Accelerate IT operations with AI-driven Automation
Automation in IT operations enable agility, resilience, and operational excellence, paving the way for organizations to adapt swiftly to changing environments, deliver superior services, and achieve sustainable success in today's dynamic digital landscape.
Driving Innovation with Next-gen Application Management
Next-generation application management fueled by AIOps is revolutionizing how organizations monitor performance, modernize applications, and manage the entire application lifecycle.
AI-powered Analytics: Transforming Data into Actionable Insights
AIOps and analytics foster a culture of continuous improvement by providing organizations with actionable intelligence to optimize workflows, enhance service quality, and align IT operations with business goals.
What if your most valuable insights were locked in separate systems that don’t speak to each other?
That’s the reality for many enterprises today. Data lives everywhere, on-premises, in the cloud, across CRMs, ERPs, and legacy databases. Yet without seamless access to this data, decision-making stalls, productivity drops, and opportunities slip away.
Enterprise data integration (EDI) solves this by connecting the dots between your systems, delivering unified, accurate, and real-time information needed to run your business in a smarter way. The result? No more data silos. No more guesswork.
According to market forecasts, the global enterprise data integration market is expected to reach $43.38 billion by 2033, more than triple its size in 2023. Why? Because the benefits of enterprise data integration go far beyond IT efficiency, they impact growth, agility, compliance, and customer experience.
In this blog, we’ll explore the core types of enterprise data integration, unpack the key benefits, and highlight real-world examples that show why integration is the foundation of effective business intelligence today. Whether you’re a CIO modernizing your data architecture or a business analyst building a data-driven culture, this guide is for you.
But first let us understand, what is enterprise data integration?
Enterprise Data Integration is the process of combining data from various sources across an organization such as databases, applications, cloud platforms, and legacy systems into a unified, consistent view. It’s not just about moving data from point A to point B; it’s about ensuring that information from different departments, systems, or technologies can work together seamlessly.
At its core, enterprise data integration helps break down data silos that often exist in large organizations. By synchronizing and standardizing data across systems, it enables more accurate reporting, streamlined operations, and a stronger foundation for analytics, AI, and real-time decision-making.
A recent survey found that 48% of M&A professionals are now using AI in their due diligence processes, a substantial increase from just 20% in 2018, highlighting the growing recognition of AI’s potential to transform M&A practices.
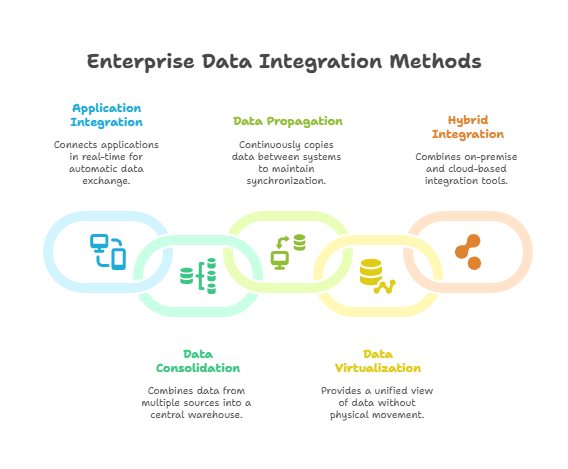
Types of Data Integration
Enterprise data integration can be achieved through several fundamental approaches. The optimal method (or combination of methods) depends on an organization’s specific needs, systems, and goals. Below we highlight the types of enterprise data integration, each with its purpose and use case:
1. Application Integration (EAI)
This involves connecting applications in real time so they can exchange data automatically. Commonly used to sync ERP, CRM, finance, and logistics systems via APIs or middleware. The goal is to ensure that updates in one system (e.g. a new customer in CRM) automatically propagate to other systems (e.g. billing or ERP) through event-driven messaging or APIs. Effective EAI eliminates fragmented processes and ensures the enterprise software ecosystem operates as a unified whole.
