Accelerate IT operations with AI-driven Automation
Automation in IT operations enable agility, resilience, and operational excellence, paving the way for organizations to adapt swiftly to changing environments, deliver superior services, and achieve sustainable success in today's dynamic digital landscape.
Driving Innovation with Next-gen Application Management
Next-generation application management fueled by AIOps is revolutionizing how organizations monitor performance, modernize applications, and manage the entire application lifecycle.
AI-powered Analytics: Transforming Data into Actionable Insights
AIOps and analytics foster a culture of continuous improvement by providing organizations with actionable intelligence to optimize workflows, enhance service quality, and align IT operations with business goals.
In the evolving world of enterprise software development, manual testing often feels like a bottleneck rather than a solution. While manual testing plays a critical role in understanding user experience and catching nuanced issues, it struggles to keep pace with the rapid release cycles, increasing complexity, and scale of modern applications. This mismatch leads to longer delivery times, inconsistent test coverage, and a higher risk of defects slipping into production – issues that can significantly impact business outcomes and customer trust.
This is where test automation: a powerful approach that promises speed, accuracy, and scalability in testing shines as a savior. For enterprises striving to remain competitive, automation has become a necessity. Yet, success in test automation requires more than just tools; it demands the right expertise, a strategic framework, and adherence to test automation best practices. Without these, automation efforts can quickly become inefficient, brittle, and costly.
In this blog, we’ll dive into 15+ essential best practices that enterprises must follow to build robust, maintainable, and effective test automation frameworks, turning testing from a hurdle into a competitive advantage.
Understanding Test Automation and Its Transformative Role in Enterprises
Test automation is the practice of using software tools to run predefined tests on applications automatically, without human intervention. Instead of manually clicking through screens and checking outcomes, automated tests execute scripts that mimic user interactions and validate system responses, enabling faster and more reliable quality assurance.
For enterprises, where software forms the lifeblood of operations and customer engagement, test automation helps keep pace with rapid development cycles, maintain consistent quality, and reduce costs associated with manual testing efforts.
Why Test Automation is Essential for Enterprises
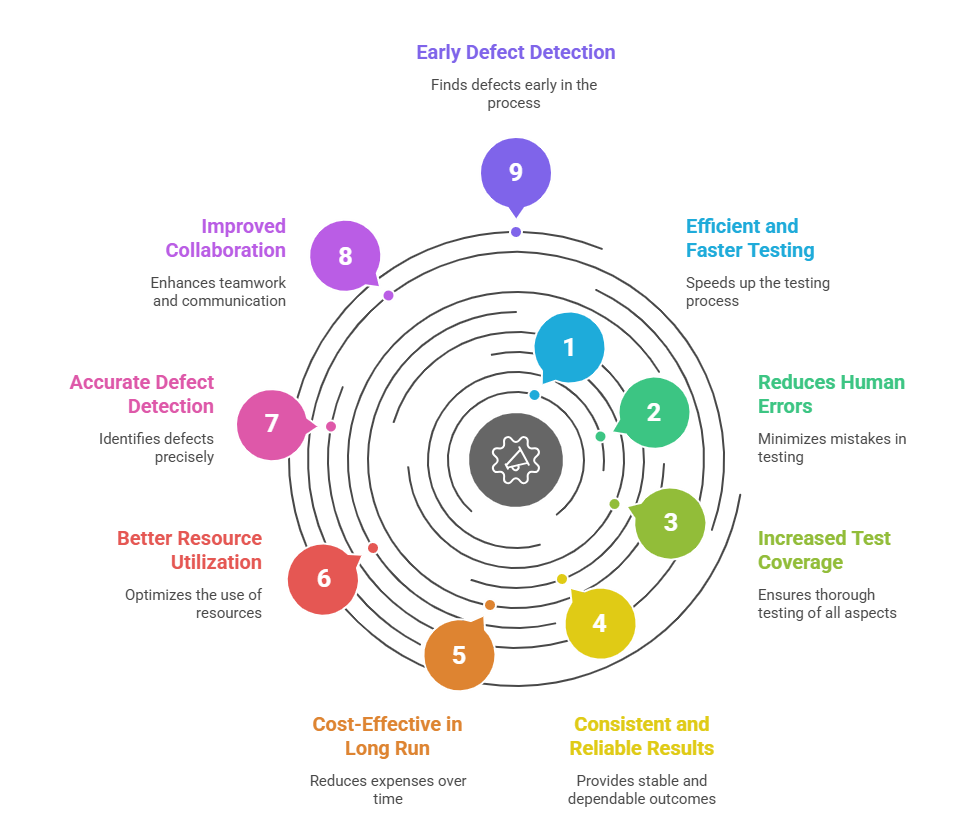
In large-scale environments, the complexity and velocity of software delivery demand a testing approach that can keep up. Here’s why automation is critical:
- Accelerating Time-to-Market: Automated testing dramatically reduces the time needed to verify new features, enabling enterprises to release updates faster and respond quickly to market demands or regulatory changes.
