Accelerate IT operations with AI-driven Automation
Automation in IT operations enable agility, resilience, and operational excellence, paving the way for organizations to adapt swiftly to changing environments, deliver superior services, and achieve sustainable success in today's dynamic digital landscape.
Driving Innovation with Next-gen Application Management
Next-generation application management fueled by AIOps is revolutionizing how organizations monitor performance, modernize applications, and manage the entire application lifecycle.
AI-powered Analytics: Transforming Data into Actionable Insights
AIOps and analytics foster a culture of continuous improvement by providing organizations with actionable intelligence to optimize workflows, enhance service quality, and align IT operations with business goals.
Enterprise applications are the digital backbone of modern businesses. They are not merely software tools but sophisticated ecosystems that integrate multiple facets of an organization’s operations. Whether it’s managing customer interactions through Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems, optimizing supply chains and financials via Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) platforms, or supporting specialized processes like human resources, procurement, and analytics, these applications are deeply woven into the operational fabric of enterprises.
Given the critical role enterprise applications play, any downtime, performance bottleneck, or security vulnerability can result in significant financial losses, damage to brand reputation, or even legal repercussions. This reality places enterprise application testing at the core of digital strategy. Comprehensive testing ensures that these systems not only function as intended under everyday conditions but also maintain robustness under peak loads and evolving security threats.
Enterprise application testing involves a broad spectrum of methodologies—functional testing to verify core features, performance testing to assess scalability and speed, security testing to protect against cyber threats, and integration testing to guarantee smooth interoperability with other systems. By proactively identifying and resolving issues before deployment, enterprises safeguard their investments and enable their technology to serve as a true catalyst for innovation and growth.
In this blog, we’ll explore the full scope of enterprise application testing, including types of enterprise apps, testing strategies, key benefits, challenges, best practices, and real-world considerations. Before that, we’ll discuss how Software Testing has evolved over the years.
Evolution of Testing:
Software testing has evolved dramatically over the last few decades, driven by both technological advances and changing market demands. Traditional manual testing, characterized by a reliance on human intervention, is labor-intensive and error-prone, resulting in:
- Speed Vs quality trade off:
44% of organizations compromise on quality when trying to accelerate time-to-market. As a result, QA teams often struggle in balancing speed and quality with traditional testing approaches.
- Lack of agility:
70% of failed software projects are linked to poor adaptability in testing processes and inability to keep up with changing requirements.
- High in process & post-production cost:
Most of the customers observe over 15% of defect slippage into production. Defects found after release are exponentially more expensive to fix than those found earlier in the process.
Data source: The Next-Gen Testing Blueprint: Shift SMART with Intelligent Quality (IQ)
As technology advanced, test automation became a core part of the testing landscape, offering speed, consistency, and repeatability. However, even with automation, organizations continued to face challenges around coverage, speed, and accuracy, limiting their ability to rapidly innovate.
The next major leap in the evolution of software testing comes with Intelligent Quality (IQ), where smart agents enabled by artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and advanced automation converge to redefine testing paradigms. This shift is not just about faster testing but about smarter, more reliable, and scalable testing solutions that can keep pace with the demands of modern software development.
What Is Enterprise Application Testing?
Enterprise application testing is the process of validating the functionality, performance, security, scalability, integration, and user experience of large-scale software systems used across an organization. It’s not just about bug detection; it ensures applications meet business goals, regulatory requirements, and continuity expectations.
Unlike traditional testing methodologies, enterprise software testing involves interconnected systems, APIs, multiple user roles, and cross-functional workflows, making it inherently more complex.
Key objectives of enterprise application testing:
- Ensure mission-critical functionality remains stable across updates.
- Identify integration failures across interconnected systems.
- Verify compliance with internal governance and industry regulations.
- Simulate real-world load and user behaviors for scalability assurance.
For more insights into how testing impacts business outcomes, read: Why QA Testing Matters in Software Development
Why Enterprise Application Testing Matters?
Enterprise applications are the engines that drive critical operations, strategic decisions, and customer interactions. Unlike simple consumer apps, enterprise applications handle complex workflows, integrate diverse systems, and process massive volumes of sensitive data. This inherent complexity makes testing not just a technical step but a fundamental business imperative.
