Accelerate IT operations with AI-driven Automation
Automation in IT operations enable agility, resilience, and operational excellence, paving the way for organizations to adapt swiftly to changing environments, deliver superior services, and achieve sustainable success in today's dynamic digital landscape.
Driving Innovation with Next-gen Application Management
Next-generation application management fueled by AIOps is revolutionizing how organizations monitor performance, modernize applications, and manage the entire application lifecycle.
AI-powered Analytics: Transforming Data into Actionable Insights
AIOps and analytics foster a culture of continuous improvement by providing organizations with actionable intelligence to optimize workflows, enhance service quality, and align IT operations with business goals.
When your CEO asks, “How many of our customers who bought Product X also opened a support ticket in the last 30 days?”, how quickly can your teams answer? Is it an immediate, confident reply, or does it trigger a five-day scramble involving three different departments, two manual file exports, and a prayer that the IDs match up?
The real bottleneck in today’s businesses isn’t technology or even data volume-it’s the human effort wasted on connecting the dots. Analysts, engineers, and executives waste hours stitching together data from tools that were never designed to talk to each other. The result: slow decisions, inconsistent reports, and missed opportunities. Imagine instead asking that same question and getting one clear, verified answer – instantly.
That’s the promise of Data Integration: unifying your organization’s information into one coherent, trusted source of truth. When done right, it frees teams from endless data wrangling and gives leaders the clarity to move fast with confidence.
This blog post will demystify data integration, moving beyond technical jargon to explore its tangible examples and the real-world use cases that are fundamentally transforming how organizations operate, innovate, and lead their markets.
A recent survey found that 48% of M&A professionals are now using AI in their due diligence processes, a substantial increase from just 20% in 2018, highlighting the growing recognition of AI’s potential to transform M&A practices.
What is Data Integration?
At its core, Data Integration is a comprehensive process and set of technologies that combine data from disparate sources into a unified, coherent, and valuable view. Its primary purpose is to address the data fragmentation inherent in modern business architectures, which often rely on dozens, if not hundreds, of specialized applications and databases.
Think of it as creating a universal translator and highway system for your organization’s information. It’s not just about moving data; it’s about contextualizing and preparing it for its final, most valuable use: informing a decision or powering an application.
The Problem: Data Silos and Heterogeneity
To appreciate the value of data integration, we must understand the challenge. Organizations typically suffer from two primary data problems:
