Accelerate IT operations with AI-driven Automation
Automation in IT operations enable agility, resilience, and operational excellence, paving the way for organizations to adapt swiftly to changing environments, deliver superior services, and achieve sustainable success in today's dynamic digital landscape.
Driving Innovation with Next-gen Application Management
Next-generation application management fueled by AIOps is revolutionizing how organizations monitor performance, modernize applications, and manage the entire application lifecycle.
AI-powered Analytics: Transforming Data into Actionable Insights
AIOps and analytics foster a culture of continuous improvement by providing organizations with actionable intelligence to optimize workflows, enhance service quality, and align IT operations with business goals.
With the global data creation expected to reach 180 zettabytes by 2025 (Forbes), organizations are under increasing pressure to move, modernize, and manage vast volumes of data efficiently. Whether it’s to migrate legacy systems to the cloud, shift to more scalable applications, or unify disparate data sources, data migration has become a cornerstone of digital transformation.
But data migration is not just a technical shift; it’s a strategic move. Poorly executed migrations can lead to costly downtime, data loss, regulatory risks, and operational disruptions. In fact, Gartner estimates that 83% of data migration projects either fail outright or exceed their budgets and timelines. Another study by McKinsey, shows that on average, large IT projects exceed their budget and timeline by 45% and 7% respectively, while delivering 56 percent less value than predicted.
So, how can organizations approach data migration with confidence, clarity, and control?
This comprehensive blog walks you through what data migration is, its business drivers, key types, a step-by-step process, strategies, best practices, and common challenges – with practical tips and industry examples throughout.
A recent survey found that 48% of M&A professionals are now using AI in their due diligence processes, a substantial increase from just 20% in 2018, highlighting the growing recognition of AI’s potential to transform M&A practices.
What is Data Migration? And how does secure migration look like?
Data migration is the process of transferring data from one location, system, format, or application to another – typically during system upgrades, cloud adoption, or digital transformation initiatives.
At its core, it’s not just a lift and shift operation but a strategic initiative that ensures your data remains accurate, accessible, secure, and aligned with modern systems that support business growth.
What Does Secure Migration Involve?
A secure data migration ensures:
- Confidentiality: Data is encrypted in transit and at rest (e.g., using AES-256, TLS).
- Access Control: Only authorized users can access or handle the data, using RBAC and MFA.
- Integrity: The data remains unchanged and complete through validation checks.
- Compliance: Aligns with regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, and CCPA.
- Auditability: Logs and traceability throughout the migration process
In short, a secure migration is planned, encrypted, validated, and monitored at every step; because the cost of getting it wrong is far higher than the cost of doing it right.
Business Benefits of Migrating Your Data
By relocating data to modern infrastructure like the cloud or integrated platforms, organizations unlock faster operations, better compliance, lower costs, and more flexibility. Here’s how modernizing your data landscape through migration unlocks key business advantages:
1. Increased Performance & Scalability
Legacy systems often struggle to handle growing data volumes, user demands, and real-time workloads. By migrating to modern platforms especially cloud infrastructure; businesses benefit from auto-scaling capabilities, high-speed access, and improved uptime. These systems can dynamically scale up or down based on need, which is vital in peak usage periods.
Over 90% of organizations now use cloud services, with 48% planning to migrate more workloads in the next year, reflecting the recognized need for performance and scalability. [Source – Cloud Zero]
2. Improved Data Governance & Compliance
Modern platforms come with advanced data governance features like automated access controls, data lineage, audit trails, and policy enforcement. These features help businesses manage sensitive data responsibly while staying compliant with global regulations (like GDPR, HIPAA, CCPA).
3. Cost Reduction
Maintaining on-premises systems involves hardware purchases, software licensing, dedicated IT staff, and continuous maintenance. Cloud platforms eliminate many of these fixed costs and offer pay-as-you-go pricing models, reducing CapEx and OpEx. According to Mckinsey Research, companies can save up to 60% on infrastructure costs post-migration.
4. Operational Efficiency
Migrated systems are typically more integrated, easier to automate, and simpler to manage. This reduces manual processes, minimizes errors, and enables teams to focus on value-added tasks like innovation, analytics, and decision-making.
