Accelerate IT operations with AI-driven Automation
Automation in IT operations enable agility, resilience, and operational excellence, paving the way for organizations to adapt swiftly to changing environments, deliver superior services, and achieve sustainable success in today's dynamic digital landscape.
Driving Innovation with Next-gen Application Management
Next-generation application management fueled by AIOps is revolutionizing how organizations monitor performance, modernize applications, and manage the entire application lifecycle.
AI-powered Analytics: Transforming Data into Actionable Insights
AIOps and analytics foster a culture of continuous improvement by providing organizations with actionable intelligence to optimize workflows, enhance service quality, and align IT operations with business goals.
In a world where speed, scalability, and customer experience dictate market leadership, clinging to legacy systems is now a strategic risk more than a technical issue. These systems and applications while once reliable, are now roadblocks to innovation, agility, and growth as they were designed for a completely different era of technology and business expectations.
A recent Gartner report highlights that nearly two-thirds of enterprise applications still fall into the legacy category, burdening IT departments with outdated architecture and fragile integrations. As a result, over 60–80% of IT budgets in many large organizations are funneled into maintaining these aging systems, leaving little room for modernization or innovation. To put the scale into perspective, IDC estimates that companies worldwide collectively spend more than $2.5 trillion each year on legacy system upkeep – an amount that rivals the GDP of some of the world’s largest economies.
And yet, although many businesses realize the need to upgrade to modern infrastructure, they often hesitate to modernize, as completely rebuilding applications from the ground up is often expensive, disruptive, and time-consuming. So, the solution?
This is where application replatforming offers the way forward. Rather than starting from scratch, replatforming takes existing applications and migrates them to modern, cloud-native environments, introducing key optimizations along the way, without touching the core architecture.
The result? Better performance, higher operational efficiency, lower costs, and faster time to market.
In this blog, let us deep dive into why replatforming is becoming essential for organizations that want to stay competitive in today’s digital-first world and how it can unlock both immediate and long-term business value.
What is Replatforming?
Replatforming is the process of moving an existing application from one platform (often on-premises or outdated infrastructure) to a new, more modern platform typically a cloud environment all while making minimal changes to the core architecture or codebase.
Think of it as renovating a house: you’re keeping the foundational structure intact, but updating key components like plumbing, electrical systems, and interior design to match modern needs.
Replatforming aims to enhance an application’s performance, scalability, and ease of maintenance without the disruption, expense, or complexity of a complete rebuild. It offers a balanced path to modernization by upgrading what matters most while preserving the core functionality that keeps the business running.
Unlike a rehost (lift-and-shift), replatforming may involve:
- Modifying middleware or runtime environments
- Updating databases for cloud compatibility
- Adjusting configurations for autoscaling or load balancing
- Introducing managed services for logging, caching, or monitoring
Replatforming is often described as “lift, tinker, and shift”- a more intelligent approach to migration that preserves the core logic of an application while unlocking the benefits of modern infrastructure.
Why and When to Replatform?
Not every application needs replatforming, and not every business is ready to pursue it. However, several clear indicators suggest when replatforming makes sense.
When to Consider Replatforming:
- Infrastructure Limitations: If your on-premises or outdated infrastructure is unable to support the growing needs of your applications due to storage constraints, performance issues, or cost inefficiencies, replatforming is a logical next step.
- Cloud Adoption Initiatives: Organizations embracing cloud-native architecture often start with replatforming to incrementally modernize workloads without disrupting services.
- High Maintenance Costs: Legacy systems demand high maintenance and specialized skill sets. Replatforming reduces technical debt and simplifies ongoing management.
- Compliance and Security Requirements: Modern cloud platforms offer built-in compliance and security features. Moving to these platforms through replatforming can help meet evolving regulatory standards.
- Improving Agility: If your development cycles are slow due to legacy constraints, replatforming can help unlock agility by enabling CI/CD pipelines and scalable environments.
- End-of-Life Software: When core components of your application stack are no longer supported, replatforming gives you an opportunity to modernize without completely refactoring.
Why Legacy Application Replatforming Over Other Options?
Replatforming provides a pragmatic balance, allowing organizations to future-proof their applications with significantly lower risk and effort compared to a total rewrite.