- Silos: Data is locked in separate, isolated systems (e.g., the CRM, the ERP, the accounting software, the website analytics platform). These systems don’t automatically talk to each other, creating blind spots.
- Heterogeneity: Even when data can be accessed, it exists in wildly different formats, structures, and quality levels. A customer’s name might be “John D.” in one system, “Doe, John” in another, and a missing field in a third. Date formats, currency codes, and key identifiers are rarely consistent.
The Solution: The Four Pillars of Data Integration
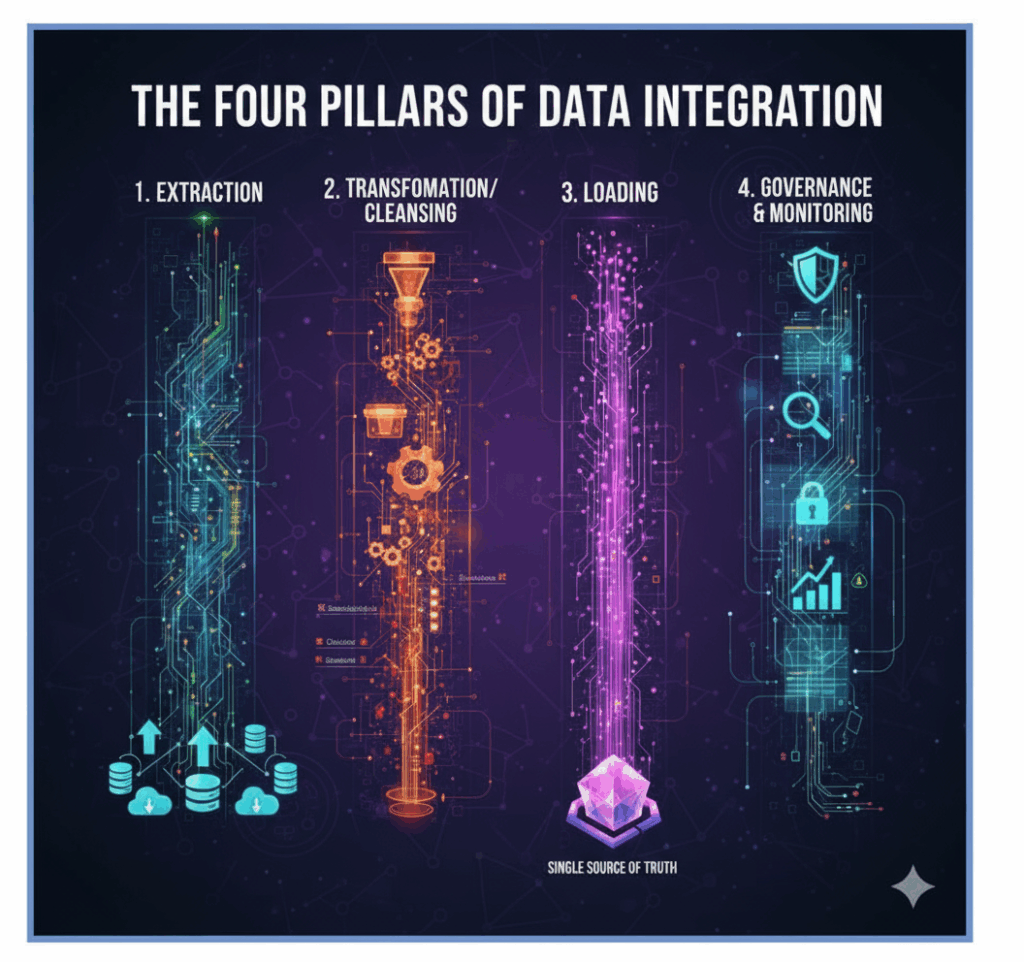
Data integration systematically overcomes these hurdles through a structured process, most commonly defined by a pattern of Extraction, Transformation, and Loading (ETL), or its modern counterpart, Extract, Load, and Transform (ELT). Regardless of the chosen pattern, the process involves four crucial pillars:
1. Extraction: Pulling data from the source systems. This could involve direct database connections, reading APIs, or ingesting files. This step must be robust, secure, and capable of handling data at any velocity–from massive nightly batches to continuous, real-time streams.
2. Transformation/Cleansing: This is arguably the most critical step. Raw data is inherently messy. Transformation involves:
- Standardization: Ensuring all fields (like addresses, names, or dates) follow a single, agreed-upon format.
- Cleansing: Identifying and correcting errors, filling missing values, and removing duplicate or corrupt records.
- Mapping: Translating data codes and structures from the source format to the target format (e.g., converting product category “4A” from the legacy systems to “Electronics” in the new data warehouse).
- Aggregation: Summarizing or joining data sets (e.g., combining a customer’s last five orders into a single “Total Lifetime Value” metric).
3. Loading: Moving the clean, transformed data into a unified target system, which is often a Data Warehouse, Data Lake, or a Master Data Management (MDM) system. This centralized repository becomes the organization’s “Single Source of Truth.”
4. Governance & Monitoring: Beyond the initial move, true integration requires continuous monitoring to ensure data pipelines are running smoothly, data quality remains high, and access controls (governance) and compliance standards are enforced at every step. This ongoing discipline is what sustains trust in the integrated data.
To delve deeper into the strategic importance of this discipline within the enterprise data landscape, you can explore the insights on enterprise data integration.
Common Data Integration Examples
Data integration manifests in several tactical examples, each designed to solve a specific problem of data movement, timing, or access. Understanding these examples illuminates the versatility of a robust integration platform.
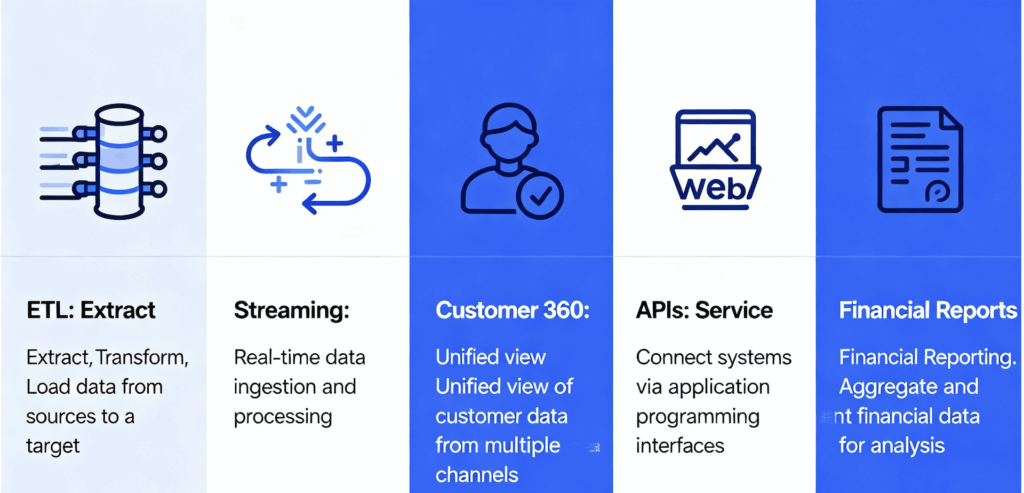
1. Traditional ETL for Business Intelligence (BI)
This is the classic example. A company needs to run a comprehensive quarterly report on its financial performance, marketing ROI, and sales pipeline.