1. Ensuring Operational Continuity
Enterprise applications often support mission-critical processes such as order processing, financial transactions, or employee management that organizations rely on daily. Any malfunction, slow performance, or system outage can halt operations, causing cascading disruptions across departments. Rigorous testing helps identify and eliminate defects before deployment, ensuring that applications remain reliable under all conditions, thereby safeguarding uninterrupted business continuity.
2. Protecting Data Integrity and Security
With enterprises managing vast amounts of confidential data, from customer records and financial details to intellectual property, any vulnerability can lead to disastrous breaches or data loss. Enterprise application testing encompasses stringent security assessments, including vulnerability scanning, penetration testing, and access control verification. These measures protect sensitive information against cyberattacks, unauthorized access, and data corruption, reinforcing trust with customers and regulatory bodies.
3. Validating Complex Business Logic
Enterprise software embodies intricate business rules and workflows tailored to specific organizational needs. Testing confirms that these rules function correctly across various scenarios, ensuring compliance with industry standards, internal policies, and legal regulations. For example, an ERP system must accurately enforce tax laws, or an HCM platform must adhere to labor policies. Thorough testing guarantees that the software behaves as intended, reducing costly errors and legal risks.
4. Optimizing Performance and Scalability
Enterprise applications must handle fluctuating workloads, from routine daily tasks to peak business periods like holiday sales or fiscal year-end closings. Performance testing simulates these conditions to verify that the application maintains speed, responsiveness, and stability without crashing or slowing down. Scalability testing ensures the system can grow alongside the business, accommodating increasing users, transactions, and data volumes without degradation
5. Enhancing User Experience
Poorly designed interfaces, inconsistent user experiences across devices, or convoluted workflows can lead to user frustration and errors. While user-centric testing covering UI/UX validation, accessibility checks, and cross-platform compatibility ensures that the software is intuitive, efficient, and accessible, ultimately driving adoption and maximizing return on investment.
6. Facilitating Seamless Integration
Integration testing ensures that enterprise applications correctly communicate with legacy systems, cloud services, APIs, and third-party software. By verifying data consistency and interaction workflows, testing prevents costly synchronization errors and operational bottlenecks.
7. Supporting Continuous Improvement and Innovation
Automated and continuous testing practices enable rapid, reliable updates without compromising stability. This agility allows businesses to innovate faster, respond to customer needs promptly, and maintain a competitive edge.
Types of Enterprise Applications (And What to Test in Each)
Understanding the distinct categories of enterprise applications is essential for effectively directing testing efforts and ensuring that each system performs optimally in alignment with business objectives. Each category carries specific functional demands, user expectations, and integration complexities that require tailored testing approaches.
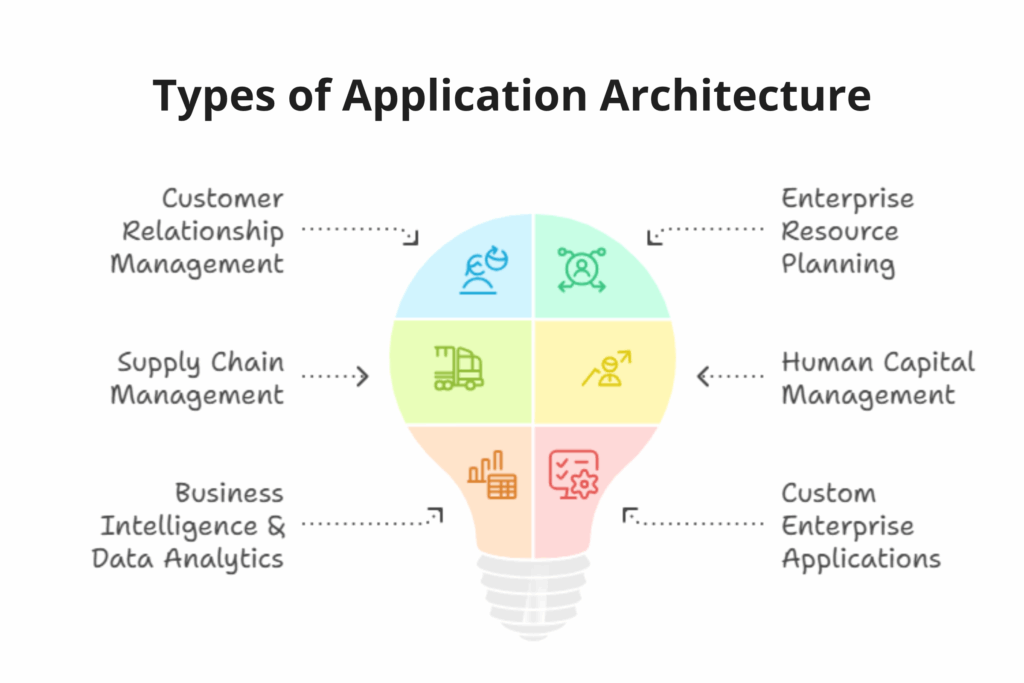
Let’s explore the major types of enterprise applications and their critical testing focus areas:
1. Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
CRM systems helps in managing an organization’s interactions and relationships with current and potential customers. Testing priorities here revolve around:
- Contact Management: Ensuring accurate and consistent handling of customer data, including creation, updates, and deletion across the system.