For instance, enterprise application integration services from providers like Quinnox leverage proven middleware technologies and APIs to unify robust systems, enabling operational excellence and better customer experiences. Explore more: enterprise application integration
2. Data Consolidation (ETL/ELT)
This involves combining data from multiple sources into a central warehouse or data lake using ETL (Extract, Transform, Load).
The aim is to provide one “single source of truth” for reporting and Business Intelligence. By merging disparate datasets into one database, organizations break down silos and improve data consistency. A consolidated data warehouse accelerates access to information and streamlines analytical workflows across the enterprise. This approach is ideal when you need historical trend analysis, comprehensive dashboards, or advanced analytics that draw on all parts of the business.
3. Data Propagation (Replication)
Data propagation refers to copying or moving data from one system to another on a continuous or scheduled basis. Unlike one-time ETL, propagation usually implies ongoing synchronization to keep systems in sync (e.g. replicating transactional data from a production database to a reporting database in near real-time). This approach is useful to “avoid redundant data entry across applications” and ensure different systems have the data they need when they need it.
For example, customer data from a CRM might be propagated into a separate customer support system so that both have up-to-date information. Data propagation techniques include change data capture (CDC), event streaming, or scheduled batch transfers. It’s especially common in scenarios like synchronizing prod databases to test environments (with masking of sensitive data) or feeding data lakes with incremental updates.
4. Data Virtualization
Data virtualization provides a unified, real-time view of data from multiple distributed sources without physically moving the data. In this approach, an integration layer or virtualization tool queries underlying source systems on-demand and presents the results as a single combined dataset or virtual database.
The benefit here is agility wherein business users get up-to-date data without waiting for batch processes, and there’s no need for a separate storage repository. Data virtualization is ideal for scenarios where data needs to remain at its source (for compliance or latency reasons) but still be queried together, for instance, an executive dashboard pulling live metrics from several systems.
5. Hybrid Integration
Modern enterprises often employ a hybrid integration strategy, combining on premise integration tools and cloud-based integration services. For example, an organization might use an on premise ETL tool for securely integrating legacy databases, while also using a cloud Integration-Platform-as-a-Service (iPaaS) for connecting SaaS applications. Many vendors provide hybrid integration platforms that allow deploying integration runtimes both on prem and in cloud, enabling a seamless blend. This category isn’t a distinct technique like the above, but rather an architectural choice to use a mix of integration approaches optimized for different environments.
Adopting a hybrid integration framework ensures that whether your data resides in a local data centre or various clouds, you can integrate it all under a unified strategy. Gartner even highlights “hybrid data integration platforms” as a must-have for competitive advantage, given most enterprises operate in hybrid IT landscape
Top Benefits of Enterprise Data Integration
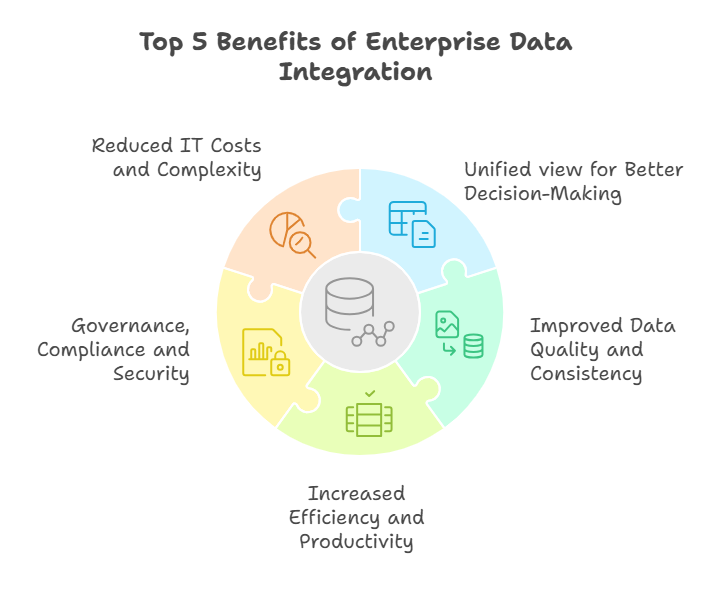
Integrating enterprise data delivers a wide range of business and IT benefits, transforming how organizations use information. Below are some of the major benefits of enterprise data integration:
1. Unified View for Better Decision-Making
By breaking down data silos and consolidating information, EDI provides leaders with a holistic view of operations, customers, and performance. This unified data view enables more informed, data-driven decisions. Executives are no longer guessing with fragmented reports; instead, they can analyse comprehensive dashboards that draw on all relevant data in real time. The result is improved strategic planning and faster, better decision-making, which is a critical advantage in today’s fast-paced business environment.
