Why So Many Data Migrations Go Wrong? On paper, data migration sounds deceptively simple – just move data from one system to another, right? In reality, it’s rarely that straightforward. Many CIOs begin with the belief that it’s a mere “lift-and-shift,” only to watch projects derail due to underestimated complexity, unclean data, or lack of planning.
In fact, Gartner estimates 83% of data migration projects either fail or run over budget and schedule – a staggering figure that highlights how fragile the process can be. Why such a high failure rate? Often, it is not the technology at fault, but rather the assumptions made before the first byte moves. From missing governance frameworks to incompatible data structures, even small oversights can snowball into costly disruptions.
Before moving a single record, technical project managers must anticipate these issues and devise strategies to overcome them. This article explores the top data migration pitfalls you must address upfront to ensure a smooth transition. By understanding these challenges and how to mitigate them, you can turn data migration from a risky venture into a strategic win for your organization.
Top 7 Data Migration Challenges You Must Address
Let’s look at the seven most common data migration challenges organizations must address before moving a single byte – and how to overcome them effectively.
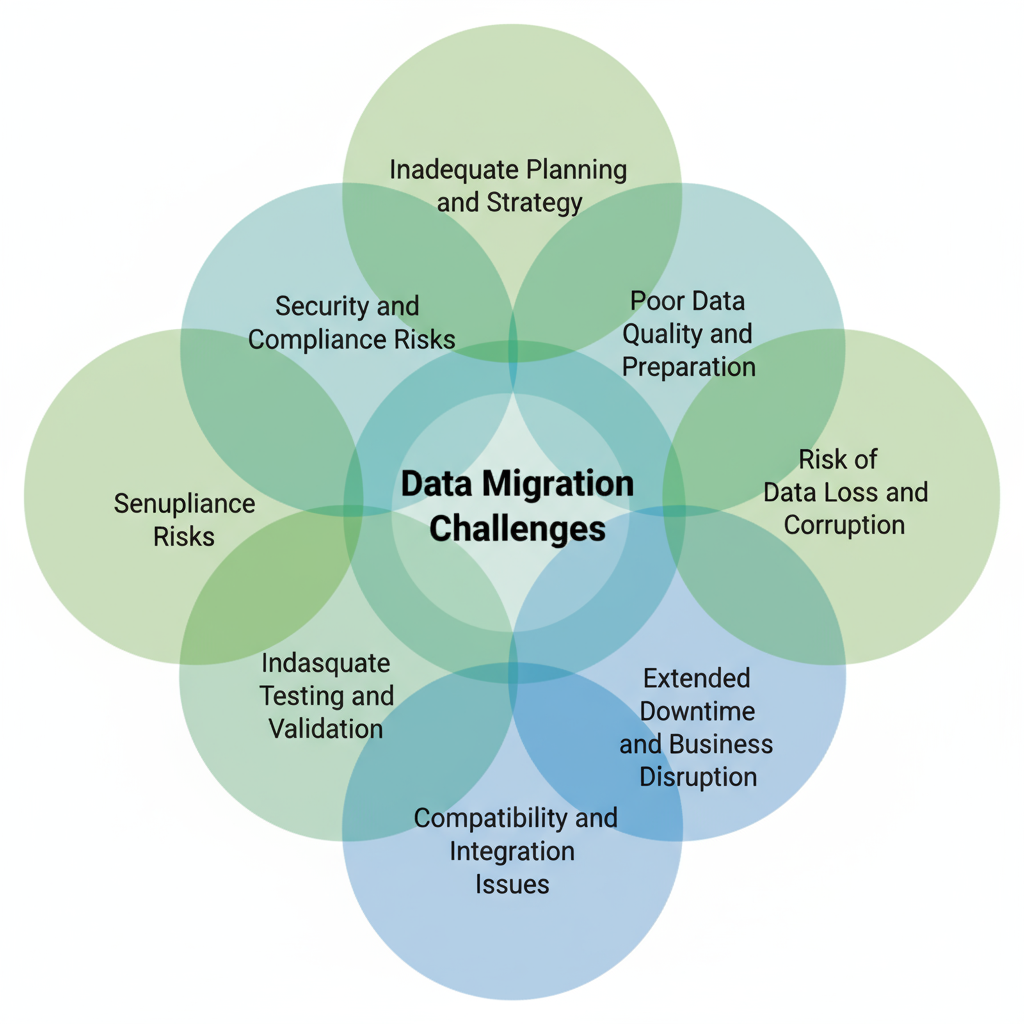
1. Inadequate Planning and Strategy
If there’s one root cause behind most failed data migrations, it’s this – poor or incomplete planning. Many teams dive into migration with an oversimplified view of the effort required, assuming technical execution alone will carry them through. But a data migration without a clear strategy is like building a bridge without a blueprint.