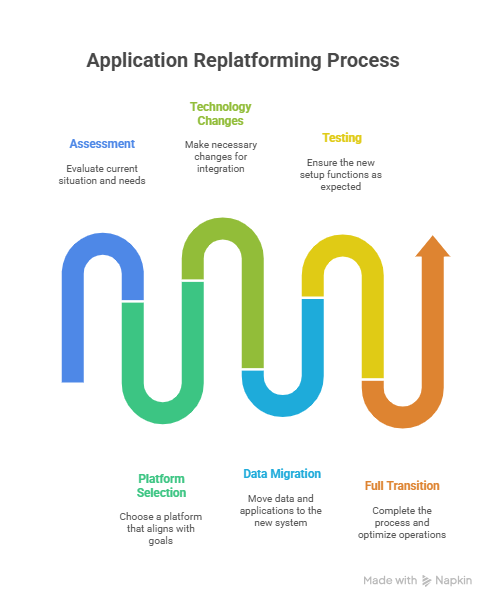
How Replatforming Works
A successful replatforming project typically follows a structured, phased approach that aligns technical execution with business goals. Here’s a breakdown of how legacy modernization approach with replatforming works:
1. Discovery and Assessment
This foundational stage is all about understanding what you have before deciding where you’re going. The goal is to evaluate your current application landscape, assess technical feasibility, and identify which systems are good candidates for replatforming.
Key activities include:
- Inventory of current workloads: Catalog all applications, services, and workloads, including their infrastructure, usage patterns, and technical specifications.
- Assessment of dependencies: Map out integrations and data flows both internal and external to uncover hidden complexity or bottlenecks.
- Performance benchmarking: Analyze system performance under different loads to set a baseline and define performance improvement targets post-migration.
- Security and compliance audits: Identify gaps in security posture or compliance risks that need to be addressed during replatforming.
- Business impact analysis: Evaluate how each application contributes to operations, revenue, and customer experience to prioritize the replatforming effort accordingly.
This step helps avoid surprises later and ensures technical decisions are aligned with business priorities.
2. Platform and Tool Selection
Once your application landscape is mapped, the next step is choosing the right destination and the tools to get you there. The chosen cloud or container platform should support your current and future scalability needs, while integrating well with existing systems.
Considerations include:
- Cloud provider selection: Choose between major providers like AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud based on your existing contracts, in-house skills, geographic compliance needs, and required services.
- Containerization strategy: Determine whether the application would benefit from containerization (e.g., Docker, Kubernetes) to improve portability and orchestration.
- Tooling ecosystem: Select supporting tools for logging, infrastructure as code (IaC), CI/CD, monitoring, and automated testing to ensure smooth ongoing operations.
- Cost and licensing: Evaluate not just the feature set, but also licensing models, cost predictability, and scalability of the tools and platforms.
A well-matched platform will simplify future optimizations and support long-term digital transformation goals.
3. Target Architecture Design
Before any code is touched, it’s important to define what the application will look like in its new environment. This is where architecture planning happens.
Key design decisions include:
- Defining which components are retained, replaced, or enhanced: For example, you may choose to keep the core logic but switch to managed cloud databases or adopt container orchestration for better scalability.
- Service modernization: Introduce services such as API gateways, message queues, or caching layers to improve responsiveness and reliability.
- Autoscaling and load balancing: Architect for elasticity by enabling applications to scale automatically in response to load.
- High availability and disaster recovery: Incorporate strategies for failover, redundancy, and backup to ensure business continuity.
4. Application Modification
This step is where replatforming differentiates itself from rehosting. Instead of just lifting and shifting, you make small but meaningful changes to optimize the application for the new platform.
Common modifications include:
- Database migration: Transitioning from on-prem or proprietary databases to cloud-native or managed database services (e.g., Amazon RDS, Azure SQL).
- Updating API endpoints: Adapting internal and external APIs for compatibility with new services or networking configurations.
- Introducing load balancing: Configuring load balancers to distribute traffic efficiently and maintain high availability.
- Autoscaling configuration: Enabling dynamic resource allocation to handle peak loads and minimize underutilized capacity.