- Data Integrity: Maintaining synchronization and consistency between various CRM modules and external databases to prevent data corruption or duplication.
- UI/UX Across Devices: Verifying that interfaces adapt fluidly and maintain usability on desktops, tablets, and mobile devices for a cohesive user experience.
- Role-Based Permissions: Testing access controls to safeguard sensitive customer information, ensuring users see only the data relevant to their roles.
- Third-Party Integrations: Validating seamless connectivity with external tools such as email marketing platforms, social media channels, and customer support systems.
2. Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)
ERP platforms integrate diverse business functions into a unified system, demanding comprehensive testing of interconnected modules:
- Cross-Module Data Flow: Confirming that information flows flawlessly between departments like finance, HR, procurement, and inventory, avoiding discrepancies.
- Business Rules Validation: Testing the correct application of complex policies and regulations embedded in workflows.
- Transaction Accuracy: Verifying the precision and reliability of financial and operational transactions.
- Load Handling: Ensuring stability and responsiveness through system performance assessment under peak workloads.
- Localization & Currency Handling: Ensuring the software adapts correctly to regional languages, legal requirements, and multi-currency operations.
3. Supply Chain Management (SCM)
SCM applications coordinate the flow of goods, information, and finances from supplier to customer, emphasizing real-time accuracy:
- Inventory Updates: Testing real-time reflection of stock levels across multiple warehouses and sales points.
- Supplier Communication: Validating electronic data interchange (EDI) processes for smooth supplier interactions and order placements.
- Logistics Tracking: Ensuring shipment statuses and delivery timelines are accurately tracked and updated.
- Real-Time Order Processing: Verifying the correct sequencing and handling of orders from initiation through fulfillment.
- IoT Integration: Testing interactions with connected devices like RFID readers or sensors to enhance inventory and asset management.
4. Human Capital Management (HCM)
HCM systems manage employee lifecycle processes, emphasizing compliance, privacy, and ease of use:
- Payroll Processing: Ensuring accurate computation of salaries, taxes, benefits, and deductions.
- Policy Enforcement: Validating adherence to company rules for leave management, attendance, and performance evaluations.
- Workflow Automation: Testing the smooth functioning of approval processes for leave requests and other employee actions.
- Data Privacy: Ensuring robust protection of personal and sensitive employee data in compliance with regulations.
- Mobile Accessibility: Verifying that employees can conveniently access HCM features on mobile devices.
- Report Generation: Ensuring reports are accurate, comprehensive, and customizable for various HR needs.
5. Business Intelligence & Data Analytics
These applications turn raw data into actionable insights, placing heavy emphasis on accuracy and performance:
- Data Pipeline Integrity: Testing that data is correctly ingested, transformed, and loaded from diverse sources.
- Transformation Accuracy: Ensuring that calculations, aggregations, and data manipulations reflect true business metrics.
- Dashboard Performance: Measuring load times and responsiveness of complex visualizations.
- Visualization Accuracy: Validating that charts, graphs, and tables accurately represent the underlying data.
- Role-Based Data Access: Confirming that users only access analytics data permitted by their role or clearance level.
