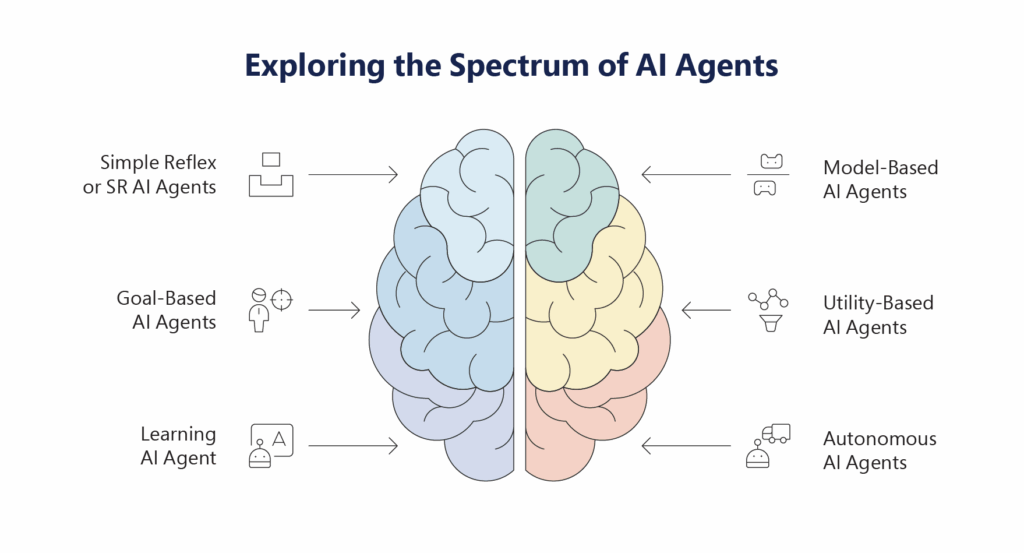
1. Simple Reflex Agents:
The most basic type, which operate purely on predefined rules: “if X happens, then do Y.” Think of autoreply to systems in customer service or spam filters that flag messages based on keywords. They’re lightning fast but limited in adaptability.
According to a Forbes report, AI agents now can manage about 80% of all customer service interactions, reducing operational costs by 30%.
2. Model-Based AI Agents:
These agents take things a step further by maintaining an internal state that gives them memory of past inputs. This allows them to respond more intelligently based on historical context.
For example, a process automation agent in a banking application might remember a user’s last login behavior and escalate alerts only when a deviation is detected. In dynamic environments like logistics or workflow automation, this model enables more nuanced, context-aware decisions, especially crucial when conditions are constantly changing.
3. Goal-Based Agents:
This type of agent doesn’t just react; they plan. These agents consider multiple pathways and take actions that help achieve a defined end goal. A classic example would be a product recommendation engine on an e-commerce site that suggests items not randomly but based on the user’s intent to buy something specific. These systems use goal inference to improve relevance and, as per McKinsey, personalized recommendation agents can boost conversion rates by up to 30%.
4. Utility-Based Agents:
Most advanced agents that introduce the concept of evaluating outcomes based on utility or in business terms, value. These agents analyze all possible actions and choose the one that maximizes the expected benefit. In enterprise settings, utility-based agents are commonly used in supply chain optimization, where they weigh cost, delivery time, and risk before making procurement decisions.
5. Learning Agents:
Learning agents bring adaptability into the picture. These agents don’t rely solely on pre-coded logic; they improve through data and feedback over time. Modern chatbots and AI assistants, like those used by companies such as H&M or Sephora, constantly learn from customer interactions to provide more relevant responses, improving CSAT scores by up to 20% in some cases.
They evolve in real time, tuning their performance based on user feedback and system outcomes, making them highly effective in dynamic environments like customer service or fraud detection.
6. Autonomous Agents:
These agents are capable of managing entire workflows end-to-end with minimal or no human intervention. They can not only make decisions but also collaborate with other agents, reprioritize tasks, and adapt goals on the fly.
A powerful example is seen in intelligent RPA platforms used in large insurance firms, where autonomous agents handle claims from submission to approval—including verification, documentation, and payout—freeing human agents for more complex cases. Organizations implementing autonomous agents in claims processing have reported up to 70% faster cycle times and a 40% reduction in operational costs.
Benefits of Using AI Agents in Business
1. Increased Efficiency
AI agents drastically reduce time spent on repetitive, manual tasks—freeing up human teams for more value-added work. Whether it’s processing invoices, triaging IT tickets, or routing customer queries, these agents speed up execution and reduce bottlenecks.
2. Proactive Decision-Making
Unlike traditional automation that reacts to inputs, AI agents can detect patterns and anticipate issues before they occur triggering alerts or actions in real time. For example, in IT operations, AIOps agents can predict outages or security breaches and intervene early, reducing downtime and risk.
3. Scalability Without New Headcount
4. Cost Savings
By automating tasks, reducing errors, and improving speed, AI agents directly reduce operational costs. Companies using intelligent automation report saving millions annually. A case in point: American Express integrated AI agents in fraud detection, reducing false positives by 20% and saving millions in processing overhead (Forbes)
5. Consistency and Reliability
Human error is inevitable—but AI agents execute tasks with predictable accuracy and consistency, making them ideal for compliance-heavy industries like banking, insurance, and healthcare. Whether processing claims or analyzing contracts, agents follow defined logic with precision. According to PwC, 54% of executives cite “improved quality and accuracy” as a primary benefit of AI deployment.
