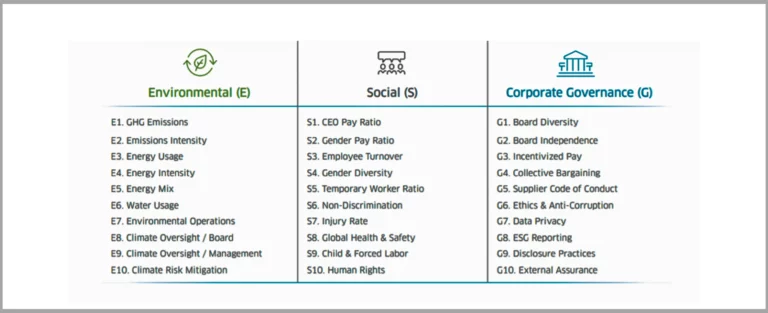
Here are some KPIs that organizations can use to generate data to better analyze their sustainability performance, set goals for improvement, and make data-driven decisions to save the planet just like Nestle did:
To determine the company’s success in terms of energy efficiency, the energy consumption rate can be used to provide an overview of how much energy is being utilized by the firm. This can then be compared to previous months and the best months. This might result in goals for lower energy use and a smaller carbon footprint.
Effective waste management can protect the environment and reduce operational costs. Measuring waste management can help businesses identify their waste generation, distinguish different types of waste and quantify their amount. Using the data, enterprises can create strategies like ‘zero waste to landfill’ and ‘closed-loop recycling’ that boost their sustainability performance.
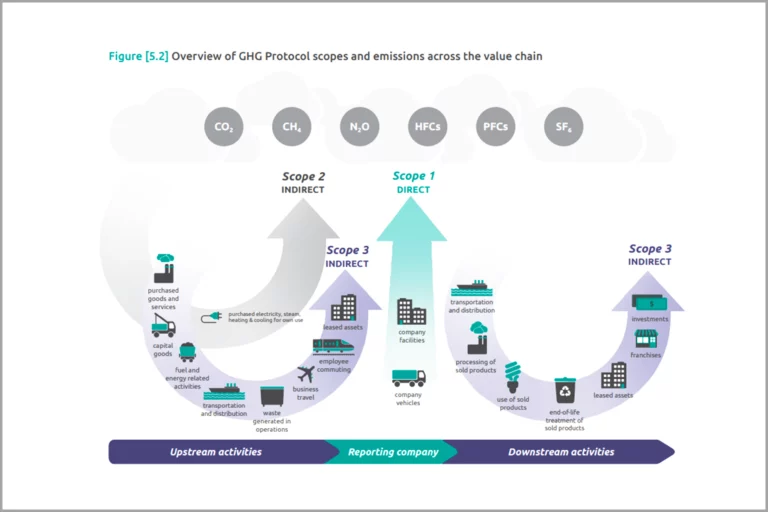
A company’s carbon footprint is one of the most critical KPIs to be measured as the businesses can analyze how the market presence of their goods and services is affected by climatic changes. This can be done by examining the scope 1, 2, and 3 emissions.
For businesses and organizations, greenhouse gas emissions are segmented into three categories known as Scope 1, Scope 2, and Scope 3. To reach globally established targets for mitigating climate change, companies are required to reduce emissions in all three scopes. According to estimates, nearly 75%-85% of emissions come within Scope 3, which cu generate through the use of a company’s products, are notoriously difficult to measure and address.
The Greenhouse Gas Protocol has designed the Scope 1, 2, and 3 frameworks to aid in monitoring advancements towards significant reductions necessary to restrict the surge of global temperatures to a maximum of 2°C, which is the fundamental objective of the Paris Agreement. The division of emissions into three categories is meant to facilitate the measurement of progress in achieving this goal.
Whenever a business claims to be decreasing or neutralizing its carbon emissions, finding out what specific emissions can be targeted is a good idea. The below figure depicts Scope 1, 2, and 3 emission activities.
Social sustainability is equally important for businesses, and employee welfare is a critical aspect. Businesses can assess employee welfare through metrics such as employee retention, satisfaction, absenteeism, and workplace accidents and illnesses. By monitoring these metrics, managers can improve employee satisfaction and reduce turnover.
Pay differences at an individual level are influenced by factors such as gender-based workplace discrimination and work environments. To create a fair society and incentivize everyone’s potential, equal pay between genders is essential. This is where as an important social metric of ESG initiatives, the gender pay gap is measured in terms of the ratio of what men earn in comparison to what women earn for the same job role.