- Middleware updates: Replacing outdated middleware components with cloud-native versions to ensure compatibility and better performance.
These changes are strategic not wholesale rewrites but enough to improve how the application performs and behaves in its new home.
5. Testing and Validation
Once modifications are complete, the system needs to be thoroughly tested to ensure that nothing breaks during or after the move. Skipping or rushing this phase can lead to performance issues, security gaps, or business disruption.
Testing types include:
- Functional testing: Ensuring all features work as expected in the new environment.
- Performance testing: Validating that the application meets or exceeds performance benchmarks from the assessment phase.
- Security testing: Verifying that encryption, access controls, and vulnerability patches are correctly implemented.
- Regression testing: Ensures that recent changes haven’t disrupted any existing functionality.
- Integration testing: Confirming that APIs, data pipelines, and third-party services continue to function seamlessly.
Testing should mimic real-world conditions as closely as possible and involve both technical teams and business users.
6. Deployment
Deployment is where your application officially moves to the new platform. It should be executed with minimal downtime and full rollback capability.
Preferred strategies include:
- Blue-green deployment: Running two production environments – one live and one staged so that traffic can be switched instantly with minimal risk.
- Canary releases: Rolling out changes to limited set of users in phrases before scaling up, to catch issues early.
- Phased migration: Moving components or services in stages to reduce complexity and better isolate problems.
Thorough planning here ensures users remain unaffected while the transition happens in the background.
7. Post-Migration Optimization
After the application is live in its new environment, the job isn’t over. Continuous monitoring and fine-tuning are essential to ensure it performs as expected and takes full advantage of the platform’s capabilities.
Activities include:
- Performance monitoring: Use real-time analytics and APM tools to monitor response times, error rates, and system load.
- User behavior analysis: Understand how end-users interact with the system to identify areas for UX or workflow improvement.
- Cost optimization: Review resource utilization and eliminate over-provisioned or underutilized components to reduce operating costs.
- Security audits: Ensure all configurations align with the latest security standards and that logs, alerts, and backups are functioning properly.
- Feedback loops: Gather input from users and technical teams to guide further iterations or enhancements.
Post-migration tuning often turns a “good” replatforming effort into a “great” one, maximizing ROI and reinforcing internal confidence in future modernization initiatives.
| Strategy | Description | Complexity | Cost | Time | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rehosting | Lift-and-shift migration with no code changes | Low | Low | Fast | Non-critical apps or fast cloud adoption |
| Replatforming | Move with minor optimizations to leverage cloud features | Moderate | Moderate | Medium | Apps needing performance or scalability improvements |