- Ensuring Consistency and Reliability: Automated tests perform exactly the same steps every run, eliminating human error and providing consistent, repeatable results. This consistency is vital when validating mission-critical applications.
- Scaling Coverage Efficiently: Enterprises deal with sprawling applications, multiple platforms, and countless scenarios. Automation allows thousands of tests to run in parallel across diverse environments, something impossible with manual efforts alone.
- Lowering Long-Term Costs: Though initial setup requires investment, automation reduces ongoing manual labor, minimizes costly post-release defects, and enables early detection of issues—saving time and money over the software lifecycle.
- Empowering Teams to Innovate: By automating routine checks, QA professionals can focus on exploratory testing and complex scenarios, driving innovation and uncovering deeper insights that machines alone can’t detect.
15+ Test Automation Best Practices to Follow
Here are proven automation best practices in software testing that can set your team up for success.
1. Define Clear Objectives
Before starting, clarify why you need automation. Is it to speed up regression testing, ensure cross-platform compatibility, or support continuous delivery? Defined goals help guide tool selection, framework design, and test coverage.
2. Select the Right Tool for Your Needs
Choosing the right test automation tool is critical for enterprises aiming to build a scalable, efficient, and reliable testing process. The ideal tool must not only align with the technology stack and workflows but also be flexible enough to adapt as applications evolve. A poor choice can lead to fragile tests, high maintenance costs, and gaps in coverage that ultimately undermine software quality and slow down delivery.
This is where AI-powered end-to-end test automation platform, Qyrus addresses the common challenges enterprises face by intelligently automating test creation and maintenance, offering self-healing capabilities that reduce manual effort, and providing comprehensive coverage across UI, API, and backend layers.
3. Build a Scalable Test Automation Framework
Creating a scalable test automation framework is essential for enterprises that want to sustain long-term quality and agility as their software grows in complexity and scale. A scalable framework is not just about writing a bunch of automated scripts; it’s about designing a flexible, maintainable, and robust foundation that can evolve alongside your applications and business needs.
Without a scalable framework, test automation efforts become brittle, cumbersome, and costly to maintain. Tests break frequently, require constant rewrites, and ultimately lose their value as teams struggle to keep up.
4. Start Small, Then Scale
Don’t attempt to automate every test case at once. Begin with high-value, repetitive regression tests. Once stable, scale automation to cover more functional, API, and non-functional scenarios.
5. Automate the Right Test Cases
Not every test benefits from automation. Prioritize:
- Regression tests
- Smoke and sanity tests
- Data-driven scenarios
- Repetitive workflows
Avoid tests requiring subjective validation or those that change frequently.
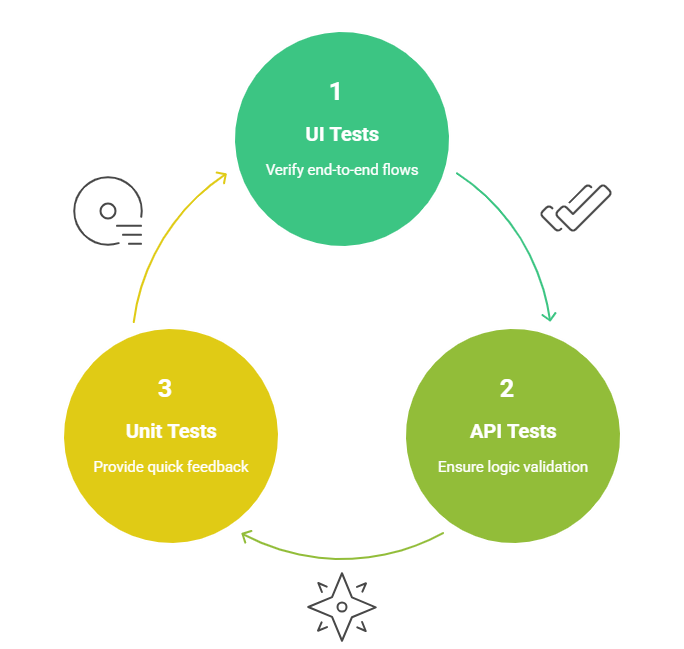
6. Follow the Test Automation Pyramid
Balance your efforts across unit, API, and UI layers. Unit tests provide quick feedback, API tests ensure logic validation, and UI tests verify end-to-end flows. Over-relying on UI automation can lead to brittle test suites.