Post-migration, HSBC saw a 300% scalability boost, while Pacific Dental Services and GAF achieved efficiency gains of 40% and 20%, respectively. [Source – Splunk]
The Hidden Cost of Not Migrating Your Data
While the benefits of modernizing your data infrastructure are clear, failing to migrate can quietly erode your business from within. Legacy systems might still “work,” but they’re increasingly unfit for today’s digital demands. Here’s what organizations risk by not making the move:
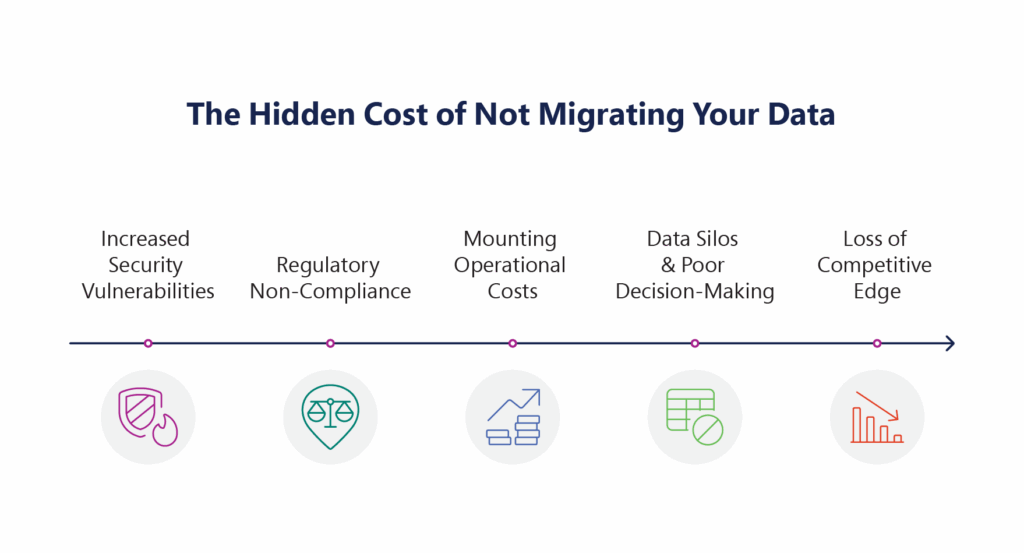
1. Increased Security Vulnerabilities: Outdated systems lack modern security features like real-time threat detection, encryption, and automated patching. This makes them prime targets for cyberattacks.
2. Regulatory Non-Compliance: Older platforms often can’t support new data privacy and security regulations (like GDPR, HIPAA, or CCPA). This increases the risk of hefty fines and reputational damage. According to CNBC News, in 2023, Meta was fined $1.3 billion under GDPR for data transfers failing to meet compliance standards.
3. Mounting Operational Costs: Legacy systems are expensive to maintain and require specialized talent, which is becoming scarce and costly. These sunk costs only grow with time.
4. Data Silos & Poor Decision-Making: Without integration or centralization, legacy environments create fragmented data, limiting visibility and making real-time analytics almost impossible. And the result? Missed opportunities, slow responses, and gut-based decisions that lack data support.
5. Loss of Competitive Edge: In a digital-first world, speed matters. Inflexible, outdated systems slow down innovation, time-to-market, and customer experience.
A Step-by-Step Process to Data Migration
A structured and strategic data migration process helps manage the complexity and reduce the risk of data loss, corruption, or downtime. Here’s a breakdown of the five critical steps every data migration project should follow to ensure minimal risk and maximum value:
1. Assessment & Planning
Before touching any data, organizations must define the scope, goals, and governance structure of the migration project. This step is all about clarity, alignment, and minimizing surprises.
Key activities include:
- Identifying source and target systems
- Determining what data will be migrated (and what will be archived)
- Assembling the migration team (IT, data architects, compliance, business users)
- Setting timelines, budgets, KPIs, and risk mitigation plans
- Choosing the right tools and migration approach (big bang vs. trickle)
2. Data Auditing and Cleaning
Before migrating, it’s essential to understand the state of your current data and clean it up.
Key activities include:
- Data profiling: Analyze structure, quality, formats, and dependencies
- Identifying and removing duplicate, outdated, or redundant records (DRO)
- Resolving inconsistencies in naming, formatting, and schema
- Tagging or flagging sensitive or regulated data for special handling
3. ETL (Extract, Transform, Load)
ETL is the technical heart of any data migration project. It refers to the process of:
- Extracting data from source systems
- Transforming it into compatible formats, structures, or standards
- Loading it into the new system
Some key considerations include:
- Mapping source fields to target fields
- Standardizing formats (e.g., date/time, currencies, units)
- Applying business rules or calculations during transformation
- Maintaining referential integrity and dependencies between datasets
Use case: During a financial services migration, Talend was used to mask sensitive PII data during transformation, ensuring compliance with GDPR.