Lack of planning leads to scope creep, timeline slippage, and internal confusion. When roles aren’t clearly defined, decision-making slows. When dependencies aren’t mapped, critical tasks fall through the cracks. Oracle notes that over 80% of migration projects miss their targets because organizations “neglect migration planning and underestimate risk.”
To mitigate this, start by creating a comprehensive data migration roadmap that covers:

Also, don’t underestimate cross-functional alignment. Engage both IT and business stakeholders early. Their insights on data dependencies and reporting requirements often prevent last-minute surprises.
As the old saying goes: “Plan for the worst, and your migration will deliver the best.”
2. Poor Data Quality and Preparation
Another top challenge is poor data quality in source systems. A data migration is only as good as the data being moved. Unfortunately, most organizations discover too late that their source data is full of inconsistencies, duplicates, and incomplete fields. According to Experian’s Global Data Management Report, 95% of businesses suspect their data might be inaccurate, yet less than half have consistent quality checks in place.
Migrating “dirty” data – duplicates, inconsistencies, missing fields, will simply transfer problems from the old system to the new. The result? Failed validation tests, mismatched fields, and inaccurate analytics post-migration. Without addressing this, migrations can fail validation or produce faulty results.
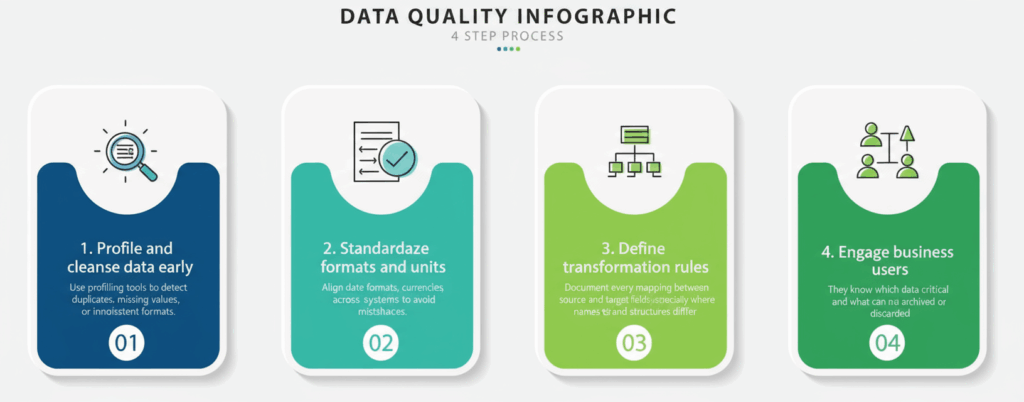
A strong data preparation phase not only ensures compatibility but also improves downstream analytics accuracy.
3. Risk of Data Loss and Corruption
Data loss is every CIO’s nightmare during migration. Whether due to technical glitches, mismapped fields, or human error, there is a very real risk that some records will not make it to the target system intact. In the process of moving millions of records, it is easy for some data to not be transmitted, which if not caught could result in irrevocably lost information.
IDC estimates that unplanned data loss incidents cost enterprises over $1.7 trillion annually in downtime and recovery efforts. The consequences of lost or corrupted data range from inaccurate analytics to regulatory non-compliance if critical records disappear.

