Accelerate IT operations with AI-driven Automation
Automation in IT operations enable agility, resilience, and operational excellence, paving the way for organizations to adapt swiftly to changing environments, deliver superior services, and achieve sustainable success in today's dynamic digital landscape.
Driving Innovation with Next-gen Application Management
Next-generation application management fueled by AIOps is revolutionizing how organizations monitor performance, modernize applications, and manage the entire application lifecycle.
AI-powered Analytics: Transforming Data into Actionable Insights
AIOps and analytics foster a culture of continuous improvement by providing organizations with actionable intelligence to optimize workflows, enhance service quality, and align IT operations with business goals.
When traditional ITSM hits its limits – It begins with a surge in access requests. Then a system patch triggers unexpected outages. By mid-afternoon, hundreds of tickets are queued – same issues; same confusion. The service desk is overwhelmed, and resolution timelines are slipping. Meanwhile, business leaders are measuring the fallout in real dollars.
This isn’t an isolated scenario. For many IT departments, it’s a recurring theme. According to Forbes Research , 58% of IT teams spend up to 20 hours a week wrestling with repetitive issues that drain time and morale. And according to Gartner, downtime costs $5,600 per minute; reactive service models aren’t just inefficient; they’re unsustainable.
IT Service Management was designed to bring structure to chaos. But in today’s high-velocity digital landscape, structure alone isn’t enough. Enterprises need adaptive, intelligent systems that not only resolve issues but prevent them.
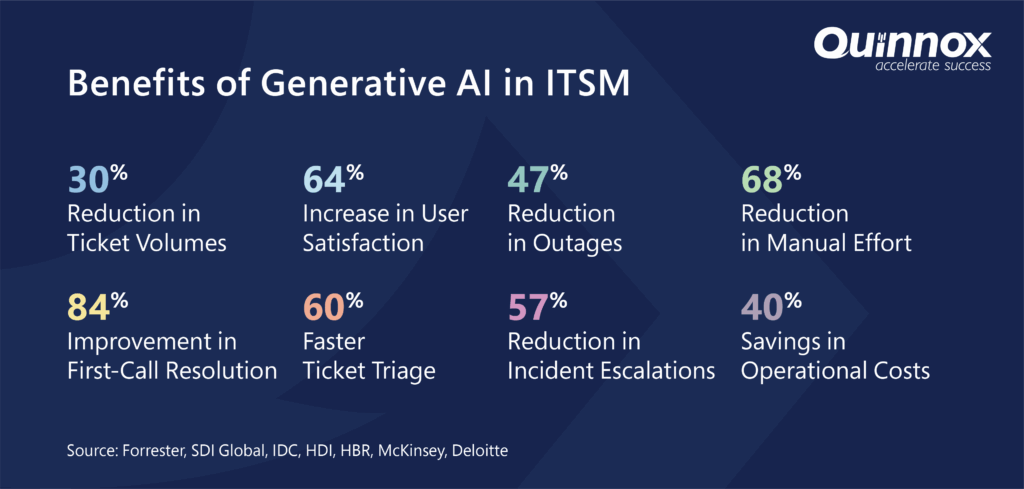
That’s where Generative AI steps in. By learning from historical data, identifying patterns, and creating contextual responses, it transforms ITSM from a reactive function into a proactive powerhouse. Early adopters are already seeing up to 75% reductions in ticket resolution time, alongside significant improvements in user experience and operational agility. These numbers make it quite evident that the generative AI revolution in ITSM isn’t a trend- it’s a transformation.
Generative AI isn’t just helping ITSM do more with less; it’s actually redefining what’s possible. This blog explores how forward-thinking organizations are embracing this shift, not to replace people, but to elevate IT from a support function to a strategic driver of digital excellence.
Let’s explore what this transformation looks like and why the time to act is now.
A recent survey found that 48% of M&A professionals are now using AI in their due diligence processes, a substantial increase from just 20% in 2018, highlighting the growing recognition of AI’s potential to transform M&A practices.