2. Improved Data Quality and Consistency
When data from multiple systems is integrated, organizations can enforce data quality standards and consistency across the board. Integration involves reconciling inconsistencies (e.g. standardizing codes or customer IDs) and eliminating duplicates to create a single source of truth. Higher data quality translates to more trustworthy reports and analytics. Teams can confidently act on insights, knowing they aren’t seeing conflicting figures from different departments.
3. Increased Efficiency & Productivity
Enterprise data integration automates the flow of data between systems, eliminating manual data entry and redundant processes. This streamlining of workflows leads to substantial efficiency gains and cost savings. For example, instead of an employee manually exporting sales data from one system and importing to another, an integrated pipeline does it automatically in seconds.
4. Governance, Compliance and Security
When done correctly, integrating data can also improve data governance and compliance. For instance, Centralized data movement simplifies audit trails, access control, and regulatory compliance (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA). Centralizing data movement through a controlled integration layer means data usage can be logged and audited more easily.
Modern integration platforms come with robust security features and monitoring, ensuring that as data flows between systems it remains protected. Moreover, by eliminating shadow IT data flows and spreadsheets, organizations reduce the risk of data breaches or errors. An integrated, well-governed data environment thus strengthens the overall security and compliance posture of the enterprise.
5. Reduced IT Costs and Complexity
By consolidating data platforms and automating pipelines, enterprise data integration can lead to significant cost savings in IT and data management. Maintaining one coherent data architecture is typically cheaper and easier than supporting numerous isolated systems and one-off interfaces. Organizations can retire costly legacy point-to-point scripts or manual processes. Many companies find that an upfront investment in a robust integration solution pays off quickly in the form of lower maintenance effort and more efficient use of IT personnel.
To summarise, the benefits of enterprise data integration span from tactical improvements (efficiency, cost savings) to strategic enablement (better decisions, innovation). By putting the right data in the right hands at the right time, EDI allows enterprises to leverage information as a true competitive asset which helps in driving smarter operations, happier customers, and more informed leadership.
Real-world Examples of Enterprise Data Integration Across Different Industries
1. Banking and Financial Services
Financial institutions handle vast amounts of data from customer profiles and transactions to fraud alerts and regulatory policies. Traditionally, these data streams exist in separate systems: core banking platforms, CRM systems, fraud detection engines, and external credit bureaus.
With EDI, banks can integrate all these systems to create a unified data ecosystem. This unified view enables real-time credit scoring, personalized offers, and automated compliance reporting aligned with regulations like Basel and FATCA.
The outcomes include significantly faster loan approvals, improved fraud detection through cross-channel insights, and streamlined regulatory reporting that minimizes audit efforts and reduces the risk of non-compliance.
2. Manufacturing
Manufacturing organizations generate data across ERP systems, MES (Manufacturing Execution Systems), IoT sensors, supplier networks, and quality assurance tools. Historically, these systems operate in isolation, creating challenges in visibility, coordination, and quality control.
With EDI, manufacturers can integrate shop floor operations, supply chain inputs, and equipment performance data into a unified operational intelligence layer. This integration supports predictive maintenance, real-time production monitoring, and end-to-end traceability.
The results include reduced equipment downtime, higher production efficiency, improved quality control through early defect detection, and better supplier collaboration based on shared, real-time data.
3. Energy and Utilities
Energy providers manage a complex mix of data from SCADA systems, smart meters, GIS mapping, CRM platforms, and regulatory bodies. These systems are often siloed, limiting responsiveness and operational optimization.