Success Story in Action: A Quinnox-led migration for a leading bank demonstrated the importance of this approach. The team implemented automated reconciliation checks across 16 legacy systems, identifying missing records in early test cycles. The result was 100% data accuracy in production cutover – proof that prevention beats recovery. Check out the full success story here.
4. Extended Downtime and Business Disruption
No organization wants to hear the words “systems are down”, even less so as a planned part of migration. Yet one of the common data migration challenges is managing downtime. If the migration process requires taking systems offline for hours or days, the business can suffer operational paralysis – particularly in industries like banking, retail or logistics.
The challenge lies in balancing data integrity with uptime. Traditional “big bang” migrations require taking systems offline for extended periods, which can be risky for global enterprises that operate 24/7.

Forward-thinking organizations treat downtime management as a design consideration, not an afterthought. As migrations grow more complex, parallel run environments – where old and new systems coexist temporarily – are increasingly used to ensure business continuity.
5. Compatibility and Integration Issues
Another important challenge lies in integration and compatibility with other systems and applications. When you move data into a new platform, it is not happening in isolation that data likely interacts with various downstream applications, APIs, and reports. A migration that ignores these interdependencies can create downstream chaos. You might move data successfully, only to find dashboards failing, integrations breaking, or automated workflows halting.
Integration issues often stem from schema mismatches, outdated connectors, or undocumented dependencies. This challenge is particularly acute in hybrid or multi-cloud environments where legacy systems interact with modern platforms.
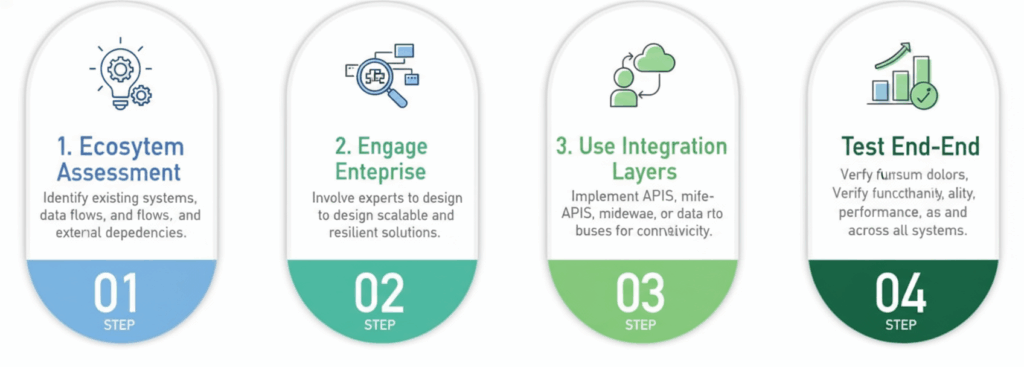
Treat your migration as an ecosystem upgrade – not just a database swap. When data flows seamlessly across systems post-migration, business users notice the difference instantly.
6. Inadequate Testing and Validation
Lastly, a data migration is not complete when the data is moved, it is complete when the data is verified in the new environment and all systems are running correctly. It is essential to validate that the migrated data is correct, complete, and usable. Too often, validation is left until after the go-live, when errors are costly to fix.