Generative AI: The Modern Cornerstone of ITSM
Generative AI refers to AI models, such as large language models (LLMs), that can understand, generate, and summarize natural language at a near-human level. In the ITSM context, GenAI is trained on service desk tickets, knowledge articles, user interactions, system logs, and configuration data to:
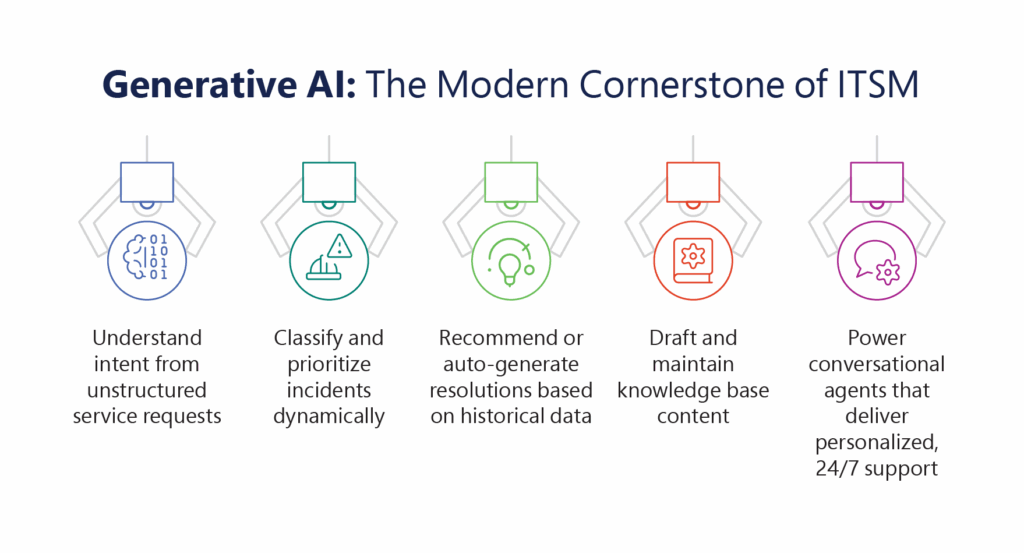
Unlike traditional automation, which is rule-based and deterministic – Generative AI adds adaptability and context-awareness to service operations, making ITSM workflows more intelligent and self-optimizing.

The Limitations of Traditional ITSM
Despite decades of refinement, traditional ITSM frameworks such as ITIL are increasingly seen as insufficient to meet the demands of modern digital enterprises. While they offer structure and governance, their execution often suffers from rigidity, fragmentation, and a lack of adaptability.
1. Static Workflows:
Predefined, rules-based workflows lack the flexibility to handle unstructured, ambiguous, or evolving service requests, leading to misrouted tickets and resolution delays.
2. Repetitive Manual Tasks:
Service desks are burdened with repetitive, low-value requests (e.g., password resets, access provisioning). These consume a large portion of L1 bandwidth and cause SLA breaches due to human queue dependencies.
3. Siloed Knowledge:
Knowledge bases often become outdated or difficult to navigate. Agents spend excessive time searching for resolutions, and users avoid self-service due to poor discovery experiences.
4. Poor User Experience:
Legacy service portals and chatbots offer limited natural interaction. Employees find them frustrating and often escalate directly to agents, undermining self-service adoption.
5. Lack of Intelligence and Proactivity:
Traditional ITSM is reactive by design. Incident patterns, recurring failures, and early warning signals are rarely harnessed to proactively resolve or prevent issues.
These gaps don’t just slow down IT; they ripple across the organization, hampering employee productivity, delaying project timelines, and eroding trust in IT services.
The Foundation of Next - Gen AI-Powered ITSM
Where traditional ITSM hits a ceiling, Generative AI breaks through. The shift isn’t just from manual to automated; it’s from automated to agentic. This means moving beyond scripted bots and static workflows to systems that understand, reason, and act independently.