7. Integrate with CI/CD Pipelines
Automation provides the most value when integrated into CI/CD workflows. Running automated suites with every build ensures immediate feedback and prevents defects from reaching production.
8. Use Reliable Test Data
Good test data management is critical. Use synthetic or masked datasets instead of live production data. For repetitive runs, leverage data-driven testing to enhance coverage without creating new scripts.
9. Ensure Test Independence
Each test should run independently to avoid cascading failures. Tests that depend on prior runs become fragile and difficult to maintain.
10. Implement Robust Reporting and Analytics
Without proper reporting, automation loses impact. By leveraging real-time dashboards, detailed logs, and intelligent alerts, organizations can quickly identify failures, track progress, and make data-driven decisions to improve test coverage and software quality. This transparency not only accelerates issue resolution but also helps prioritize testing efforts, making testing automation more effective and aligned with business goals.
11. Adopt Page Object Model (POM) or Similar Patterns
Framework design patterns like POM decouple test scripts from UI locators, making maintenance easier when UI changes occur.
12. Parallel and Cross-Browser Execution
Run tests in parallel across different browsers and devices to save time and ensure real-world compatibility. Cloud-based services make scaling easier.
13. Regularly Review and Update Test Suites
Automation is not a one-time activity. Conduct periodic reviews to remove obsolete tests, optimize redundant ones, and add new high-value scenarios.
14. Monitor for Flaky Tests
Flaky tests waste time and reduce trust in automation. Identify unstable tests early, fix environment dependencies, and maintain consistency across runs.
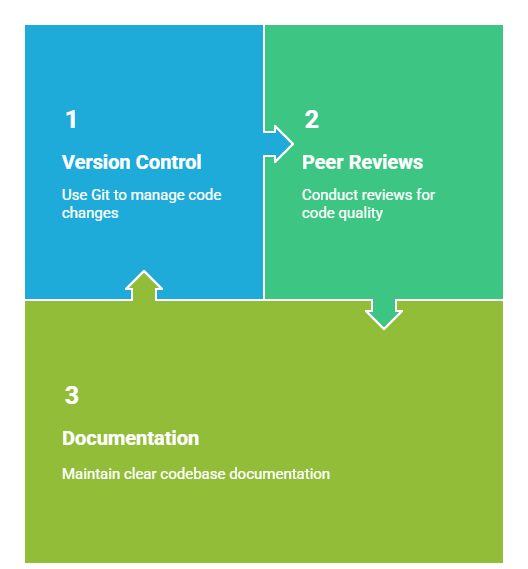
15. Treat Test Scripts as Code
Follow the same coding standards you would for development:
- Version control with Git
- Peer reviews
- Documentation
This prevents technical debt and ensures maintainability.
16. Include Non-Functional Testing Where Possible
Beyond functional automation, consider automating aspects of performance, load, and security testing. This ensures applications don’t just work—they scale under pressure.
17. Collaborate Across Teams
Automation is not solely QA’s responsibility. Involve developers, business analysts, and DevOps teams to align coverage with business priorities.
18. Upskill and Train Your Team
Invest in training to ensure your team can fully leverage tools, frameworks, and platforms. The success of automation depends on people as much as technology.
By implementing these automation best practices, organizations can achieve faster releases, greater confidence in quality, and higher test coverage.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Test Automation
Even the most sophisticated engineering teams can fall into traps that quietly undermine their automation strategy. Understanding these common missteps and why they persist is key to building a resilient and impactful automation framework. Here are pitfalls to avoid:
1. Automating Everything: A Misguided Pursuit of Coverage
It’s easy to equate more automation with better quality assurance. But indiscriminately automating every possible scenario is a fast track to diminishing returns. Not all tests offer equal value when automated. Moreover, highly dynamic, low-risk, or rarely executed scenarios often cost more to maintain than they save.
Hence, teams should focus on test automation as an investment – one that’s justified by its return in speed, confidence, and reduced manual effort. Also, prioritize stable, high-impact areas that are executed frequently and likely to break in the face of change.
Insight: Effective automation is not about testing more; it’s about testing smarter.
2. Neglecting Maintenance: Automation Is Not a ‘Set-and-Forget’ Tool
Automation scripts age poorly without active upkeep. As applications evolve, even the most robust tests can become obsolete triggering false alarms or, worse, missing real issues. When these scripts are ignored, they create noise instead of clarity, draining developer trust and slowing down releases.
Establishing ownership and review cycles for automated tests is crucial. Just as code is refactored over time, your test suite must be actively curated to stay relevant and effective.
Insight: The cost of ignoring test maintenance is not just technical – it’s cultural. Teams lose faith in broken tests.
