Accelerate IT operations with AI-driven Automation
Automation in IT operations enable agility, resilience, and operational excellence, paving the way for organizations to adapt swiftly to changing environments, deliver superior services, and achieve sustainable success in today's dynamic digital landscape.
Driving Innovation with Next-gen Application Management
Next-generation application management fueled by AIOps is revolutionizing how organizations monitor performance, modernize applications, and manage the entire application lifecycle.
AI-powered Analytics: Transforming Data into Actionable Insights
AIOps and analytics foster a culture of continuous improvement by providing organizations with actionable intelligence to optimize workflows, enhance service quality, and align IT operations with business goals.
Every byte of data tells a story of customer journeys, business decisions, and innovation. Yet, when organizations embark on moving that critical information – from aging legacy systems to agile, hybrid or multi-cloud environments – the risks multiply quickly.
Imagine halting critical operations, losing data integrity, or being hit by unexpected delays and ballooning costs. The stakes are real: According to Bloor Group, over 80% of data migration projects run over budget or miss deadlines, with time delays averaging 30%–41%, and cost overruns averaging 30% or more.
In 2025, data migrations aren’t simple transfers; they’re intricate transformations that must account for continuous data flows, rigorous compliance, and automated validation. A successful data migration plan is the foundation for doing this securely and efficiently while protecting business continuity.
This guide breaks down the modern data migration process into clear, actionable steps. You will see how to prepare, execute, and validate migrations with minimal risk, drawing on best practices and real-world data migration plan examples.
What is a Data Migration Plan?
A data migration plan is a structured roadmap that outlines how an organization will move data from one system, platform, or storage environment to another while ensuring accuracy, security, and minimal disruption. It defines the scope, objectives, timelines, resources, tools, and validation processes needed to complete the migration successfully.
A data migration plan is more than just a checklist for transferring files. We’re talking about dynamic ecosystems: hybrid clouds, distributed databases, real-time data streaming, AI-powered error detection, and evolving global compliance laws.
