Accelerate IT operations with AI-driven Automation
Automation in IT operations enable agility, resilience, and operational excellence, paving the way for organizations to adapt swiftly to changing environments, deliver superior services, and achieve sustainable success in today's dynamic digital landscape.
Driving Innovation with Next-gen Application Management
Next-generation application management fueled by AIOps is revolutionizing how organizations monitor performance, modernize applications, and manage the entire application lifecycle.
AI-powered Analytics: Transforming Data into Actionable Insights
AIOps and analytics foster a culture of continuous improvement by providing organizations with actionable intelligence to optimize workflows, enhance service quality, and align IT operations with business goals.
Across industries, enterprises are overwhelmed by application sprawl—a tangled mess of legacy systems, redundant tools, and underused software that quietly drain budgets, slow innovation, and increase security risks. It’s like trying to run a Formula 1 race while towing a trailer full of obsolete tech.
That’s where Application Rationalization (AppRat) steps in as a structured, strategic approach to evaluate, streamline, and optimize your software portfolio. Done right, it clears the clutter, boosts efficiency, and paves the way for smoother digital transformation.
But here’s the catch: most businesses do it wrong. According to Global Newswire Press Release, organizations reported underutilization or wasted IT spending of 36% for desktop software, 33% for data center software, 32% for SaaS, and 32% for IaaS/PaaS.
Despite the staggering numbers, enterprises continue to fall into the same traps—treating rationalization like a spring-cleaning sprint, trimming critical apps just to cut costs, or leaving out business users who rely on these systems.
Don’t be that team. In this blog, we’ll break down 7 of the most common (and costly) application rationalization mistakes, with clear, actionable fixes. And because we’ve seen even mature organizations fumble, we’re throwing in an 8th bonus mistake you’ll want to avoid in 2025 and beyond.
Let’s declutter that IT drawer—before it crashes your digital strategy.
A recent survey found that 48% of M&A professionals are now using AI in their due diligence processes, a substantial increase from just 20% in 2018, highlighting the growing recognition of AI’s potential to transform M&A practices.
What is Application Rationalization?
Application rationalization is the strategic process of evaluating and optimizing an organization’s application portfolio to reduce redundancy, improve efficiency, and lower costs. It’s not just about eliminating outdated software—it’s about aligning your IT assets with business objectives.
Organizations are increasingly pursuing an application rationalization strategy to simplify their IT landscape, eliminate technical debt, and accelerate modernization.
This process not only streamlines your portfolio but also ensures effective migration to the cloud and consolidation of data centers.
Top Mistakes in Application Rationalization (And How to Fix Them)