Once the model proves effective, extend it to other teams and apps. Provide training so testers can interpret AI insights and offer feedback. Successful teams embed AI into their culture – treating it as a co-pilot, not a black box. This helps scale intelligently while keeping quality front and center.
6. Custom Enterprise Applications
Custom applications are aligned to unique organizational needs so they require specialized testing focus:
- Domain-Specific Processes: Thoroughly validating workflows and features that address unique business requirements.
- User Journey Testing: Ensuring the application supports seamless and logical user experiences from start to finish.
- Extensibility Checks: Testing the application’s ability to evolve through future enhancements without destabilizing existing functionality.
- System Integration: Validating interactions with other internal systems, third-party APIs, and cloud services.
- Maintainability: Assessing code quality and documentation to facilitate long-term support and upgrades.
Core Components of an Enterprise Testing Strategy
Developing a robust enterprise testing strategy is essential for ensuring software quality at scale while aligning with business objectives. Such a strategy must be adaptable, deeply integrated with organizational workflows, and leverage automation to accelerate testing cycles without compromising thoroughness. Let’s dive into the foundational components that make an enterprise testing strategy both effective and sustainable:
1. Requirements & Traceability
A strong testing strategy begins with a crystal-clear understanding of what needs to be tested and why. This involves:
- Defining Acceptance Criteria Aligned to Business Goals: Every test case should be directly tied to measurable business outcomes, ensuring the software delivers real value. Clear acceptance criteria prevent ambiguity, guide development, and provide benchmarks for success.
- Maintaining Traceability: Utilizing tools like JIRA, Qyrus, or Confluence to link requirements, test cases, and defects creates an auditable trail. Traceability helps teams track progress, identify gaps, and ensure that all business needs are covered, reducing the risk of missed features or unintended consequences.
2. Environment & Data Management
Accurate testing requires environments and data that closely mirror real-world conditions:
- Replicating Production Environments: Testing should occur in environments that reflect the production setup in architecture, configurations, and network conditions, helping uncover environment-specific issues early, preventing surprises post-deployment.
- Using Anonymized or Synthetic Data: To comply with data privacy laws such as GDPR and HIPAA, sensitive data must be masked or replaced with synthetic datasets. This safeguards customer and employee information while enabling realistic and compliant testing scenarios.
3. Test Automation
Automation is a cornerstone for enterprise testing that allows frequent, repeatable, and efficient validation:
- Automating Regression, Performance, and Smoke Tests: Automation accelerates the verification of critical functionality with every code change. It helps detect regressions, measure system responsiveness, and ensure basic operability without manual overhead.
- Leveraging Testing Frameworks: Tools like Selenium for UI automation, Qyrus for end-to-end testing, TestNG and JUnit for unit and integration tests provide scalable platforms to build reusable, maintainable test suites.
4. Performance & Load Testing
Enterprise applications often have to withstand high traffic volumes and complex transactions:
- Simulating Concurrent Users: Tools such as JMeter, LoadRunner, and Qyrus enable teams to mimic thousands of simultaneous users interacting with the system, helping identify bottlenecks, memory leaks, and response time issues before production.
- Measuring System Resilience: Beyond just load, performance testing validates scalability, resource usage, and system recovery under stress, ensuring the application can handle real-world demands.
5. Security Testing
Protecting enterprise data and systems from vulnerabilities is non-negotiable:
- Conducting Vulnerability Assessments and Penetration Testing: Regular scans and ethical hacking simulate attacks to uncover weaknesses and verify that security controls are effective.
- Ensuring Regulatory Compliance: Testing must validate adherence to industry standards and legal requirements such as GDPR for data protection, HIPAA for healthcare, and OWASP Top 10 for web application security risks, mitigating legal and reputational risks.
6. Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) Integration
Embedding testing into CI/CD pipelines transforms quality assurance into a continuous, automated process:
- Enabling Faster Release Cycles: Automated tests run on every code commit provide immediate feedback, catching defects early and allowing rapid iterations without compromising quality.
- Supporting DevOps Culture: Integrating testing into DevOps workflows fosters collaboration between development, operations, and QA teams, accelerating delivery while maintaining robust safeguards.