3. Over-Relying on UI Tests: Fragile and Expensive by Design
While UI tests offer a valuable end-to-end perspective, they are inherently brittle. Minor changes in layout or styling can break test flows even when core functionality remains intact. This creates an illusion of instability and demands constant patching.
A well-balanced automation strategy leans on API and unit tests for fast, reliable feedback, reserving UI tests for critical user journeys. This layered approach ensures faster pipelines, better isolation of bugs, and reduced flakiness.
Insight: Think of UI tests as the tip of the testing pyramid, not its foundation.
4. Poor Documentation: Automation Without Context Is a Liability
When test scripts are poorly documented or worse, not documented at all – they become cryptic assets that only the original author understands. This makes onboarding difficult, stifles collaboration, and slows down future enhancements.
Clear naming conventions, comments that explain intent (not just what’s happening), and supporting documentation for the automation framework can make all the difference. The goal is to make your test suite readable and approachable, even for someone new to the team.
Insight: A test suite should serve as a source of clarity, not confusion.
5. Lack of Collaboration: Siloed Automation Leads to Blind Spots
Test automation cannot thrive as a side project owned solely by the QA team. When testers work in isolation, their scripts often miss the broader picture, leading to gaps in test coverage, duplication of effort, or misalignment with business goals.
Bringing developers, product owners, and QA into the same conversation ensures that automation supports the product, not just the process. Shared responsibility and visibility turn testing into a cross-functional asset.
Insight: Treat automation like code, which is collaborative, reviewed, and integrated into the development lifecycle.
6. Ignoring Flaky Tests: Death by a Thousand Inconsistencies
Flaky tests are like broken smoke alarms—they might go off, but you never know if there’s a real fire. When teams start to ignore intermittent failures, they also risk overlooking actual regressions. And when tests are unreliable, confidence in the entire automation suite erodes.
Every flaky test deserves attention. Whether the root cause is timing issues, async behavior, or infrastructure instability, unresolved flakiness is a silent killer of productivity.
Insight: Trust is the currency of automation. Flaky tests spend it fast.
How AI-Powered Test Automation is Changing the Game
While traditional automation revolutionized testing, AI-powered test automation is ushering in a new era, making the process smarter, more adaptive, and even more efficient.
- Intelligent Test Creation and Maintenance: AI algorithms analyze application changes and user behavior to automatically generate and update test cases. This reduces the manual effort of scripting and maintains test suites that evolve alongside the software, rather than becoming outdated.
- Enhanced Test Coverage and Prioritization: AI can identify high-risk areas and prioritize tests, accordingly, ensuring that critical functionality is always validated first. This dynamic risk-based approach maximizes value from limited testing windows.
- Self-Healing Tests: One of the biggest challenges in automation is flaky tests caused by minor UI changes or environment shifts. AI-powered tools can detect these changes and adjust tests automatically, reducing false failures and boosting trust in automated suites.
- Predictive Analytics for Quality Insights: AI doesn’t just run tests; it learns from results, predicting potential failure points and highlighting systemic risks before they impact users. This proactive quality assurance allows enterprises to fix issues earlier and improve software resilience.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP) for Accessibility: AI enables writing tests using natural language or business terminology, bridging the gap between technical teams and business stakeholders. This democratizes testing and improves collaboration.
Conclusion
Adopting automated testing best practices is not about following a checklist—it’s about embedding automation into the DNA of your software development lifecycle. By defining clear goals, choosing the right tools, building maintainable frameworks, and integrating with CI/CD, teams can maximize their ROI from automation.
At Quinnox, our software testing solutions are designed to help organizations achieve speed and quality with confidence. From intelligent testing automation services to advanced platforms like Qyrus, we empower businesses to scale automation seamlessly.
Interested to build reliable, resilient, and scalable test automation processes that support innovation and business growth? Reach our experts today!
FAQs About Test Automation Best Practices
They are proven methods and guidelines that improve the effectiveness of automation. Examples include choosing the right test cases, using frameworks, ensuring test independence, integrating with CI/CD, and maintaining reliable test data.
They ensure automation adds value rather than becoming a burden. Following best practices improves coverage, reduces cost of maintenance, accelerates feedback, and enhances software quality.
Key practices include defining goals, selecting the right tools, building robust frameworks, balancing UI/API/unit tests, integrating with CI/CD, and adopting coding standards for test scripts.
Common challenges include tool selection, skill gaps in the team, maintaining test data, managing flaky tests, and ensuring scalability across devices and environments.
Automation enables faster feedback loops, ensures repeatable and reliable tests, and reduces human error. By catching defects early and running tests continuously, it improves quality while speeding up delivery cycles.