Despite good intentions, many organizations encounter pitfalls that hinder the success of their application rationalization initiatives. Below are critical (and common) mistakes—with practical ways to avoid them
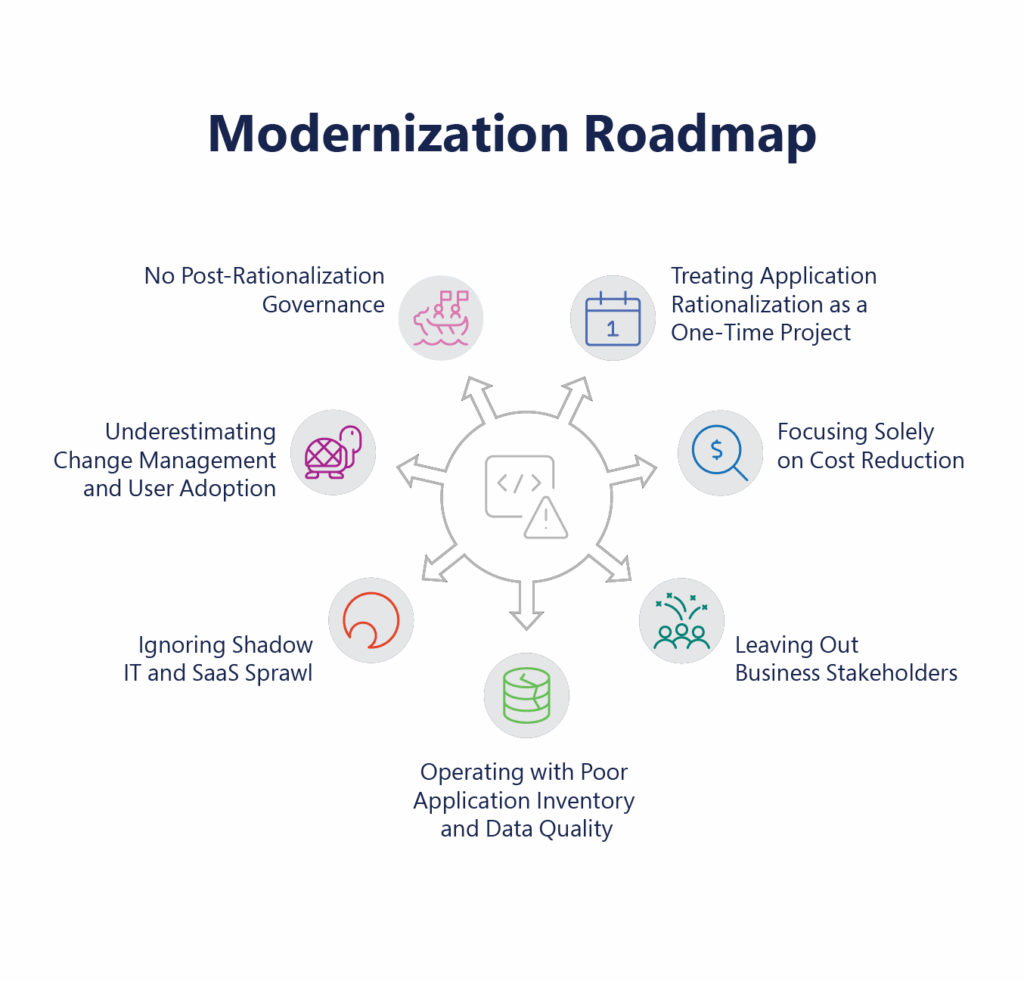
Mistake 1: Treating Application Rationalization as a One-Time Project
One of the most widespread misconceptions about application rationalization is that it’s a “do it once and done” task. Enterprises typically undertake it as part of a larger digital transformation or cost-saving initiative, and once completed, they move on to other priorities. However, this short-term mindset leads to rapid regression—applications re-enter the portfolio via mergers, departmental purchases, or new projects, returning the organization to square one.
Modern IT environments are constantly evolving, with new technologies, security risks, and compliance standards emerging regularly. An outdated rationalization effort becomes obsolete within a year, negating previous gains and compounding complexity over time.
How to Fix It:
Establish application rationalization strategy as a continuous, lifecycle-driven process. Embed it into your IT governance and architecture review boards. Use platforms like Qinfinite to continuously monitor application usage, performance, and redundancy. Treat rationalization not as a project—but as a mindset.
Mistake 2: Leaving Out Business Stakeholders
A purely IT-led rationalization effort often overlooks how deeply embedded certain applications are within daily business operations. Business users understand functional dependencies and operational nuances that IT may miss. When stakeholders are excluded, critical applications are misclassified or retired prematurely, causing frustration and lost productivity.
Moreover, change resistance increases when rationalization is perceived as a top-down IT cost-cutting mandate rather than a strategic optimization initiative.
How to Fix It:
Engage cross-functional teams early. Include representatives from finance, operations, sales, HR, and compliance. Conduct application value workshops where users can highlight the importance, pain points, and impact of each app. This collaborative approach enhances decision quality and user buy-in.
Mistake 3: Operating with Poor Application Inventory and Data Quality
Organizations frequently begin rationalization with an incomplete or inaccurate inventory of their applications. This includes untracked legacy apps, shadow IT, duplicate tools under different names, or forgotten tools purchased by specific departments. Without reliable data on ownership, usage, performance, and cost, rationalization becomes guesswork.
A flawed inventory leads to missed savings, security blind spots, and decisions that do more harm than good.
How to Fix It:
Use automated discovery tools to build a real-time application inventory. Integrate your CMDB (Configuration Management Database) and financial systems to ensure accurate metadata—usage logs, ownership, cost, and licensing data. Periodically audit and refresh this inventory as part of ITSM best practices.