1. From Automation to Agentic Intelligence
Traditional automation follows fixed scripts. GenAI, on the other hand, introduces intelligent agents that interpret context, make real-time decisions, learn from outcomes, and adjust behavior without human intervention.

2. Adaptive, Context-Aware Service Delivery
Agentic AI enables the ITSM system to adapt to evolving service conditions, user behavior, and business priorities. It delivers support that is dynamic, personalized, and continuously improving.
3. Collaboration Between Human and Machine
Rather than replacing service desk professionals, GenAI augments them. AI agents handle routine tasks, flag anomalies, and surface recommendations, freeing human experts to focus on complex problem-solving and strategic improvement.
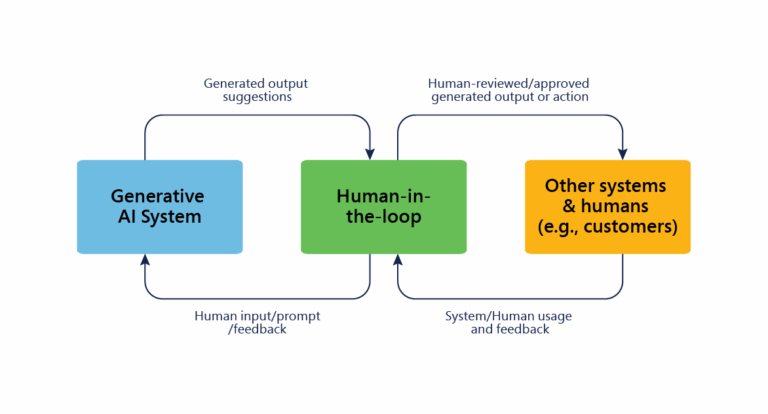
4. Intelligent Knowledge Evolution
With GenAI, knowledge is no longer static. It’s generated, updated, and contextualized in real time – ensuring relevance and discoverability across all service touchpoints.
This next-gen approach fundamentally transforms the ITSM operating model; from process execution to experience orchestration paving the way for predictive, scalable, and AI-first service ecosystems.
The Shift: From Reactive to Predictive and Autonomous
| Characteristic | Traditional ITSM | GenAI-Powered ITSM |
|---|---|---|
| Approach | Reactive | Proactive and Predictive |
| Interaction | Form-based or scripted | Conversational and personalized |
| Resolution Speed | Dependent on human triage | Instant in many cases |
| Scalability | Limited by human capacity | Scales dynamically with data |
| Knowledge Management | Manual, easily outdated | AI-curated, auto-updated |
| Cost Efficiency | Labor-intensive | Automated and resource-light |
This shift represents a foundational evolution not just in tooling but in mindset. ITSM is no longer just about service delivery; its intelligent experience orchestration using AI to anticipate, resolve, and continuously improve IT support outcomes.
5 Key Benefits of Using Generative AI in ITSM
1. Intelligent Ticketing & Automated Resolution
One of the most visible benefits of GenAI is its ability to streamline ticket management by automating categorization, prioritization, and even resolution of routine service requests. AI models trained on historical ticket data can understand the context behind unstructured user inputs, route them accurately, and suggest or execute resolutions autonomously. This minimizes the need for manual triaging and reduces response times. Over 70% of routine IT support tickets can be resolved autonomously using NLP and contextual understanding.
2. Improved Agent Productivity
Support teams often spend 30–40% of their time managing repetitive tasks; password resets, access requests, basic troubleshooting. GenAI frees them from this “busy work” by handling L0 and L1 issues autonomously, allowing agents to focus on higher-value, complex problems that require human judgment.
But GenAI doesn’t stop at ticket automation. It acts as a virtual co-pilot for agents by recommending the best response based on ticket history, summarizing long incident threads, or even drafting knowledge articles after a resolution. This real-time assistance reduces cognitive load and minimizes errors.
Gartner predicts that by 2025, 80% of customer service organizations will apply some form of generative AI to boost agent productivity and enhance customer experience.