7. User Acceptance Testing (UAT)
The final validation stage focuses on real-world usability and stakeholder confidence:
- Involving Business Stakeholders: End-users and business analysts participate in validating that the application meets practical needs, workflows, and expectations.
- Testing Usability and Workflow Integrity: UAT goes beyond functionality, focusing on ease of use, intuitiveness, and alignment with business processes to ensure the software delivers tangible operational benefits.
Explore Quinnox’s Testing and Test Automation Services to build a future-ready testing strategy.
Benefits of Enterprise Application Testing
When done right, testing becomes a catalyst for stronger business performance, resilience, and innovation. Here’s a closer look at what organizations gain through disciplined enterprise testing practices:
1. Improved Software Quality
One of the immediate benefits of thorough enterprise testing is the enhancement of software quality. By detecting defects early in the development lifecycle, organizations can significantly reduce costly rework, minimize technical debt, and prevent cascading issues later on. This proactive defect management ensures that applications function as intended, with fewer interruptions, bugs, or inconsistencies.
2. Risk Mitigation
Testing reduces the risk of severe system failures, data corruption, or security breaches by uncovering vulnerabilities before they reach production. Rigorous testing scenarios, including stress, security, and integration tests, ensure that potential weak points are identified and resolved. This vigilance helps safeguard the organization’s assets, reputation, and compliance standing, lowering the chances of costly incidents.
3. Business Continuity
Unexpected downtime can have devastating financial and operational consequences. Enterprise testing validates essential backup, failover, and disaster recovery processes, confirming that systems can quickly bounce back from disruptions. By simulating failure conditions and recovery procedures, testing assures that business operations remain uninterrupted or are restored swiftly, minimizing the impact of outages on customers and internal teams.
4. Operational Efficiency
When systems are reliable and performant, employees experience fewer interruptions and spend less time troubleshooting. This increased operational efficiency boosts productivity, reduces manual intervention, and enables teams to focus on strategic initiatives rather than firefighting technical issues. Testing ensures that all integrated components work cohesively, driving seamless day-to-day operations.
5. Regulatory Compliance
Enterprise application testing plays a pivotal role in validating compliance with standards such as GDPR for data protection, SOX for financial transparency, HIPAA for healthcare privacy, and other sector-specific mandates. By embedding compliance verification into testing protocols, organizations can avoid legal penalties, audits, and reputational damage while reinforcing stakeholder confidence.
6. Faster Time-to-Market
Automated testing frameworks integrated with DevOps pipelines accelerate development cycles by enabling continuous validation with every code change. This seamless integration reduces manual bottlenecks and allows teams to deploy confidently and frequently. As a result, organizations can respond more quickly to market demands, customer feedback, and innovation opportunities.
7. Enhanced Customer Experience
At its core, enterprise application testing takes care of end-to-end software testing so that only reliable, intuitive, and responsive software reaches the end user. Well-tested applications minimize glitches and performance issues, while user-focused testing ensures that interfaces and workflows align with user expectations. This positive experience drives higher adoption rates, better user engagement, and stronger customer loyalty- key factors in sustaining competitive advantage.
Challenges in Enterprise Testing
Organizations face numerous obstacles that complicate the testing process, often requiring innovative solutions and strategic planning. Understanding these challenges is the first step toward overcoming them effectively.
1. Complex System Architecture
Enterprise applications today are rarely monolithic; they often consist of interconnected microservices, APIs, middleware, and multiple data layers. This distributed architecture introduces intricate interdependencies that complicate comprehensive test coverage. Ensuring that changes in one service don’t inadvertently break others demands sophisticated testing strategies, including contract testing, end-to-end automation, and continuous monitoring. Mapping these relationships and testing them exhaustively is a daunting but necessary task to maintain system integrity.
2. Rapid Release Cycles
The rise of Agile and DevOps methodologies has accelerated release cadences dramatically. While this enables faster delivery of features and fixes, it simultaneously shrinks the window available for thorough testing. QA teams must create and execute tests rapidly, often under tight deadlines, while ensuring quality is not compromised.
3. Data Privacy & Management
Testing requires data that reflects real-world scenarios. However, enterprise data is often highly sensitive, subject to stringent privacy regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, and CCPA. Creating realistic test data sets without exposing or mishandling personal or confidential information presents a major challenge. Data masking, synthetic data generation, and secure data management practices become essential to maintain compliance and protect privacy while supporting meaningful test coverage.