Why does this matter? Because data migrations are complex, and failure is far more common than anyone admits. According to Gartner, 83% of data migration projects fail or significantly deviate from initial targets, with budget overruns. Another study by McKinsey, shows that on average, large IT projects exceed their budget and timeline by 45% and 7% respectively, while delivering 56 percent less value than predicted. A modern data migration plan does more than move files – it preserves integrity, ensures compliance, maintains operations, and streamlines structure for tomorrow’s needs.
What Does a Well-Designed Data Migration Plan Include?
A well-designed data migration plan isn’t just a list of tasks – it’s a carefully orchestrated blueprint that guides every step of your journey, ensuring your data reaches its destination intact, secure, and ready to deliver value. Let’s break down the essential elements that make a migration plan robust and reliable:
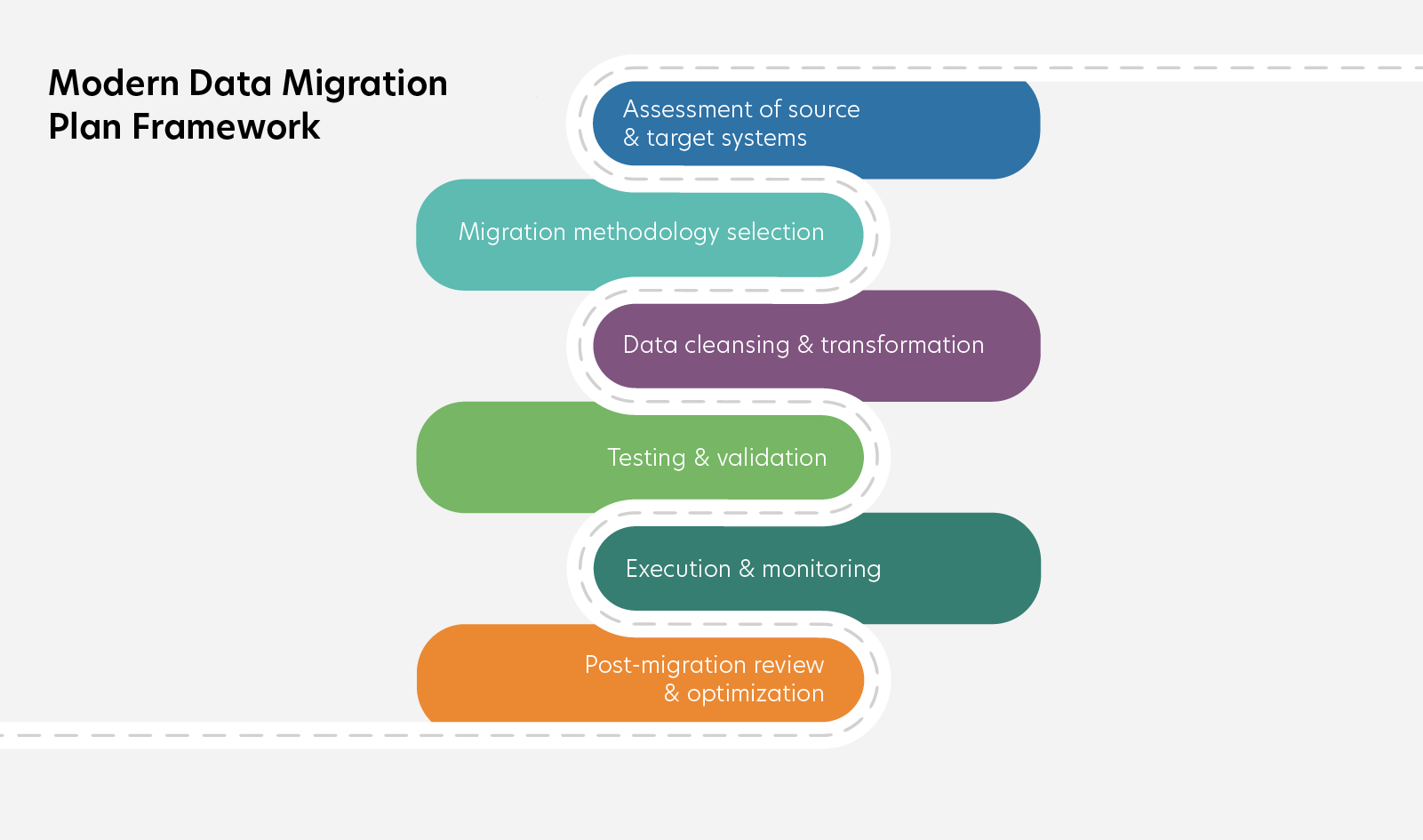
1. Assessment of Source and Target Environments
Before you move a single byte, you need a deep understanding of both where your data lives now and where it’s headed. This means assessing compatibility between systems –file formats, database schemas, APIs, and infrastructure capabilities. What’s the volume and velocity of your data? Are there any hidden bottlenecks, legacy constraints, or security gaps? Identifying these early lets you anticipate risks and design mitigation strategies that keep the migration smooth and predictable.
2. Clear Migration Methodology
Choosing the right migration approach sets the rhythm for your project. Will you perform a “big bang” cutover, moving everything at once? Or adopt a phased strategy that migrates data in stages to minimize downtime? Perhaps a hybrid method, balancing speed and safety by combining bulk and streaming techniques? Each approach has its trade-offs in speed, risk, complexity, and cost. Your plan must clearly define this methodology, tailored to your business needs and technical realities.
3. Data Cleansing and Transformation
Migration is the perfect moment to improve your data’s quality. Cleaning duplicates, standardizing formats, and transforming data to fit the target system’s structure not only reduces errors during migration but also enhances analytics and operations post-move. A detailed transformation rulebook documents every change, ensuring transparency and traceability for audits or troubleshooting.
4. Testing and Validation Processes
Testing isn’t an afterthought – it’s a continuous process throughout the migration lifecycle. From dry runs in staging environments to performance benchmarking and end-to-end validation, these steps confirm that data moves accurately and systems perform reliably. Without rigorous testing, you risk costly data corruption, system failures, or business disruption.