Having a job for life at one company isn’t enough anymore. Specialization and mastery of skills aren’t enough to ensure economic stability since these skills may become redundant over time. In order to adapt to changing labor needs, workers need the means and sponsorship to acquire new skills and knowledge. In this space, a company’s ESG efforts are measured in terms of the investment and opportunities they are providing to the employees to help them reskill to keep pace with the evolving job roles.
In addition to products, businesses can contribute to communities by creating wealth. This can be through the creation of jobs, infrastructure, roads, and other forms of community involvement. By reinvesting in communities rather than taking profits, more money is in circulation, which stimulates economic growth and reduces wealth inequality. Here, the company’s social efforts are measured in terms of its investments in infrastructure, small businesses, new products, and services that help generate more wealth in the society they operate.
Governance is an essential aspect of ESG performance, and companies can use metrics like executive compensation, Board diversity, and other governance data for evaluation. Sound governance enables businesses to make fair and responsible decisions crucial for enhancing customer trust, improving stakeholder relationships, and achieving long-term sustainability objectives. Let’s have a look at the governance metrics that are measured as part of overall ESG efforts:
This metric helps compare an executive’s compensation in relation to an average employee’s compensation to evaluate the nature of value creation and wealth inequality.
If the leadership’s behavior is inappropriate or there is an internal conflict of interest, mistrust, and unethical behavior will likely flourish within the organization. Hence, to prevent that and ensure the makeup and background of the board members and executive team are top-notch regarding their affiliations and positions. To measure organizational diversity and quality, the diversity ratio of the board and the number of other commitments are evaluated.
It refers to the standard framework of ethics and the anti-corruption measures that are in place within an organization. This policy applies at all levels of the organization, from the executive to the entry-level, and is measured in terms of how many employees are abiding by the policy and how many are not.
Companies are evaluated in terms of the tax they pay in relation to the revenue they earn to ensure they are not exploiting loopholes in the tax system to spend as little tax as possible.
The ESG ecosystem of a company, includes vendors, suppliers, etc., who are collectively responsible to meet ESG goals and obligations. If one company in the ecosystem fails to meet ESG objectives, other partners are considered accountable as they indirectly support the defiant by doing business.
By using these indicators, businesses can understand their impact and take steps to mitigate their negative effects and improve their long-term sustainability performance.
By monitoring sustainability metrics, businesses can identify opportunities for innovation, optimize resource consumption, and differentiate themselves in an increasingly competitive market. Measuring Sustainability can also provide transparency and accountability to stakeholders, including investors, customers, and employees, who demand responsible and ethical business practices.
Measuring Sustainability can help your organization in the following ways:
Organizations can monitor and evaluate the success of their sustainability investments and initiatives by measuring Sustainability. It creates uniform and high-quality sustainability metrics that will help organizations to set sustainability objectives, monitor development, and implement management techniques. This not only helps in tracking progress but also helps in evaluating or managing their sustainability goals.
Businesses are often unaware of their operating environments or the extent of their consequences. To demonstrate to the internal and external stakeholders where they operate and what effect their company’s activities and actions have, it is essential to identify and demonstrate the possible outcome of their activities. Here ESG is frequently used to portray impacts to win investor trust and increase the relevant stakeholders.
A robust and constantly measured sustainability action can protect the company from future challenges by putting out the effort necessary to prepare for any obstacles that may arise in the future. Long-term business plans that include ESG principles across different aspects of operations are more likely to deal with unpredictable socio-economic problems and disruptions.
For instance, companies performing well with robust supply chains before the pandemic faced lesser negative impacts on their businesses in the market turmoil, even during the Covid-19 pandemic.
Businesses have to upgrade to new technologies when focusing on meeting sustainable goals. As a result, being familiar with the tool can help owners, stakeholders, and project teams comprehend new technologies and sustainability best practices and predict potential new requirements.
When a company communicates openly about its success and the failures and actions that it has taken to overcome and succeed, they gain more credibility and reputation. They can build their brand value and customer loyalty. Sustainability communications are most effective when a company can show its real progress and benefits by utilizing data that is up to current.
When measuring sustainability, there is no one size fits all method. The size, scope, needs, and industry requirements of businesses make it challenging to describe exactly what ESG looks like. Additionally, because sustainability involves an increasing number of variables, it is important to consider how much data is required by firms to evaluate their performance. Moving forward, businesses must integrate sustainability into their core operations and develop a set of KPIs that the entire organization can use to gauge long-term success.
Analysis of sustainability KPIs enable businesses to monitor, manage, and regulate the level of sustainability in their company. The type and number of KPIs to track entirely depend on the business’s needs and the objectives that they are seeking to meet.
For any assistance in measuring and analysing your business sustainability, Quinnox can be your technological partner in assisting in tracking your progress, reducing your carbon footprint, and meeting new technological requirements and upgrades on your sustainability goals.