3. Dynamic Knowledge Creation and Management
Knowledge is the backbone of ITSM, yet maintaining updated documentation is a persistent challenge. Generative AI can auto-generate knowledge base articles, FAQs, and SOPs from past tickets and expert interactions, ensuring information is always current and relevant. GenAI also enhances discoverability by summarizing and personalizing content for each user or agent query, reducing time spent searching for resolutions.
4. Cost Optimization
Operational efficiency often translates directly to cost savings, and Generative AI enables both. By deflecting Tier-0 and Tier-1 tickets through intelligent automation and conversational agents, organizations can reduce the need for additional headcount and avoid outsourcing low-level support functions.
Furthermore, GenAI optimizes resource allocation. It predicts ticket volumes, identifies process inefficiencies, and helps IT leaders make data-driven decisions on team capacity and infrastructure investment.
BCG Research found that enterprises implementing GenAI in service operations achieved cost savings ranging from 20–40% in their IT support functions. These savings stem from reduced manual labor, fewer escalations, lower resolution times, and optimized use of ITSM tools. Also, a study supports that Generative AI-based conversational assistant improves user productivity to perform 14% more user requests in an hour.
5. Continuous Compliance and Intelligent Security Enforcement
Modern ITSM must align not only with operational goals but also with regulatory and cybersecurity mandates. GenAI can monitor system activities, generate compliance reports, and trigger automated actions when anomalies or policy violations are detected. By integrating with ITSM workflows, GenAI supports real-time governance, flagging risks, automating audit trails, and adapting controls based on evolving compliance needs.
Real-World ITSM Use Cases with Generative AI
The promise of GenAI in ITSM is no longer theoretical; enterprises across sectors are actively deploying it to enhance productivity, improve service quality, and reduce operational overhead.
Here are few compelling examples that demonstrate how Generative AI is driving real impact in IT Service Management:
- A large insurance provider partnered with Orion Innovation to integrate GenAI into their ITSM environment. By deploying a semantic search engine and a conversational self-service chatbot, they enabled faster ticket resolutions and improved self-help experiences. The result? A 30% boost in agent productivity, smarter triaging, and enhanced security with features like data masking and audit logging. (Source)
- Financial institutions like Lloyds and UBS are applying GenAI internally to support their teams. Lloyds uses GenAI to auto-generate support documents and FAQs, while UBS equips staff with AI-powered advisors for instant troubleshooting and compliance guidance. These tools have helped both banks improve internal efficiency, accelerate onboarding, and deliver better service with fewer delays. (Source)
Challenges & Considerations in Implementing Gen AI in ITSM
While the potential of Gen AI in ITSM is transformative, implementation isn’t without its complexities. Organizations must navigate technical, ethical, and organizational hurdles to unlock their full potential.
Here are the key challenges and critical considerations to address before scaling GenAI across your IT service landscape:
1. Data Quality and Contextual Training
Generative AI models are only as effective as the data they are trained on. In ITSM, ticket histories, knowledge base articles, and configuration logs often contain inconsistencies, unstructured language, or duplicate entries. Poor-quality data can lead to hallucinated responses, irrelevant resolutions, or incorrect ticket classification, eroding trust in AI recommendations.
Consideration:
Organizations must prioritize data hygiene by cleansing, labeling, and continuously updating their ITSM datasets. Fine-tuning GenAI on domain-specific, role-based, and context-aware inputs ensures that recommendations are accurate and grounded.
2. Change Management and Cultural Resistance
Adopting GenAI requires a shift in mindset; from reactive ticketing to proactive intelligence. However, this can meet resistance from support teams who fear job displacement or struggle to trust AI-generated responses. Even the best GenAI models will fail to deliver results if agents resist adoption or bypass AI workflows in favor of manual processes.
Consideration:
Leaders must invest in change management programs, involving IT agents early in the design and training process. Positioning GenAI as a co-pilot (not a replacement) and providing ongoing upskilling support are essential to long-term success.