6. 24/7 Operations
Unlike human teams, AI agents never sleep. They work round the clock, ensuring uninterrupted operations across global time zones. This is especially crucial for businesses with critical infrastructure or customer support that demands always-on availability.

How Are Enterprises Using AI Agents Today?
AI agents are no longer future tech; they’re actively transforming core business usecases across industries. Here are just a few ways they’re being deployed today:
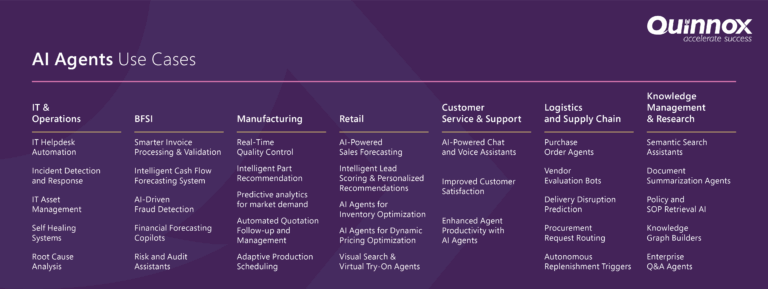
- IT Operations & AIOps: AI agents autonomously monitor systems, detect anomalies, and resolve incidents, reducing MTTR and boost system reliability.
- Customer Service: From chatbots to intelligent case routing, agents handle tier-1 support and escalate complex issues based on customer sentiment, enhancing CSAT while slashing response times.
- BFSI: Agents reconcile transactions, flag discrepancies, and even forecast expenses, enabling real-time financial visibility and reduced human effort.
- Supply Chain: Intelligent agents dynamically adjust orders, anticipate disruptions, and optimize logistics, ensuring agility even in volatile environments.
Navigating the Pain Points of AI Agents
While AI agents are reshaping enterprises, the path to adoption isn’t without its hurdles. To truly harness their potential, organizations must understand and prepare for the following roadblocks:
- Data Dependency: AI agents thrive on high-quality, diverse, and up-to-date data. But when trained on incomplete, outdated, or biased datasets, these agents can generate inaccurate or skewed outputs. For instance, a supply chain agent working off flawed demand data might overstock low-demand items or underdeliver during peaks.
- Security Risks: Autonomous agents, especially those operating across critical systems, pose security concerns if not tightly governed. Without proper access controls, role-based permissions, and monitoring, there’s a risk of agents triggering unintended actions or being exploited through adversarial attacks. Organizations need robust AI security frameworks similar to Zero Trust models in cybersecurity.
- Lack of Explainability: Many advanced AI agents operate as black boxes, making decisions that even their developers can’t fully trace. In regulated industries like finance or healthcare, this poses a serious problem. Explainable AI (XAI) is emerging to bridge this gap, but as of now, only 35% of enterprise AI leaders feel confident in explaining their model outcomes to business stakeholders
- Integration Complexity: Legacy infrastructure doesn’t always play well with modern AI agents. Whether it’s old CRMs, ERPs, or siloed data systems, integrating agents without disrupting business-as-usual requires middleware, APIs, and sometimes full-scale modernization. This complexity can stall or inflate the cost of adoption.
- Human Trust & Organizational Buy-In: Despite the tech readiness, cultural resistance can stall AI adoption. Employees may worry about job displacement, while leaders may hesitate due to the perceived risks. Building trust involves transparent implementation, clear communication of benefits, and starting with low-risk, high-value use cases to demonstrate quick wins.
And The Fix? A well-structured AI governance strategy is no longer optional. It must include ethical frameworks, risk assessment protocols, transparent auditing mechanisms, and compliance monitoring to ensure AI agents serve business goals responsibly and reliably.
Wrap Up
AI agents have moved from concept to cornerstone reshaping how modern enterprises operate. But to fully unlock their potential, organizations need more than isolated pilots or siloed use cases. They need an integrated approach that scales intelligence across the business.
That’s where Qinfinite, Quinnox’s intelligent application management platform makes the difference. With its agentic AI architecture and real-time digital twin capabilities, it doesn’t just run AI agents—it orchestrates them to predict, adapt, and self-optimize operations at scale.
Meanwhile, Quinnox AI (QAI) Studio accelerates AI innovation with purpose-built, domain-specific agents—be it for finance, customer engagement, or risk mitigation. It ensures your AI isn’t just functional, but truly transformative.
Together, they help businesses move from automation to autonomy; turning AI agents into strategic enablers of speed, precision, and continuous growth.
FAQs Related to Knowledge Graph
Agentic AI is an advanced form of artificial intelligence that enables systems to reason, learn, and act independently—without continuous human instruction. These agents can assess goals, adapt to their environment, and make decisions dynamically, making them ideal for complex and evolving enterprise scenarios.
Traditional automation operates on static, rule-based scripts—it does exactly what it’s programmed to do; nothing more. Autonomous agents, on the other hand, learn from data, adapt to changing conditions, and make decisions based on goals or outcomes—bringing flexibility and intelligence to automation.
Yes, but only with the right guardrails. AI agents can improve reliability in critical systems if deployed with strong governance, real-time monitoring, and explainable AI frameworks. Ensuring transparency behind agent decisions is essential for trust and regulatory compliance.
Successfully implementing AI agents requires cross-functional expertise: data scientists to build models, DevOps engineers to deploy and scale, and business/domain experts to guide relevance. Collaborating with AI solution partners often speeds up implementation and reduces risk.