Mistake 4: Focusing Solely on Cost Reduction
While cost reduction is often the trigger for application rationalization programs, making it the only metric is risky. IT teams sometimes target expensive applications without considering the full scope of business value, technical necessity, or user dependence. Eliminating a costly app that supports mission-critical workflows or regulatory compliance can disrupt operations and erode stakeholder trust.
Conversely, low-cost apps may look insignificant in terms of spending but could be indispensable to users or linked to strategic initiatives like customer analytics, automation, or AI.
How to Fix It:
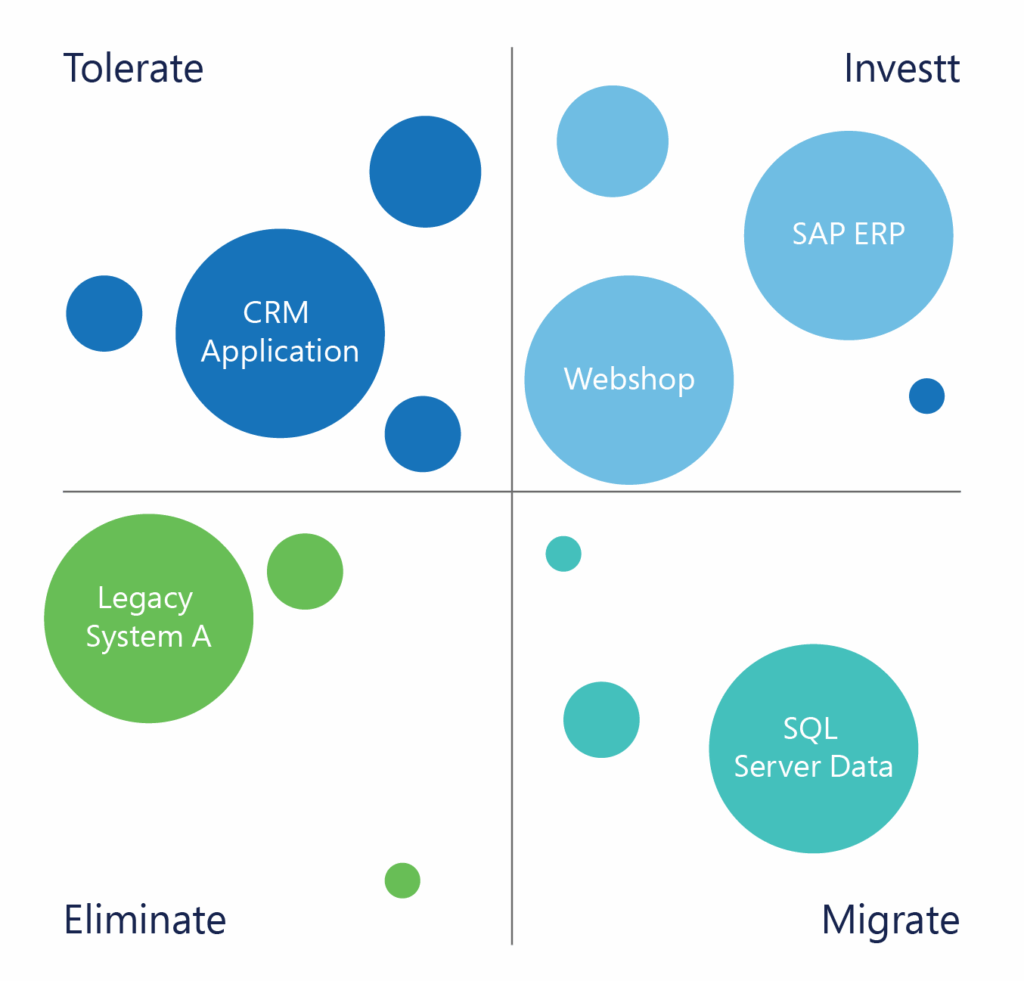
Go beyond dollars. Implement a balanced application scoring model that considers business value, usage frequency, risk, and technical fit—alongside cost. Frameworks like TIME (Tolerate, Invest, Migrate, Eliminate) can help prioritize rationalization decisions more holistically.