ETL ensures that migrated data is accurate, consistent, and usable in the new environment—without introducing disruption or errors.
4. Migration Execution
This is where the actual migration happens. It involves transferring the cleaned and transformed data from the legacy system into the new target environment.
Key methods:
- Big bang migration: Entire data is migrated in one go—fast but can lead to longer downtime and rollback risks.
- Incremental (trickle) migration: Data is moved in phases or batches—reduces risk and downtime but takes longer.
Without proper execution, businesses face risks of data loss, corruption, or extended downtime—which can result in revenue loss and customer dissatisfaction. Execution is the most visible part of the migration, and any hiccups here affect business continuity and user confidence.
5. Post-Migration Testing and Support
Once data has been migrated, the job isn’t done. This phase ensures that everything functions as expected in the new environment.
Testing activities include:
- Data validation: Check if record counts, values, and relationships are intact
- System integration testing (SIT): Ensure apps and systems work together correctly
- User acceptance testing (UAT): Let end-users validate that functionality and data integrity meet business needs
Post-migration testing builds trust in the new system, prevents future issues, and provides documentation for regulatory audits or internal governance.
Each phase of successful data migration builds on the previous and skipping any step could compromise the integrity, usability and value of your data in its new environment.

What is a Data Migration Strategy and Why it Matters?
A data migration strategy is a structured blueprint that outlines how an organization will move data from one system to another—defining what data to move, when and how to move it, and who will be involved. It ensures alignment with business goals, reduces the risk of data loss or downtime, and supports regulatory compliance and data integrity. Without a clear strategy, migration efforts can spiral into delays, errors, and unexpected costs.
Now that you understand the importance of having a strategy, let’s look at the key considerations you need to plan a successful data migration project.
Key Considerations to Plan a Data Migration Project
A data migration project plan is not just a technical task—it’s a strategic initiative that requires collaboration between IT, business stakeholders, data owners, and end-users.
Key elements of a successful data migration project include:
- Clear goals and KPIs: Define what success look like—data accuracy, uptime, user adoption, etc.
- Stakeholder alignment: Ensure that decision-makers, technical teams, and users are aligned.
- Data governance: Assign data stewards and establish protocols for data quality and ownership.
- Budget and resource planning: Allocate necessary technical and human resources.
- Risk management: Develop contingency plans for potential issues like data loss or prolonged downtime.
Neglecting these elements can lead to failed migrations, lost productivity, and even regulatory penalties.
How to Choose the Right Data Migration Strategy
Your data migration approach should align with business goals, system complexity, and downtime tolerance. Here are the most commonly used strategies:
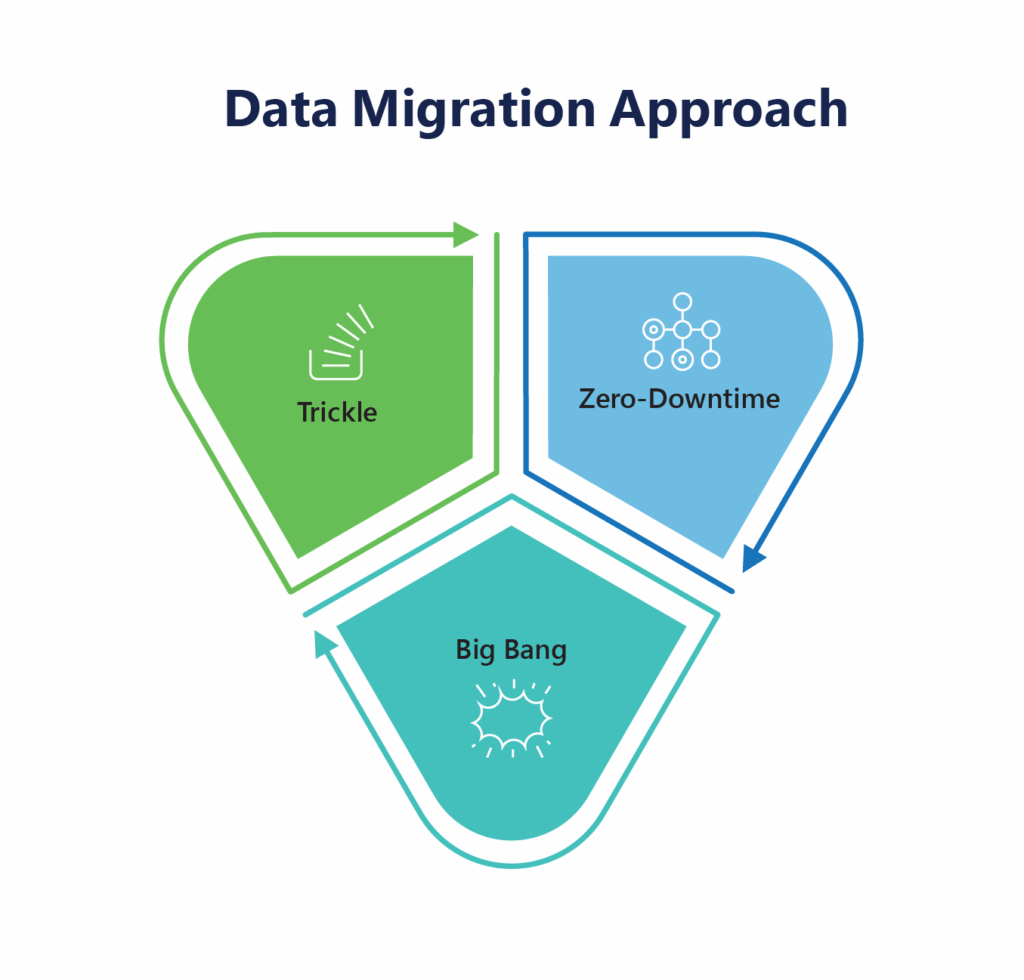
1. Big Bang Migration
All data is moved in a single event, usually during a scheduled downtime window. It’s fast and cost-effective but can be risky if issues arise post-migration.
Best for: Smaller systems or low-risk migrations with minimal dependencies.
2. Trickle or Phased Migration
Data is migrated in stages while both the source and target systems run in parallel. This allows for continuous operation and testing between phases.
Best for: Large-scale or mission-critical environments where uptime is essential.
3. Zero-Downtime Migration
Zero-downtime migration ensures that data is moved without disrupting ongoing business operations. Techniques like replication, data synchronization, and blue-green deployments are used to switch over seamlessly, allowing users to access systems without experiencing outages.
Best for: Enterprises that cannot afford any service interruption—such as financial services, e-commerce, and healthcare systems where business continuity is critical.
Data Migration Best Practices
A data migration can be disruptive if not carefully managed. To mitigate risks and ensure success, follow these data migration best practices:
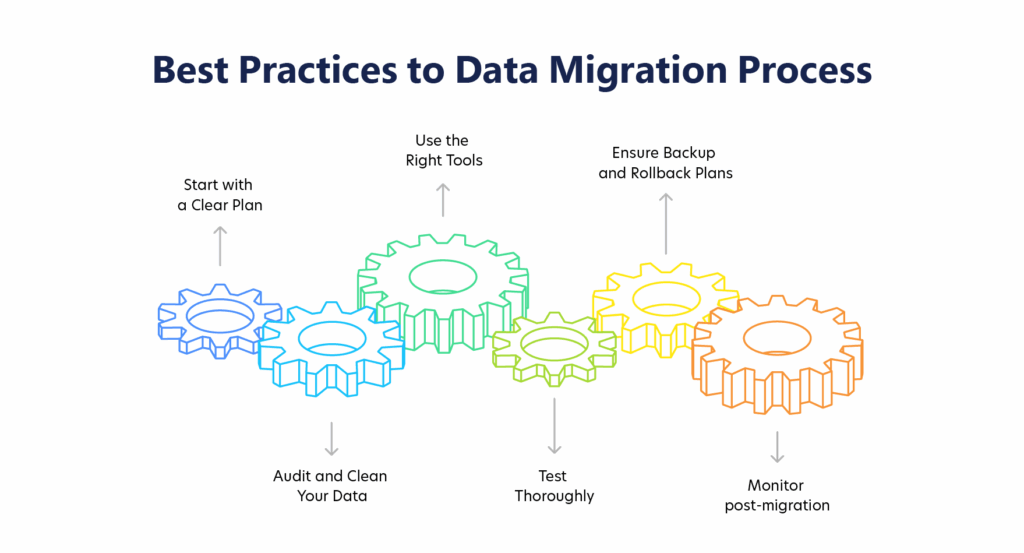
1. Start with a Clear Plan
- Begin the migration process by developing a comprehensive and detailed data migration plan that clearly defines the entire scope of the project. This should include identifying all relevant stakeholders such as IT teams, business units, data owners, and external vendors who will be involved or affected by the migration.
- Establish realistic timelines that consider potential challenges and contingencies, ensuring sufficient buffer time for unexpected delays.