5. Contingency Measures
Even the best plans can face unexpected hiccups. That’s why your migration blueprint must include contingency measures – rollback protocols, checkpointing, sandbox testing, and rapid escalation paths. These safety nets enable quick recovery and minimize downtime, turning potential disasters into manageable challenges.
Without these critical components, migrations risk spiraling into chaos – data corruption, regulatory violations, extended downtime, ballooning costs, and loss of stakeholder trust. But with a formal, well-designed migration plan, you build a strong foundation for a seamless, secure, and future-ready data environment that fuels business success and resilience.
Step-by-Step Guide to Building a Data Migration Plan
Whether you’re moving to a new cloud platform, modernizing legacy systems, or integrating business units after a merger, a thoughtfully crafted migration plan turns chaos into clarity. This step-by-step guide breaks down the complex migration journey into manageable, actionable phases.
Each stage builds on the last, helping you reduce risks, stay aligned with business goals, and deliver a seamless transition that protects your data’s integrity and ensures operational continuity.

1. Define Scope and Objectives
The first step is clarity: what data moves, why, and under what constraints? Begin by:
- Inventory All Assets: Catalogue every dataset, schema, database object, application interface, and dependent business process. This inventory avoids surprises and highlights dependencies that could complicate migration.
- Set Quantifiable KPIs: Define metrics for downtime tolerance, error thresholds, migration speed, data freshness, and post-migration performance. A Forbes Study show that, organizations that fail to define KPIs early often fall victim to schedule slips and budget blowouts – only 36% of projects stay within budget, and just 46% meet deadlines
- Business Alignment: Ensure scope reflects business priorities, regulatory compliance requirements, operational continuity and digital transformation goals.
- Stakeholder Engagement: Document business owners, technical leads, compliance officers, and operational managers, along with decision rights. This shared clarity reduces miscommunication and keeps the project aligned with strategic objectives.
2. Audit and Profile Your Data
Before moving data, you must understand its health and quirks. Use:
- Data Profiling Tools: Use profiling utilities to analyze data distribution, detect anomalies, identify nulls, and check referential integrity. For example, uncovering 14% more duplicates or 20% missing values early can save weeks in remediation.
- Compliance Readiness: Identify sensitive data such as Personally Identifiable Information (PII), Protected Health Information (PHI), or payment details. These require masking, tokenization, or encryption to comply with GDPR, HIPAA, or PCI DSS regulations..
- Dependency Mapping: Trace interdependencies across data pipelines, ETL pipelines, APIs, and downstream reporting to avoid breaking business processes
- Legacy System Constraints: Evaluate data locked in obsolete platforms or proprietary formats, requiring special extraction methods. Assessing feasibility early prevents last-minute surprises.
Skipping this phase risks moving bad or incomplete data, resulting in compliance violations, inaccurate analytics, or operational failures.
3. Choose the Right Migration Strategy
Selecting the correct migration strategy is a critical decision that shapes the entire data migration process. The choice depends on factors such as data volume, interdependencies, business continuity requirements, and acceptable downtime.
Here are the three most common strategies, compared side-by-side for clarity:
| Strategy | Pros | Cons | Best Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|
| Big Bang | Fast cutover with minimal coordination windows, simpler execution | Higher downtime risk, limited rollback flexibility | Smaller datasets, low complexity systems with minimal interdependencies |
| Phased | Reduced downtime, easier rollback between stages | Longer project timelines, potential for data inconsistency between phases | Large enterprise systems, mission-critical environments where uptime is essential |
| Hybrid | Balances speed and safety, allows parallel batch and streaming processes | More complex to manage, higher tooling requirements | Multi-region deployments, environments with a mix of static and frequently updated data |
Decision Matrix Factors:
- Data size
- Criticality
- Interdependency
- Peak vs. off-peak usage patterns
- Rollback complexity
When evaluating these factors, match them to your business and technical priorities to select the strategy that offers the best balance of speed, safety, and cost-efficiency.
Automation and Orchestration: Select tools that enable repeatable execution, automated validation, and rollback scripting. Automation reduces human error, accelerates migration tasks, and ensures consistency across different migration phases.