- Source Systems: ERP (Finance/Operations), CRM (Sales), Marketing Automation Tool, and Web Analytics.
- Integration Task: Extract data from all four systems nightly. Transform the data by calculating metrics (e.g., converting raw clicks into cost-per-acquisition, or summing up monthly revenue). Load the clean, structured data into a central data warehouse.
- Result: The BI team can now query the data warehouse and generate a single, accurate dashboard that correlates marketing spend with actual closed deals and revenue, a task impossible when the data was isolated in four different tools.
2. Real-Time Data Streaming for Operational Agility
In a high-stakes, real-time scenario, batch processing is too slow.
- Example Scenario: A multinational logistics company is tracking thousands of shipments globally.
- Source Systems: IoT sensors on trucks, warehouse inventory systems, and customer-facing tracking portals.
- Integration Task: Use a real-time streaming method to ingest constant data feeds from IoT sensors (location, temperature) and immediately combine it with inventory data (product type, destination).
- Result: If a truck’s refrigeration unit sensor data indicates a temperature spike (a pre-defined threshold), the integrated system can instantly trigger an alert that updates the operational dashboard and sends a notification to the driver and maintenance team, preventing spoilage – all within seconds.
3. Customer 360-degree view
This is the most human-centric example of integration, focusing on synthesizing all customer touchpoints.
- Source Systems: E-commerce platform (purchase history), Service Desk/Helpdesk (support tickets), Social Media Listening Tool, and Mobile App.
- Integration Task: Integrate all systems to match disparate identifiers (e.g., social handle, email, phone number) to a single Master Customer ID. Transform and clean the data to create a unified customer profile.
- Result: A customer service agent, upon receiving a call, instantly sees the customer’s entire history on one screen: their last purchase, their recent support tickets, and even a recent complaint they posted on social media. This integrated view transforms a generic support interaction into a highly personalized and efficient one.
4. Enterprise Application Integration (EAI) and APIs
This focuses on enabling direct, real-time communication between different business applications to support immediate operational workflows.
- Example Scenario: A customer places an order on the e-commerce website.
- Integration Task: A dedicated API (Application Programming Interface) integration layer immediately extracts the order details from the e-commerce system and loads it directly into the ERP system’s inventory module to deduct stock, and simultaneously into the Finance system to create an invoice.
- Result: Inventory is accurate the moment the order is placed; eliminating the risk of selling out-of-stock items, and the order-to-cash process begins instantly, dramatically speeding up fulfilment and revenue cycles.
5. Financial Reporting
Finance teams often juggle data from multiple systems to close books or prepare reports, which leads to delays and inconsistencies.
- Source Systems: ERP, CRM, HR, and external market data feeds.
- Integration Task: Automated pipelines extract and standardize financial data, reconciling transactions, costs, and revenues across all systems into one governed data warehouse.
- Result: CFOs and finance teams gain real-time visibility into financial performance, accelerate month-end closures, and produce accurate compliance reports without manual effort – turning financial reporting from a reactive task into a strategic advantage.
Check out on this read: Data Integration Techniques and Methodologies Explained
Real-World Use Cases of Data Integration Across Industries
Data integration quietly powers transformation across every sector. When systems, platforms, and data sources connect, organizations unlock a level of visibility and speed that simply isn’t possible in isolation.
Here’s how different industries are using integration to drive real business outcomes.
Use Case 1: Retail and E-commerce
In retail, data integration has become the backbone of personalization. By connecting e-commerce platforms, in-store POS systems, loyalty programs, and marketing tools, brands can finally understand each customer as a single entity. A customer browsing online can receive real-time offers in-store, loyalty points update instantly, and inventory reflects the same data across channels. This unified view helps brands deliver consistent experiences, reduce churn, and grow sales – all powered by an integrated data foundation.