EDI enables integration across these disparate sources, creating a unified view of the grid, customer usage, infrastructure health, and outage data. This supports intelligent load balancing, real-time outage alerts, and data-driven maintenance planning.
The outcomes include improved grid reliability, faster outage resolution, optimized energy distribution, and enhanced compliance with sustainability and energy efficiency regulations.
4. Retail
Retailers operate across physical stores, e-commerce platforms, inventory systems, CRM tools, and marketing automation software. Often, customer behaviour, stock levels, and order fulfilment data reside in disconnected systems.
With EDI, retail businesses can unify customer journeys, inventory data, sales analytics, and campaign performance into one connected ecosystem. This empowers real-time inventory updates, personalized marketing, and seamless omnichannel experiences.
The impact includes higher conversion rates, improved stock availability, reduced order errors, and better customer retention through tailored engagement and consistent service across all channels.
5. Waste Management
Waste management companies work with route optimization tools, GPS tracking, regulatory systems, customer portals, and asset maintenance systems. These systems often function independently, leading to inefficiencies and service delays.
EDI connects operational data such as collection schedules, bin sensors, fleet management, and compliance logs into a centralized platform. This integration allows dynamic route adjustments, predictive maintenance of vehicles, and real-time compliance monitoring.
The result is improved operational efficiency, reduced fuel costs and emissions, timely regulatory reporting, and enhanced customer service through accurate tracking and scheduling.
How Quinnox Adds Value as the Best Enterprise Data Integration Tool
Quinnox provides end-to-end enterprise application integration and digital integration solutions tailored to your architecture, business priorities, and digital goals. Unlike conventional tools that simply move data, Quinnox’s advanced AI capabilities actively monitors, learns, and adapts in real time, making integration smarter, faster, and more resilient. It goes beyond static rules to make contextual decisions, enabling dynamic data mapping, anomaly detection, and self-healing pipelines that significantly reduce downtime and manual intervention.
What truly sets us apart is our ability to unify modern, cloud-native platforms with legacy systems- seamlessly and securely. Our robust library of pre-built connectors, real-time data streaming, and low-code interface empower both IT and business users to create and manage integrations with minimal friction. Whether you’re modernizing your data architecture or enabling AI-driven analytics, we ensure that clean, connected, and governed data is always at your fingertips.
Here’s how we do it differently:
- Accelerators: Ready-to-use integration patterns and connectors to speed up delivery.
- Architecture Decision Trees: To help you choose between ETL, API-led, or hybrid integration.
- Domain Experience: Telecom, manufacturing, BFSI, and consumer goods.
- Trusted Expertise: Certified teams in webMethods, AWS & Azure Integration Services, and more.
"At Quinnox, we treat integration not just as a tech task, but as a business enabler. Our goal is to simplify complexity and drive real business outcomes."
-Krishna Kumar Chakkirala, Vice President- Data and AI, Quinnox
Conclusion
Data is your enterprise’s most valuable asset, but only when it’s accessible, trusted, and connected.
Enterprise data integration is the foundation for this. It enables better decisions, faster responses, stronger compliance, and a data-driven culture. From application integration and ETL to virtualization and hybrid cloud connectors, the right integration approach backed by the right integration partner, tools, and strategy can transform your business.
It’s not just about connecting systems; it’s about empowering your business with insight and agility. Are you ready to integrate what matters?
Explore Quinnox’s enterprise data integration capabilities today!
FAQs about EDI
Enterprise data integration is the process of combining and managing data from different systems across an organization to ensure consistent, accessible, and unified information.
Application integration (EAI)
Data consolidation (ETL/ELT)
Data propagation (replication)
Data virtualization (federated access)
Hybrid integration (cloud + on premise)
Unified data views
Higher data quality
Improved productivity
Better decisions
Enhanced compliance
Real-time responsiveness
- Lower IT costs
Legacy system compatibility
Data quality issues
Scalability and performance
Governance and security
Change management and user adoption