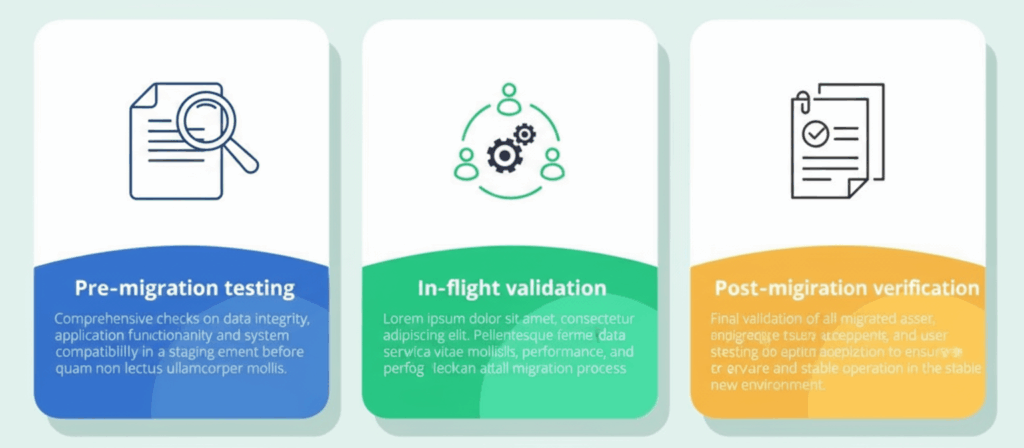
Automated testing frameworks can drastically improve accuracy and speed, flagging discrepancies in real time. Pair that with manual business validation, and you’ll have confidence that the new system is not only populated – but truly production-ready
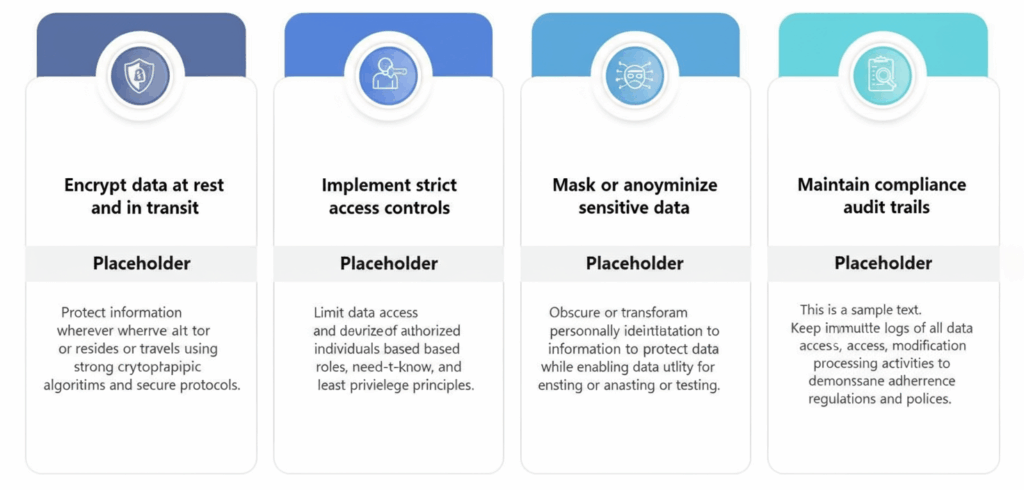
7. Security and Compliance Risks
In today’s regulatory landscape, data security and compliance are not just IT concerns – they’re business imperatives. During migration, sensitive information often moves across multiple environments, increasing the risk of unauthorized access, data leakage, or non-compliance with frameworks like GDPR, HIPAA, or CCPA.
Even a minor lapse in encryption or access control can lead to major financial and reputational damage. According to IBM’s Cost of a Data Breach Report, the average data breach now costs enterprises over $4.45 million – a number that continues to rise year after year.
Best Practices to Overcome Data Migration Challenges
Data migration is complex, but following proven best practices will reduce risks and ensure a smoother transition.