Use Case 2: Financial Services
Banks and financial institutions rely on data integration to stay compliant, secure, and customer centric. Integrated data from transaction systems, KYC databases, and fraud detection tools allows for real-time monitoring and automated alerts.
When suspicious activity occurs, it’s flagged instantly, protecting both the customer and the organization. Beyond compliance, integration helps banks gain a 360-degree view of clients, enabling smarter credit decisions, faster onboarding, and more personalized product offerings.
Use Case 3: Manufacturing and Logistics
For manufacturers, data integration bridges the gap between the factory floor, supply chain, and sales operations. Demand forecasts from CRM tools, stock data from warehouse systems, and IoT signals from production lines come together to form a live, accurate picture of the entire operation.
This visibility allows for just-in-time inventory, predictive maintenance, and faster response to supply disruptions. Instead of reacting to delays, teams can proactively reroute materials, reschedule production, and meet delivery timelines with precision.
Use Case 4: Energy and Utilities
Energy companies are using integration to turn sensor data, weather information, and operational logs into predictive insights. Real-time integration across assets like turbines, grids, and substations allows utilities to anticipate faults and schedule maintenance before breakdowns occur.
By combining IoT, geospatial, and operational data, they’re improving grid reliability, reducing downtime, and optimizing resource allocation – creating smarter, cleaner energy systems.
Related Success Story in Action: Quinnox’s data integration improves application performance for world’s largest non-alcoholic bottler
Bringing It All Together
Across industries, the pattern is clear: integration breaks silos, accelerates decisions, and powers innovation. Whether it’s a retailer understanding customer intent, a bank catching fraud in real time, or a manufacturer optimizing supply chains, data integration strategy transforms complexity into clarity – helping organizations operate with confidence and intelligence in a data-driven world.
Conclusion
The modern enterprise runs on data, yet most still struggle to turn that data into actionable intelligence. The challenge isn’t a lack of information – it’s the fragmentation that prevents insight, speed, and innovation. The ability to unify, govern, and activate data across systems is what now separates digital leaders from the rest.
Data integration is the foundation of this transformation, enabling real-time visibility, trusted analytics, and AI-driven decision-making. It is the silent force behind every modern enterprise that aims to be more agile, predictive, and customer-centric.
At Quinnox, we take this a step further through our Quinnox AI (QAI) Studio – a rapid innovation hub that brings AI dreams to life in days, not months. By combining intelligent data integration with accelerated AI prototyping, QAI Studio helps organizations move from connected data to concrete outcomes faster than ever. Whether it’s predictive insights, intelligent automation, or advanced analytics, QAI Studio transforms your integrated data foundation into a launchpad for real innovation.
With Quinnox as your partner, your data does more than flow – it evolves, learns, and drives growth. That’s the power of intelligent integration, fueled by QAI Studio, and it’s how future-ready enterprises are built today.
Get in touch with our Experts today!
FAQs on Data Integration
Data integration connects information from multiple systems into a single, consistent view. It eliminates silos, improves decision-making, and ensures that business teams work with accurate, real-time data.
A common example is creating a Customer 360 view by combining CRM data, ERP billing details, and marketing engagement history into one unified customer profile. This gives teams a single, reliable version of the truth for better insights and personalization.
Common examples include aligning sales and marketing data, automating financial reporting, gaining supply chain visibility, and unifying customer analytics. In each case, data is synchronized between core systems like Salesforce, SAP, or cloud-based data platforms.
There are several techniques used to integrate data depending on business needs and infrastructure. The traditional ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) process cleans and standardizes data before it is moved into a warehouse. The modern ELT (Extract, Load, Transform) method reverses the process by loading raw data first and then transforming it using powerful cloud engines. Change Data Capture (CDC) or streaming integration enables real-time synchronization between systems, ensuring information is always up to date. Data virtualization, on the other hand, provides a unified view of data across multiple systems without physically moving it, allowing instant access and faster insights.
Data integration plays a critical role across sectors. In retail, it helps deliver personalized marketing by combining online and offline customer insights. In financial services, it enables real-time fraud detection by unifying transaction and customer data. In manufacturing, integrated IoT and ERP data allow predictive maintenance and better resource planning. In healthcare, integration ensures doctors have a complete and unified patient record from different clinical systems, improving diagnosis and care quality.
It improves decision quality, boosts operational efficiency, enhances customer experience, and accelerates insights. A robust integration strategy also provides the foundation for AI, automation, and advanced analytics.