4. Environment Management
Setting up test environments that accurately mimic production is both technically complex and resource-intensive. These environments must replicate network configurations, hardware setups, software versions, and third-party integrations to uncover environment-specific issues. Additionally, managing multiple concurrent environments for development, testing, staging, and user acceptance requires significant infrastructure investment, coordination, and maintenance often becoming a bottleneck in the testing process.
5. Tool Integration
The enterprise testing landscape involves a plethora of specialized tools for test management, automation, performance testing, security scanning, and reporting. Fragmented toolchains can lead to data silos, duplication of effort, and inconsistent reporting, undermining efficiency and collaboration between teams. Hence, ensuring that these tools integrate seamlessly with each other and with CI/CD pipelines is critical for smooth workflows and reliable results.
6. Skill Shortages
The rapid evolution of technology, especially with emerging trends like AI-driven testing, test automation frameworks, and complex enterprise architectures, has outpaced the availability of skilled QA professionals. Finding talent that possesses a deep understanding of both technical testing skills and business domain knowledge is a persistent challenge. This talent gap can slow down testing initiatives, increase reliance on external consultants, or lead to overburdened internal teams.
7. Legacy Technology
Many enterprises still rely on legacy systems that were built decades ago. These older platforms often lack modern APIs, proper documentation, or support for automated testing, making them notoriously difficult to test. Integrating legacy components with newer applications further complicates the testing landscape. Teams must balance maintaining legacy functionality while progressively modernizing systems often requiring creative testing approaches and specialized tools.
By anticipating these difficulties and proactively addressing them, enterprises can transform testing from a pain point into a competitive advantage ensuring resilient, secure, and high-performing software that powers business growth.
Best Practices for Enterprise Application Testing
Testing enterprise applications is a complex but crucial endeavor. To maximize effectiveness and align quality assurance efforts with business goals, organizations must adopt a holistic approach that blends technical rigor with strategic foresight. Below are best practices for a successful enterprise application testing program:
1. Align Testing with Business Outcomes
Testing efforts should never be performed in isolation from business priorities. Every test case must directly reflect a business objective whether it’s safeguarding revenue streams, enhancing customer satisfaction, or ensuring regulatory compliance.
- Traceability: Develop clear linkages between test scenarios and business requirements or risk factors. For example, test cases around payment processing should tie directly to revenue protection.
- Impact-Focused Testing: Allocate more testing effort to features that affect customer experience or legal compliance, ensuring these critical areas receive heightened scrutiny.
By maintaining this alignment, testing delivers measurable value and supports strategic decision-making.
2. Implement Risk-Based Testing
Not all components of an enterprise system carry equal risk or importance. Risk-based testing helps prioritize resources and focus on areas with the greatest potential impact:
- Customer-facing vs. Internal: User-facing modules typically require more exhaustive testing compared to internal administrative tools.
- Compliance-Driven Areas: Systems handling sensitive data or regulatory workflows should undergo stringent security and audit testing.
- Historical Defect Patterns: Use past defect data to identify fragile modules warranting deeper examination.
Risk-based prioritization ensures efficient use of limited testing bandwidth while protecting critical business functions.
3. Embrace Shift Left and Shift Right Testing
Modern quality assurance is continuous, spanning the entire software lifecycle:
- Shift Left: Early defect detection reduces remediation costs and accelerates development so start testing early in the development process by incorporating unit tests, static code analysis, and integration tests.
- Shift Right: Complement early testing with post-release monitoring and user behavior analysis in production environments. Real-time feedback helps catch issues that manifest only under live conditions and improves future release quality.
This dual approach creates a feedback-rich ecosystem that enhances both preventive and detective quality controls.
4. Reuse and Modularize Tests
Enterprise applications evolve rapidly, requiring testing strategies that are both flexible and maintainable:
- Reusable Components: Develop modular test scripts and shared libraries for common functions, reducing duplication and speeding up test development.
- Parameterization: Design tests to accept variable inputs, enabling broader coverage without rewriting scripts.