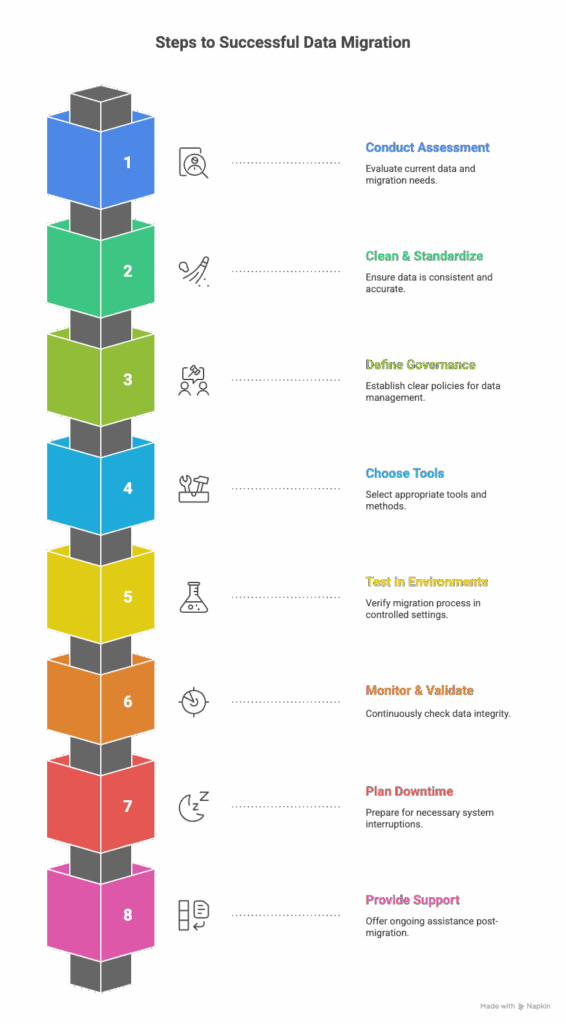
1. Conduct a Thorough Assessment
Before moving data, perform a detailed audit of your current systems. Identify the types of data, sources, dependencies, and potential risks. This helps you anticipate challenges and design a realistic migration roadmap.
2. Clean and Standardize Data
Poor quality data will only multiply issues during migration. Remove duplicate records, outdated information, and standardize formats. A clean dataset ensures better accuracy and reduces post migration errors.
3. Define Clear Governance Policies
Establish ownership and accountability for data. Define who can access, modify, and approve data at each stage. Governance frameworks ensure compliance with regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, or CCPA.
4. Choose the Right Tools and Approach
Select migration tools that align with your data volume, complexity, and compliance requirements. Decide whether a big bang migration or a phased approach works best for your business.
5. Test in Controlled Environments
Run pilot migrations in sandbox environments to validate processes and tools. Testing uncovers hidden issues and helps fine tune workflows before full-scale execution.
6. Monitor and Validate Continuously
Track migration progress in real time and validate data at each stage. Create checkpoints to ensure accuracy, consistency, and completeness. Continuous monitoring reduces the risk of unnoticed errors.
7. Plan for Downtime and Communication
Communicate expected downtime or disruptions with stakeholders in advance. A well-managed communication plan builds trust and reduces frustration during the migration.
8. Provide Post Migration Support
Migration does not end when the data is moved. Plan for user training, performance monitoring, and issue resolution after the migration to ensure long-term success.
Conclusion
Data migration is a high-stakes journey, but with careful planning and proactive risk management, it can be a catalyst for modernization rather than an obstacle. In this blog, we have highlighted the top challenges, from planning, data quality, and downtime to security, integration, validation, and beyond that CIOs and technical managers must address before moving data.
At Quinnox, we’ve seen that migration success isn’t about avoiding risk – it’s about engineering intelligence into every stage. By addressing challenges like planning gaps, poor data quality, integration issues, and downtime head-on, CIOs can turn migration from a liability into a launchpad for modernization.
If you’re ready to turn migration complexity into competitive advantage, it’s time to see intelligent migration in action – Connect with Us Today.
FAQs Related to Data Migration Challenges
The most common hurdles include unclear planning, poor data quality, data loss, extended downtime, and integration or compliance issues. Addressing these early helps avoid costly disruptions later.
Always back up production data, migrate in controlled phases, and run automated reconciliation checks to verify completeness. A “test, validate, repeat” approach prevents irreversible loss.
Clean, standardized data is the backbone of a smooth migration. It ensures accurate transfers, faster validation, and reliable business insights post-move.
Encrypt data in transit and at rest, restrict user access, and comply with frameworks like GDPR or HIPAA. Security isn’t optional – it’s foundational.
Plan comprehensively, cleanse data early, automate testing and monitoring, and always have a rollback plan. Smart, proactive planning leads to smooth and safe migrations.