Mistake 5: Ignoring Shadow IT and SaaS Sprawl
In today’s hybrid work and cloud-native environment, employees often adopt their own tools to solve productivity gaps. This has led to shadow IT—unsanctioned apps that exist outside of IT’s purview. According to CIO, shadow IT accounts for over 30-40% of technology spent in large enterprises. These tools might duplicate approved systems, increase risk exposure, or lack integration and security controls.
SaaS sprawl also contributes to overspending, as multiple departments may subscribe to similar tools independently, often at different price points and with underused licenses.
How to Fix It:
Deploy SaaS management platforms to identify all SaaS apps used across the organization. Flag redundant tools, unused licenses, and non-compliant software. Create clear procurement and approval workflows for new apps, and offer enterprise-grade alternatives to curb shadow IT.
Mistake 6: Underestimating Change Management and User Adoption
Even the best rationalization strategy can fail if users are blindsided. Removing or consolidating applications without preparing users for the transition creates resistance, loss of productivity, and operational friction. In some cases, employees revert to old tools, purchase unauthorized substitutes, or disengage entirely from new platforms.
This change fatigue can derail broader digital transformation initiatives, especially in organizations already navigating multiple parallel changes.
How to Fix It:
Treat rationalization as an organizational change—not just an IT task. Follow models like ADKAR or Kotter’s 8-Step Change Model to manage communication, training, pilot rollouts, and feedback loops. Ensure new apps are intuitive, better performing, and well-supported to accelerate user adoption.
Mistake 7: No Post-Rationalization Governance
After apps are decommissioned or merged, many organizations assume the work is done and fail to put governance mechanisms in place. This creates an open door for redundant or incompatible applications to re-enter the environment, leading to “app sprawl 2.0.” Without guidelines, departments may independently buy or subscribe to tools without central oversight.
Over time, this negates rationalization benefits, reintroduces complexity, and results in governance gaps that complicate future cloud migrations or audits.
How to Fix It:
Implement an application lifecycle governance framework. Define clear policies for how applications are evaluated, procured, reviewed, and retired. Establish a review board that includes architecture, security, procurement, and business stakeholders. Audit new apps periodically and track their alignment with enterprise architecture principles.
Don’t just rationalize, revolutionize with our exclusive guide on “2025 and Beyond: Redefining Business Intelligent Application Management (iAM)” to learn how IT leaders are transforming legacy applications navigating Complexity, Cost, and Change.
Bonus Mistake: Overlooking Environmental and ESG Impact of Applications
Aspect |
Traditional Testing |
Chaos Engineering |
| Primary Goal | Validate functional correctness of code and features | Validate system resilience under unpredictable and adverse conditions |
| Environment | Mostly runs in development or staging environments | Often runs in production or production-like environments (with safeguards) |
| Scope of Failures | Tests known scenarios like missing inputs, invalid formats | Tests unknown unknowns like service failures, latency spikes, and node crashes |
| Failure Type Simulated | Code-level bugs, unit test failures, API contract violations | Real-world incidents: disk failure, API timeout, network partition, traffic surge |
| Testing Philosophy | Assumes the environment is stable and controlled | Assumes that failures are inevitable and should be proactively tested |
| Experimentation Model | Static test cases with predefined inputs/outputs | Hypothesis-driven experiments with observable impact on system behavior |
| Blast Radius | No concept of blast radius | Introduces concept of blast radius to control experiment impact |
| Observability Need | Moderate observability — logs and some basic metrics | Heavy reliance on observability — metrics, traces, alerts are crucial |
| Metrics Focus | Focuses on test pass/fail criteria | Focuses on latency, error rates, throughput, availability, UX impact |
| Change Trigger | Runs automatically during builds or deployments | Triggered as controlled, planned experiments by SRE or DevOps teams |
| Risk Coverage | Covers expected failures | Covers unexpected, cascading, systemic failures |
| Business Impact | Validates business rules and feature compliance | Protects customer experience and SLAs under failure conditions |
| Feedback Loop | Feedback mostly confined to QA cycles | Feedback drives resilience engineering, architecture, and runbooks |
| End Goal | Ensure code quality | Ensure system reliability and operational readiness |
With growing regulatory and societal focus on Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) goals, IT departments are being called upon to reduce the digital carbon footprint. Yet, few rationalizations strategies factor in how applications contribute to energy consumption, data center emissions, or unsustainable practices.