4. Prepare and Cleanse the Data
Quality data is the backbone of successful migration. Begin with:
- Standardization: Align field formats, units of measure, naming conventions, and reference data.
- Deduplication and Enrichment: Remove duplicates, merge fragmented records, and enrich with missing metadata.
- Transformation Rulebook: Maintain detailed documentation of every transformation applied for transparency and audit.
- Data Quality Automation: Implement rules to validate constraints, value ranges, and referential integrity pre- and post-migration.
- Version Control: Store migration scripts, configuration files, and mapping documents in a source control repository.
Poor preparation here can lead to corrupted or unusable data, costing valuable time and trust.
5. Develop a Detailed Migration Plan
Translate strategy into action with a detailed plan:
- Technical Work Breakdown: Create Gantt charts with milestones for extraction, transformation, loading, and validation.
- Roles and Responsibilities (RACI): Map tasks to roles, clarifying decision authority and escalation paths.
- Tool and Infrastructure Setup: Configure migration utilities, ETL engines, integration platforms, and network bandwidth provisioning.
- Security Planning: Define encryption for data in transit and at rest, key management processes, and secure endpoints.
- Contingency Planning: Create rollback procedures, define checkpoints, and prepare sandbox environments for dry runs.
This rigorous planning minimizes risks and prepares your team to handle surprises swiftly.
6. Test the Migration Process
Testing saves lives – of projects, budgets, and reputations. Conduct:
- Dry Runs: Execute trial migrations in a staging environment with representative data volumes.
- Performance Benchmarking: Test throughput, latency, and load handling.
- End-to-End Validation: Ensure source-to-target fidelity, business rule application, and downstream system compatibility.
- Disaster Simulation: Test rollback procedures, failover systems, and recovery point objectives (RPOs) and recovery time objectives (RTOs).
Only when tests pass confidently should you move to production.
7. Execute with Real-Time Oversight
- Live Monitoring: Track throughput, error rates, resource utilization, and latency in real time.
- Issue Escalation: Predefine thresholds and escalation protocols for anomalies.
- Parallel Processing: Where possible, run batch and streaming processes in parallel to meet time windows.
- Rollback Readiness: Keep rollback scripts and previous state snapshots active until migration is validated.
8. Validate, Optimize, and Transition to BAU
- Data Reconciliation: Use row counts, checksums, hash totals, and spot validations.
- Performance Tuning: Optimize indexes, caching strategies, partitioning, and compression.
- Documentation Updates: Finalize architecture diagrams, transformation rulebooks, and operational guides.
- Operational Handover: Train support teams, update runbooks, and integrate monitoring into production dashboards.
- Continuous Improvement: Conduct a post-mortem to identify lessons learned and refine future migration playbooks.
For a detailed checklist of data migration and monitoring steps, see our Data Migration Checklist.
Post-Migration Best Practices
Completing the cutover is only part of the journey. The first few weeks after go-live are critical for ensuring the migration delivers its intended business value. A structured post-migration approach helps detect issues early, stabilize performance, and embed new processes into daily operations.
1. Early Monitoring and Alerting
Track data quality, system performance, and integration points continuously for at least the first 90 days. Automated monitoring tools can flag anomalies in real time, enabling quick resolution before they escalate into operational problems.
2. User Feedback and Adoption Checks
Engage business users to validate data accuracy, reporting reliability, and workflow changes. This feedback can highlight hidden issues and guide targeted improvements in ETL processes, data models, or dashboards.
3. Performance Benchmarking
Compare post-migration performance metrics with pre-migration baselines. Review query response times, batch processing speeds, and transaction throughput, then apply optimizations to meet or exceed previous benchmarks.
4. Compliance Verification
Confirm that the new environment meets all relevant regulatory requirements, such as GDPR, HIPAA, or PCI DSS. Document verification steps to ensure audit readiness and avoid potential compliance risks.
5. Knowledge Transfer and Documentation
Update SOPs, runbooks, and architecture diagrams to reflect the new environment. Conduct training sessions for support teams so they can resolve issues without unnecessary escalation.