- Scalable Maintenance: Modularization simplifies updates when application changes occur, making it easier to keep test suites relevant and efficient.
This practice significantly improves test coverage and reduces long-term maintenance overhead.
5. Enable Continuous Testing
Continuous testing underpins modern DevOps and Agile environments:
- Automation at Every Stage: Integrate automated tests within development, build, integration, and release pipelines. This ensures early detection of defects and maintains quality during frequent code changes.
- Rapid Feedback Loops: Automated test results provide immediate insights to developers and QA, enabling faster fixes and smoother releases.
- Broad Test Coverage: Include unit, functional, regression, performance, and security tests in the continuous suite for comprehensive validation.
Continuous testing fosters a culture of quality and resilience throughout the software delivery lifecycle.
6. Encourage Cross-Skilling and Continuous Learning
The complexity of enterprise applications demands versatile testers equipped with diverse skills:
- Technical Upskilling: Provide training on automation tools, performance testing, and emerging technologies like AI-driven testing.
- Domain Knowledge: Equip testers with business context to understand workflows, compliance needs, and user expectations.
- Learning Programs: Initiatives like Quinnox’s AI Guild demonstrate how fostering communities of practice can build internal expertise and drive innovation.
Cross-skilled testers improve collaboration, adaptability, and overall testing effectiveness.
7. Use Metrics to Drive and Refine Testing Strategy
Data-driven insights are vital for evaluating and enhancing testing efforts:
- Defect Density: To identify problematic areas, ensure that the team monitors the number of defects relative to code or functionality size at regular intervals.
- Automation Coverage: Track what percentage of tests are automated to gauge efficiency and potential gaps.
- Mean Time to Recovery (MTTR): Measure how quickly defects are resolved after detection, indicating responsiveness.
- Test Execution Rate: Assess how many tests are completed per cycle to ensure timely quality checks.
Regular analysis of these KPIs informs continuous process improvement and aligns testing outputs with business needs.
Success Story: Qyrus Intelligent Testing in Action
A leading European bank used Quinnox’s Qyrus platform to streamline regression testing across their CRM, HCM, and ERP modules. Results included:
- 95% regression test automation coverage
- 60% reduction in release cycle time
- Zero critical bugs post-production over 3 quarters
- 24/7 automated monitoring integrated with CI/CD pipeline
Their enterprise testing function is now a catalyst for innovation not a bottleneck.
Real-World Impact: Qyrus TEI Case Study
A recent Forrester Total Economic Impact™ (TEI) study of Qyrus highlights the tangible value that intelligent testing can deliver:
- 213% ROI over 3 years
- $1.03M Net Present Value (NPV)
- <6 Months Payback Period
- 90% QA & Developer Time Savings
By adopting Qyrus, a global enterprise automated 95% of its regression testing, accelerated release cycles by 60%, and achieved zero critical bugs in production over three quarters—transforming QA into a growth driver.
Final Thoughts
In a hyper-digital economy, enterprises can’t afford to treat testing as a checkbox. It must be embedded, intelligent, and business-aligned. Whether you’re rolling out a new ERP, modernizing a legacy SCM, or enabling digital self-service, robust enterprise testing is the linchpin to success.
At Quinnox, our intelligent testing platform Qyrus and services are purpose-built to help global enterprises scale, accelerate, and secure their application ecosystems with confidence.
Do you need help with your enterprise testing strategy? Reach our experts today or request for a live Qyrus demo session to get started!
FAQs about Enterprise Application Testing
Enterprise application testing validates large-scale software used across an organization for performance, security, functionality, and reliability.
It ensures mission-critical systems don’t fail, protects business continuity, and ensures compliance and user satisfaction.
Functional, integration, regression, load, security, UAT, API, and smoke testing.
Popular tools include Qyrus, Selenium, JMeter, TestRail, Jenkins, and Burp Suite.
Automation enables rapid, consistent testing across large applications—reducing manual effort, cost, and time-to-market.
Use wrapper APIs, service virtualization, and codeless automation tools. Combine exploratory testing with automated regression.
It involves higher complexity, cross-system dependencies, compliance needs, larger teams, and deeper risk impact.
Adopt AI-powered automation tools like Qyrus, build a DevOps-aligned strategy, and invest in tester training.