On-premises applications that require high computing power or inefficient code can significantly drive-up energy usage. Moreover, apps not designed for sustainability can hinder ESG reporting and compliance, especially under regulations like EU’s CSRD or the SEC climate disclosure rules in the U.S.
How to Fix It:
Incorporate green IT KPIs in your application assessment matrix. Favor cloud-native, energy-efficient, and scalable platforms that allow for auto-scaling and reduced idle time. Partner with cloud providers that offer sustainability dashboards and carbon calculators (e.g., AWS Customer Carbon Footprint Tool). Rationalizing high-emission applications can support both cost savings and ESG targets.
Make Rationalization Future-Ready with Qinfinite
Rationalizing your applications isn’t just a tactical clean-up—it’s a strategic enabler for innovation, agility, and sustainability. But to be effective, it needs more than one-time efforts or cost-cutting measures.
That’s where Qinfinite comes in.
As an intelligent application platform, Qinfinite helps you automate inventory discovery, assess application value through multiple dimensions (cost, compliance, ESG, user engagement), and enforce governance—all in one place. Its continuous intelligence engine tracks redundancy, overlap, and performance in real-time, turning application rationalization from a project into a living discipline.
With Qinfinite, your IT portfolio stays lean, green, and future-ready. Don’t wait, schedule a FREE Consultation with our experts today!
With iAM, every application becomes a node within a larger, interconnected system. The “intelligent” part isn’t merely about using AI to automate processes but about leveraging data insights to understand, predict, and improve the entire ecosystem’s functionality.
Consider the practical applications:
In the Infinite Game of application management, you can’t rely on tools designed for finite goals. You need a platform that understands the ongoing nature of application management and compounds value over time. Qinfinite is that platform that has helped businesses achieve some great success numbers as listed below:
1. Auto Discovery and Topology Mapping:
Qinfinite’s Auto Discovery continuously scans and maps your entire enterprise IT landscape, building a real-time topology of systems, applications, and their dependencies across business and IT domains. This rich understanding of the environment is captured in a Knowledge Graph, which serves as the foundation for making sense of observability data by providing vital context about upstream and downstream impacts.
2. Deep Data Analysis for Actionable Insights:
Qinfinite’s Deep Data Analysis goes beyond simply aggregating observability data. Using sophisticated AI/ML algorithms, it analyzes metrics, logs, traces, and events to detect patterns, anomalies, and correlations. By correlating this telemetry data with the Knowledge Graph, Qinfinite provides actionable insights into how incidents affect not only individual systems but also business outcomes. For example, it can pinpoint how an issue in one microservice may ripple through to other systems or impact critical business services.
3. Intelligent Incident Management: Turning Insights into Actions:
Qinfinite’s Intelligent Incident Management takes observability a step further by converting these actionable insights into automated actions. Once Deep Data Analysis surfaces insights and potential root causes, the platform offers AI-driven recommendations for remediation. But it doesn’t stop there, Qinfinite can automate the entire remediation process. From restarting services to adjusting resource allocations or reconfiguring infrastructure, the platform acts on insights autonomously, reducing the need for manual intervention and significantly speeding up recovery times.
By automating routine incident responses, Qinfinite not only shortens Mean Time to Resolution (MTTR) but also frees up IT teams to focus on strategic tasks, moving from reactive firefighting to proactive system optimization.
FAQs on Application Rationalization Mistakes
Common mistakes include treating it as a one-time project, focusing only on cost, ignoring shadow IT, excluding business users, and neglecting post-rationalization governance.
Avoid mistakes by creating a lifecycle-based rationalization program, engaging stakeholders early, using real-time inventory tools, adopting change management, and enforcing strong governance.
Success can be measured through KPIs such as reduced IT spend, improved application performance, user adoption rates, reduction in security vulnerabilities, and ESG impact metrics.
Application rationalization helps eliminate technical debt, accelerate modernization efforts, and align the IT stack with business goals—making it foundational to digital transformation.
Redundant or legacy apps can stall modernization by increasing integration complexity and cost. Rationalization removes these blockers, enabling smoother cloud migration and innovation.
Yes, platforms like Qinfinite offer automation for inventory discovery, scoring models, governance enforcement, and monitoring—dramatically increasing efficiency and accuracy.