| Refactoring | Rewrite or re-architect application for cloud-native use | High | High | Long | Legacy apps requiring complete modernization |
Replatforming hits the sweet spot: it’s less intrusive than refactoring but delivers more value than a simple rehost. It’s particularly effective for businesses seeking cloud benefits without undergoing a disruptive transformation.
Key Benefits of Application Cloud Replatforming
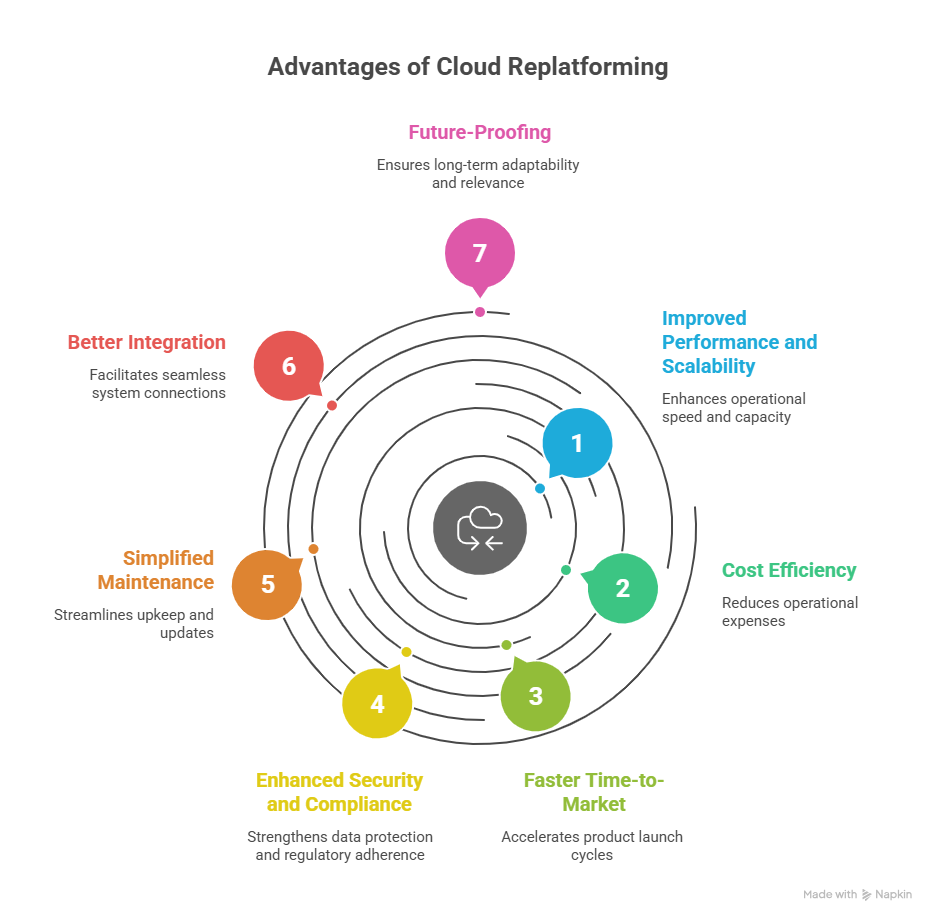
Replatforming can drive both technical and business-level advantages, including:
1. Improved Performance and Scalability
By optimizing resource usage and taking advantage of cloud-native autoscaling, applications can dynamically respond to demand spikes, reducing latency and improving user experience.
2. Cost Efficiency
Cloud-based pricing models often allow for consumption-based billing. Combined with optimized infrastructure, this leads to significant cost savings compared to legacy systems.
3. Faster Time-to-Market
Modern tools, CI/CD pipelines, and cloud infrastructure speed up the development, testing, and deployment cycles, enabling quicker innovation.
4. Enhanced Security and Compliance
Replatforming allows you to adopt modern security best practices, encryption standards, and compliance frameworks offered by cloud providers.
5. Simplified Maintenance
Using managed services (like managed databases or logging) reduces the burden on internal IT teams, allowing them to focus on innovation rather than infrastructure upkeep.
6. Better Integration
Modern platforms make it easier to integrate with APIs, microservices, analytics tools, and third-party applications, facilitating digital transformation efforts.
7. Future-Proofing
Replatformed applications are better positioned for further modernization whether it’s refactoring, containerization, or adopting serverless architecture.
How to Replatform Legacy Applications
Replatforming legacy applications requires strategic planning and execution. Here’s how to do it effectively:
1. Define Business Objectives
Before touching the code, clarify the “why.” Are you trying to reduce costs? Improve performance? Or Enable scalability? Align the replatforming effort with business outcomes.
2. Evaluate Application Suitability
Not all apps are fit for replatforming. Analyze technical debt, architecture complexity, and third-party dependencies to identify good candidates.
3. Select the Right Platform
Choose a platform that aligns with your tech stack and goals. Consider support for containers, managed services, DevOps tools, and compliance requirements.
4. Plan for Minimum Disruption
Design a migration plan that minimizes downtime. Use strategies like phased rollouts, shadow deployments, and feature toggles to ensure business continuity.
5. Leverage Automation
Use Infrastructure as Code (IaC), automated testing, and CI/CD pipelines to streamline the process, reduce manual errors, and accelerate migration timelines.
6. Upskill Your Teams
Ensure developers, DevOps, and infrastructure teams are trained on the new platform and tools. Knowledge gaps can lead to delays and post-migration issues.
7. Start Small
Start with a pilot initiative or a non-essential application. This allows teams to refine their approach and build internal confidence before scaling up.
How to Mitigate Risks During Application Replatforming
Every transformation carries risks, but a proactive approach can reduce friction and ensure success.