Additional Keys to a Successful Data Migration Plan
- Risk and Mitigation Framework: Document likely risks – such as integration failures or compliance breaches along with mitigation actions.
- Tool Selection Criteria: Define how you will choose profiling tools, ETL platforms, or orchestration frameworks.
- Compliance Management: Align with standards like GDPR, HIPAA, or PCI DSS. Include data residency considerations for multi-region migrations.
- Cost and Resource Planning: Forecast expenses for infrastructure, licensing, downtime, and staffing. Highlight cost-control measures like using open-source ETL tools or leveraging pre-trained AI models for quality checks.
- Change Management: Prepare users through training, updated SOPs, and a clear communication plan.
Data Migration Plan Use cases
1. Legacy to Cloud Migration: From webMethods to Serverless with Quinnox AWS Services
A major North American environmental services provider transformed their legacy ESB infrastructure by partnering with Quinnox to migrate from webMethods to a fully serverless ESB on AWS. The project replaced traditional ESB processes with RESTful APIs using AWS Lambda, SQS, DynamoDB, and more. As a result, the client achieved 99.99% uptime and reduced operational costs by 80%, all while streamlining CI/CD and enhancing scalability.
Read the full case study to explore our AWS-powered success story.
2. Global Retail ERP Modernization
A multinational retail chain migrated from an on-premise ERP to a cloud-based SaaS platform. They chose a hybrid strategy, bulk-loading static data over a weekend while streaming high-transaction data for two weeks to maintain operational continuity.
Automated data profiling identified 14 percent more duplicate customer records than anticipated. Pre-migration enrichment improved sales reporting accuracy by 22 percent. This reduced post-migration reconciliation time from three weeks to five days.
3. Financial Services Core Banking Upgrade
A regional bank upgraded its legacy core banking system to a modern cloud-native platform. Due to strict compliance requirements, they adopted a phased migration, starting with non-critical customer data before moving to transaction and loan data.
The migration plan included encryption in transit and at rest, tokenization of PII, and real-time validation of account balances. Performance tuning after migration reduced batch processing time for end-of-day settlement by 35 percent, improving customer-facing service availability.
Conclusion
A successful migration begins with a clear plan and ends with measurable business impact. When done right, it safeguards data integrity, ensure compliance and keeps downtime to a minimum, and sets the stage for future scalability. But this level of success demands more than checklists and spreadsheets; it requires meticulous planning, rigorous testing, and flawless execution to avoid costly missteps that can ripple across your entire organization.
That is where Qinfinite, our intelligent application management platform , changes the game. Qinfinite equips you with advanced capabilities like AI driven data profiling, automated orchestration, real time migration tracking, and post migration performance tuning. Instead of wrestling with risk and uncertainty, you move through each phase with precision and speed.
With Qinfinite, what once was a high-risk operation becomes a strategic opportunity – an opportunity to not just transfer data but to optimize, modernize, and future-proof your digital foundation. This is more than migration. It’s a transformation with precision.
Don’t just take our word for it – Schedule a FREE 120 mins Consultation with our Qinfinite Experts Today!
FAQs About Data Migration Planning
The biggest risk is transferring data that is incomplete or incorrect. Even small errors can disrupt operations, skew reporting, and create compliance issues. Careful validation before and after the move is the best way to avoid expensive fixes later.
It depends on the size and complexity of the data, the readiness of your systems, and the approach you choose. Some migrations can be completed in a few days. Larger, more complex projects may take several months to ensure accuracy and stability.
A phased migration can help reduce downtime, but it is not automatically the safest choice. Longer timelines can increase the chance of inconsistencies between systems. The best approach is the one that aligns with your systems, data dependencies, and acceptable level of risk
Start by running a data quality check. Look for missing values, duplicates, and outdated records, and confirm that formats are consistent. Fixing these issues before migration not only reduces errors but also ensures your new environment starts off clean and reliable.
Yes, modern tools like MDM platforms and ETL pipelines support rule-based and AI-assisted automation to streamline the process.