- Define clear, measurable goals and success criteria to guide the project and provide benchmarks for evaluation.
- Set achievable milestones throughout the process helps maintain momentum and keeps the team aligned on progress.
- Additionally, communicate the plan thoroughly to all stakeholders to manage expectations and ensure everyone understands their roles and responsibilities.
2. Audit and Clean Your Data
- Before initiating the migration, conduct a thorough audit of the existing data to assess its quality, completeness, and relevance. Identify and resolve issues such as duplicate records, inconsistent data formats, missing values, and outdated or irrelevant information. This step is critical because migrating poor-quality data can result in corrupted datasets, system errors, and misleading analytics post-migration.
- Implement data cleaning procedures that standardize formats, validate entries, and remove redundancies. Engaging data owners and domain experts during this phase helps ensure that business rules and compliance requirements are met.
3. Use the Right Tools
- Selecting the appropriate migration tools is essential for a successful transition. Invest in software solutions that support automation to reduce manual effort and minimize human errors during the migration. Look for tools that offer data transformation capabilities, allowing you to map and convert data from the source format to the target system accurately.
- Further, choose tools with built-in validation features to verify data integrity throughout the migration process. Evaluate tool compatibility with your existing infrastructure, scalability to handle large volumes of data, and support for various data types and sources.
4. Test Thoroughly
- Before executing the final migration, perform multiple test migrations within a controlled sandbox or staging environment that mirrors the production system. These dry runs help uncover potential issues related to data accuracy, system performance, and user access rights without risking disruption to live operations. During testing, validate that all data has been correctly transferred, transformed, and is accessible to authorized users.
- Also, don’t forget to collect feedback from end-users and stakeholders to identify usability concerns or gaps in functionality.
5. Ensure Backup and Rollback Plans
- Prior to the migration, create full, secure backups of all critical data, applications, and system configurations to safeguard against data loss or corruption.
- Develop a detailed rollback plan outlining clear steps to restore the original environment if the migration encounters major issues or fails to meet success criteria. This plan should include predefined criteria for triggering the rollback and assign responsibilities to team members for executing recovery procedures swiftly.
- Document all backup and rollback processes thoroughly and test them periodically to ensure readiness.
- Lastly, remember that the first migration attempt may not be perfect, so having robust contingency plans minimizes downtime and protects business continuity.
6. Monitor Post-Migration
- After completing the migration and going live, continuously monitor data usage, system performance, and user interactions to detect any anomalies or issues early.
- Establish key performance indicators (KPIs) such as data access speeds, error rates, and transaction volumes to track ongoing system health. Encourage end-users to provide feedback regarding usability, data accuracy, and functionality problems.
- Set up automated alerts and reporting mechanisms to identify and address issues promptly, minimizing disruptions to business operations.
- Implement a structured process for applying patches, updates, or configuration changes as necessary. Ongoing validation and monitoring are crucial to maintaining data integrity and ensuring the new system performs reliably in the long term.
Proper validation is key to a successful data migration. Follow these Data migration validation best practices to ensure your data is accurate and systems perform reliably.
Final Thoughts
Data migration is a critical enabler of digital transformation, but it’s far from simple. It demands technical expertise, rigorous planning, and strong stakeholder alignment. Whether you’re migrating to the cloud, upgrading systems, or consolidating platforms, understanding the data migration process, choosing the right approach and methodology, and following best practices are key to success.
And to help you with that, our intelligent application management platform, Qinfinite comes into picture. From automated data mapping and ETL pipelines to robust governance, security, and post-migration optimization, Qinfinite helps you unlock speed, scale, and resilience at every stage of your migration journey.
So, are ready to migrate your data? Let Qinfinite help you execute with confidence, scale intelligently, and unlock future-ready data capabilities.
Don’t just take our word for it – Schedule a FREE 120-Mins Consultation with our Qinfinite Experts Today!
FAQ’s Related to Data Migration
A data migration strategy is a structured plan that outlines how data will be moved from one system to another, ensuring minimal disruption, accuracy, and alignment with business goals.
The key phases include assessment & planning, data profiling & mapping, transformation, loading, testing & validation, and post-migration support.
Best practices include detailed planning, data quality checks, using automated tools, rigorous testing, ensuring backups, and involving key stakeholders early on.
The right approach depends on system complexity, data volume, downtime tolerance, and business needs—options include big bang, phased, or trickle migration.
Ensure data integrity by validating data before and after migration, using checksums, maintaining audit trails, and performing rigorous testing throughout the process.