1. Conduct a Thorough Assessment
Understand current application architecture, dependencies, performance metrics, and compliance needs. Skipping this step can lead to surprises mid-migration.
2. Involve Stakeholders Early
Engage business, development, operations, and security teams from the start. Misalignment between teams is one of the top reasons replatforming efforts fail.
3. Plan for Rollback
Always have a rollback strategy in place. If something goes wrong during deployment, you should be able to revert without impacting users.
4. Monitor Aggressively
Use observability tools to track performance, error rates, and system behavior during and after migration. This helps catch and resolve issues early.
5. Manage Data Migration Carefully
Data integrity is critical. Perform backups, use checksums to validate transfers, and test data-intensive components thoroughly.
6. Stay Compliant
Ensure compliance requirements are maintained throughout the process especially if you’re handling sensitive or regulated data.
7. Communicate Transparently
Keep communication channels open throughout the project. Regular updates and cross-functional alignment reduce confusion and resistance to change.
Conclusion
Application replatforming is one of the most effective strategies for businesses looking to modernize their legacy systems without undergoing a complete overhaul. Once the foundation is modern, businesses are better equipped to explore containers, microservices, and serverless architectures that pave the way for future innovation.
By carefully planning the transition, modernizing what matters most, and mitigating risks at every stage, organizations can unlock greater agility, performance, and value from their existing applications.
Whether you’re just starting your modernization journey or looking to accelerate it, replatforming is a powerful step forward.
Interested in making your replatforming journey faster, smarter, and more cost-effective? Explore our AI-powered legacy modernization services to ensure your business stays agile, secure, and future-ready.
Reach out to our experts today to explore how Quinnox can help you replatform with confidence!
FAQs About Application Replatforming
Application replatforming is the process of moving an existing application to a new platform often the cloud while making minimal changes to its core architecture. Unlike a full rewrite, replatforming involves selectively adjusting components (such as databases or middleware) to take advantage of modern infrastructure and cloud-native features like scalability and automation, without starting from scratch. This approach modernizes applications efficiently, reducing technical debt and improving performance without extensive redevelopment.
Replatforming unlocks several important advantages for businesses relying on aging systems. Here are five key benefits of replatforming legacy applications:
Enhanced Performance and Scalability: Modernizing applications on cloud platforms improves their ability to handle growing workloads efficiently.
Cost Savings: Optimizing infrastructure usage and leveraging cloud services reduces operational and maintenance expenses.
Faster Deployment and Updates: Replatforming enables quicker releases, allowing businesses to respond faster to market demands.
Reduced Risk and Disruption: Unlike full rewrites, replatforming requires fewer changes, minimizing downtime and operational impact.
Improved Security and Compliance: Moving to modern platforms offers better security controls and simplifies adherence to regulatory requirements.
While all three approaches involve moving applications, their scope and complexity vary:
Rehosting, or “lift-and-shift,” means moving applications to a new environment without changes essentially copying them as-is. It’s the quickest but least transformative approach.
Replatforming involves moving the application with selective modifications to optimize for the new environment, such as switching to cloud-native databases or enabling autoscaling. It balances modernization with minimal disruption.
Refactoring is a deep overhaul where the application’s codebase is rewritten or significantly restructured to improve architecture, performance, and scalability, often enabling full cloud-native capabilities but requiring more time and investment.
Effective replatforming starts with a thorough assessment of your existing applications and dependencies, aligned with clear business objectives. Here are the best practices to follow:
Choosing the right cloud platform and tools that fit your technical and organizational needs.
Designing a target architecture that leverages cloud-native features.
Incremental application modifications focused on critical optimizations.
Rigorous testing, including performance and security checks.
Employing staged deployment strategies like blue-green or canary releases.
Post-migration monitoring and optimization.
Despite being less invasive than a full rewrite, replatforming carries risks that need careful management.
Data loss or corruption during migration.
Performance degradation can occur if the new platform isn’t properly optimized or tested under real-world loads.
Security gaps may arise when moving sensitive data or changing network configurations, so thorough audits are essential.
Overlooking application dependencies can cause unexpected downtime or failures.
Finally, inadequate user training or change management may result in adoption challenges, engaging stakeholders early and communicating clearly can mitigate this.