3. Integration with Legacy ITSM Tools
Many enterprises still run on traditional ITSM platforms or customized workflows built over the years. Integrating GenAI into this environment can be technically challenging, especially when APIs are limited or data is siloed. Without seamless integration, the benefits of GenAI – like real-time triage, automated knowledge generation, or conversational support – will remain isolated or underutilized.
Consideration:
Organizations should assess the interoperability of their ITSM stack. Choosing platforms with open architecture, API readiness, and GenAI plug-ins can significantly reduce integration overhead.
4. Security, Privacy, and Compliance Risks
GenAI tools often require access to sensitive internal data—user profiles, ticket content, and system logs to operate effectively. This raises valid concerns around data leakage, unauthorized access, and compliance with industry regulations like GDPR or HIPAA.
A single misstep can expose confidential information or trigger compliance violations, especially in industries like finance, healthcare, and government.
Consideration:
Ensure that any GenAI implementation adheres to strict access controls, role-based permissions, and encryption standards. Where possible, prefer on-premises or private cloud deployments of AI models over public SaaS solutions for sensitive environments.
5. Measuring ROI and Business Impact
Unlike traditional automation where ROI is measured by time saved per task, GenAI impacts a wider set of KPIs – user experience, agent productivity, resolution speed, and knowledge accuracy. Measuring this impact requires a more holistic view. Without clear KPIs, leadership may struggle to justify GenAI investments beyond initial pilots, especially if outcomes aren’t immediately visible.
Consideration:
Define success metrics early. Track AI deflection rates, CSAT changes, average handle time improvements, and ticket resolution acceleration. Also monitor intangible gains like increased employee satisfaction or reduction in knowledge silos.
Wrap Up
As enterprises race to deliver faster, leaner, and more user-centric IT services, Generative AI stands out as a pivotal force not as a future concept, but as an operational reality. It’s rewriting the playbook of IT Service Management by eliminating inefficiencies, enabling predictive support, and turning service desks into strategic experience hubs.
Whether it’s reducing ticket volumes through intelligent deflection, empowering agents with AI co-pilots, or transforming knowledge management into a dynamic, self-evolving system; GenAI is delivering tangible business outcomes. Early adopters are not just solving problems faster; they are reshaping their service culture around intelligence, autonomy, and agility.
But true transformation isn’t achieved with just AI capabilities; it requires a platform that is purpose-built to bring those capabilities to life at scale, securely and seamlessly.
That’s where Quinnox’s intelligent application management platform, Qinfinite steps in.
Qinfinite’s AI-powered ITSM capabilities go beyond traditional automation. By blending large language models, semantic understanding, and domain-specific intelligence, Qinfinite empowers IT teams to predict, prevent, and resolve issues autonomously – while maintaining full control, transparency, and compliance. From intelligent ticketing and agent augmentation to adaptive knowledge and real-time compliance enforcement, Qinfinite helps IT leaders turn GenAI into a trusted engine for operational excellence.
So, ready to transform IT support from reactive to proactive? Book a FREE Consultation today and let Quinnox show you how.
FAQs Related to Gen AI in ITSM
Generative AI in ITSM refers to the use of advanced AI models—like large language models (LLMs)—that can understand, generate, and interact using natural language. These models are trained on service-related data to automate tasks such as ticket classification, resolution recommendations, knowledge creation, and conversational support.
Generative AI is being used to automate repetitive service desk tasks, power intelligent chatbots, generate and update knowledge base articles, triage incidents, and offer predictive insights to prevent issues before they occur. It enhances both agent efficiency and user experience.
Key benefits include faster ticket resolution, improved agent productivity, cost savings through automation, dynamic knowledge management, and more personalized, conversational support for end users. It helps organizations scale IT support while maintaining quality and compliance.
Yes, significantly. By automating ticket routing, suggesting solutions based on past incidents, and resolving common issues autonomously, GenAI reduces mean time to resolution (MTTR) by up to 75% in some organizations.
Challenges include ensuring high-quality, context-rich training data; integrating legacy ITSM systems; managing change within support teams; addressing privacy and compliance concerns; and measuring ROI effectively. Overcoming these requires a strategic approach and the right platform support.